A Basic Field Guide To Fraud offers a crucial understanding of fraudulent activities, including mobile ad fraud, and provides strategies for combating them. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers comprehensive resources to help individuals and organizations understand and navigate the complexities of identifying and preventing fraud. Explore diverse methods and techniques to protect your interests, leveraging insights into fraudulent schemes and risk management while developing a strong defense against illicit activities with fraud prevention tactics.
1. Understanding Mobile Ad Fraud Methodology
Mobile ad fraud employs diverse and malicious techniques, adapting based on several factors. These parameters influence the type of fraud, its scale, and the target that fraudsters aim to exploit. Understanding these methodologies is vital for robust fraud prevention strategies.
Key Factors Influencing Mobile Ad Fraud:
- Fraudster target and goal
- Exploited weaknesses or loopholes
- Available technology
- Level of sophistication
- Financial capabilities
These elements collectively dictate the fraud type, scale, and the specific target a fraudster intends to exploit. Recognizing these aspects is essential for developing effective countermeasures.
1.1. Categories of Mobile Ad Fraud
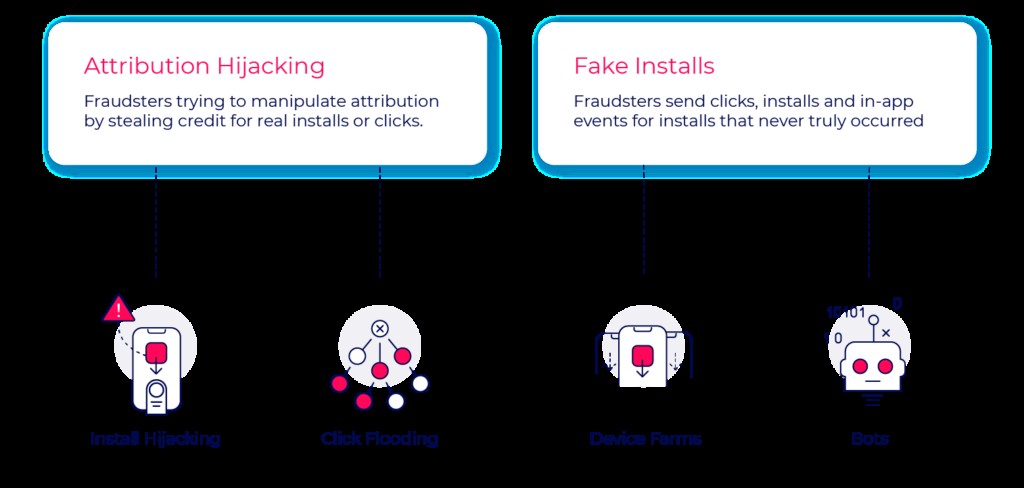
Mobile ad fraud is broadly categorized into two main types: attribution hijacking and fake installs. Understanding these categories is the first step in combating mobile ad fraud effectively.
- Attribution Hijacking: Fraudsters manipulate attribution conversion flows using fake click reports to steal credit for installs from other media sources.
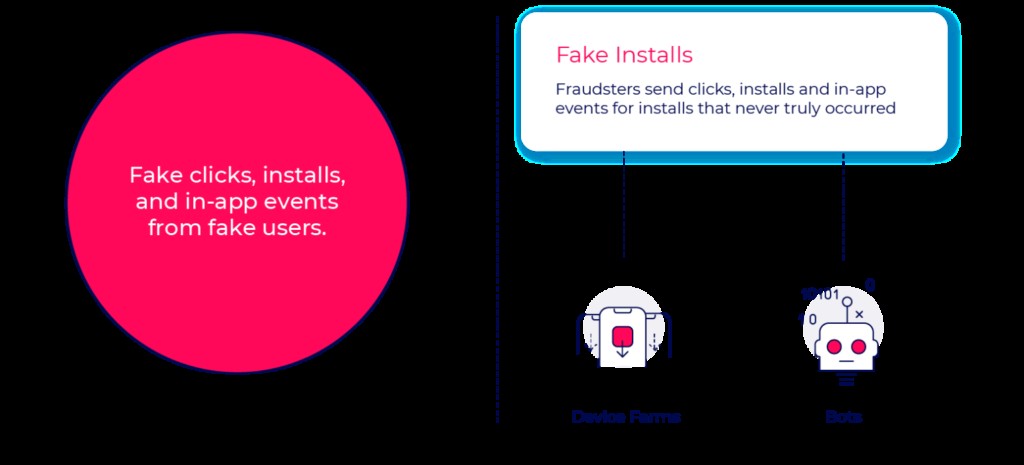
- Fake Installs: The entire user journey is fabricated, including impressions, clicks, installs, in-app events, and users, rendering user acquisition data worthless.
| Real Users | Fake Users | |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement | Real | N/A |
| Activity | Attribution Hijacking | Fake Installs |


Attribution hijacking involves real users but distorts marketing budget allocation. Fake installs, on the other hand, offer no value to advertisers, making data unreliable. Accurate fraud detection is crucial. For more insights, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
Mobile ad fraud categories
2. Attribution Hijacking Methods
Attribution hijacking is a prevalent fraud tactic that relies on manipulating real user interactions to steal credit for app installs. This section delves into specific methods, their detection, and implications for advertisers.
2.1. Install Hijacking
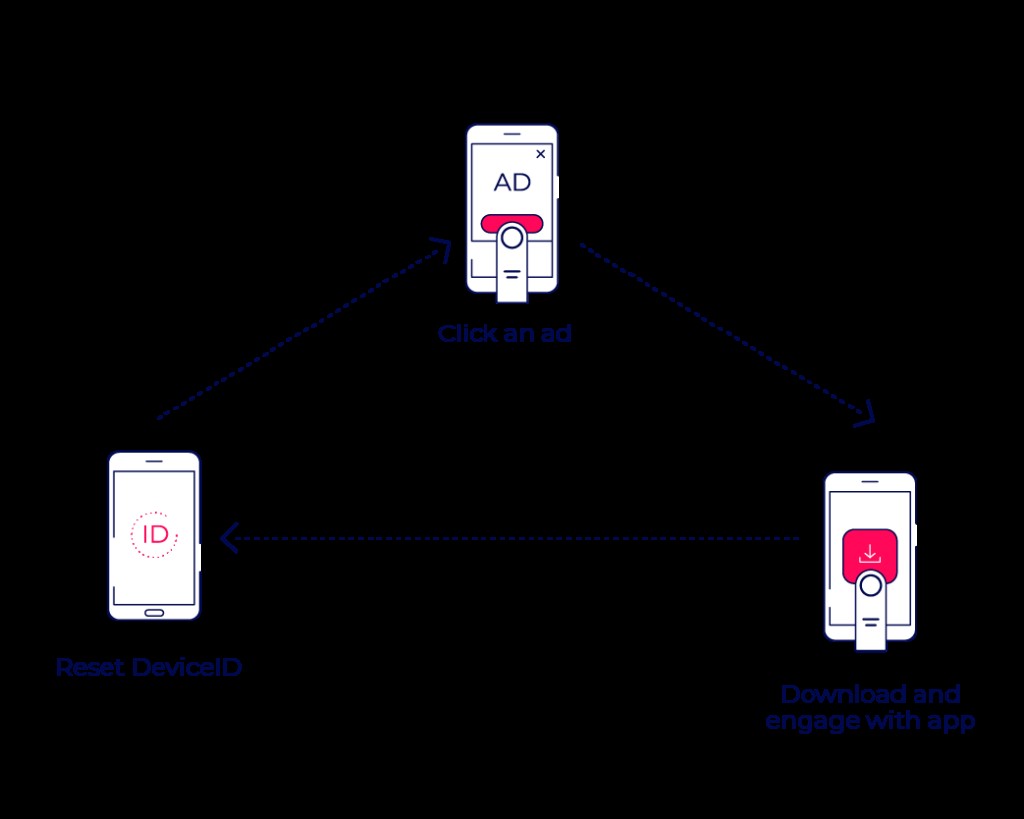
Install hijacking occurs when fraudsters steal credit for an install generated by a legitimate media source. Techniques include sending false click reports or injecting false referrer data.
How Install Hijacking Works:
- A user clicks on an ad from a legitimate media partner.
- The user is directed to the app store to download the app.
- The Android device broadcasts that a new app is being downloaded.
- Malware on the device generates a fake click report, making it appear as though the fraudster generated the install.
- Attribution is stolen upon app launch.
This method exploits the basic attribution model, but is relatively easy to identify using CTIT (Click-to-Install Time) measurements and anomaly detection.
Install hijacking fraud
2.2. Click Flooding
Click flooding involves fraudsters sending a high volume of false click reports from or on behalf of real devices. The goal is to falsely credit the sub-publisher with the install when the actual device downloads the app.
Process of Click Flooding:
- Fraudsters create publisher accounts across various attribution channels.
- They gather attribution URLs for as many apps as possible.
- Clicks are populated with real device details via malware or purchased user data.
- Clicks are generated randomly or based on user activity.
- When a user organically downloads an app, a false click is associated with them.
- The fraudster is credited with an organic install when the app is launched.
Click flooding can be identified and blocked using low conversion rates and CTIT measurements. A long CTIT rate indicates attempted click flooding. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers resources to enhance fraud detection.
Click flooding
3. Key Takeaways on Attribution Hijacking
Attribution hijacking, while seemingly simple, carries significant implications for advertisers. Understanding its complexity, potential gains, and business effects is crucial.
3.1. Complexity of Attribution Hijacking
Attribution hijacking methods are relatively simple to initiate and operate, requiring basic technology. The reliance on real user data means that much of the data is generated organically rather than falsely inserted into postback information.
3.2. Potential Gain from Attribution Hijacking
The potential gain is considered limited due to its simplicity, making it easy to detect with standard CTIT measurements. Operations are limited by the finite number of real devices to exploit.
3.3. Business Implications of Attribution Hijacking
Advertisers receive some value from real users, but marketing budget allocation is manipulated. Legitimate publishers are not rewarded, affecting future budget decisions.
4. Fake Installs Fraud Methods
Fake installs involve creating entirely fictitious user journeys, presenting a different set of challenges and implications for advertisers.
4.1. Device Farms
Device farms are locations packed with actual mobile devices clicking on ads and downloading apps, hiding behind false IP addresses and device IDs.
Characteristics of Device Farms:
- Located in remote areas or any space that can hold a large number of devices.
- Operated by low-paid employees or emulators.
- Constant app engagement and device resetting.
- Generate revenue by creating engagement and resetting device identities.
Monitoring a campaign’s New Device Rate (NDR) for anomalies can indicate device farm activity. According to AppsFlyer’s data, common NDRs should not exceed 10%-20% of a campaign’s activity. For more information on identifying device farms, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
Device ID reset fraud
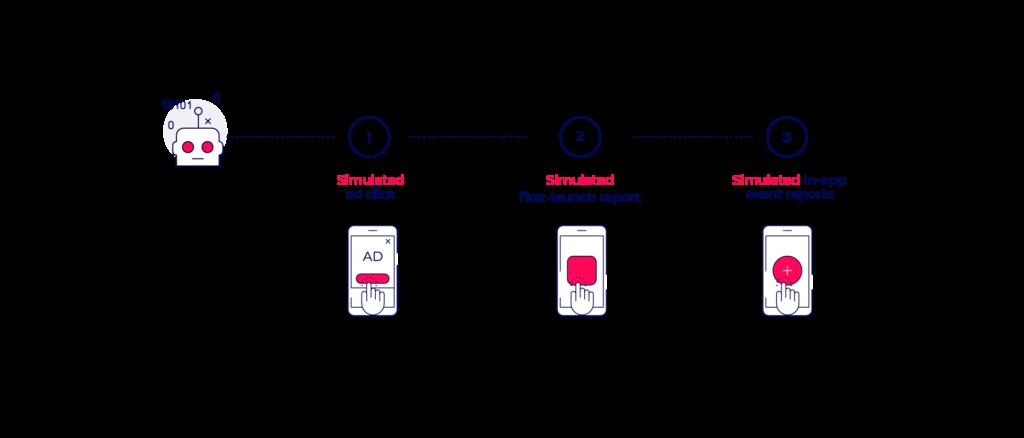
4.2. Bots
Bots are malicious codes that run a set program or action, sending clicks, installs, and in-app events for installs that never occurred.
Capabilities of Bots:
- Automate any action within the user flow or the app itself.
- Mimic real user behavior based on behavioral biometrics data.
- Trained to appear as engaged “real” users.
- Offer services such as harvesting game resources, passing levels, and generating revenue for third parties (Fraud as a Service or FAAS).
Fraudsters adapt to advanced detection logic and train bots to bypass in-app engagement measurement points.
Bot fraud
5. Key Takeaways on Fake Installs
Fake installs present different challenges compared to attribution hijacking. Understanding their complexity, potential gains, and business implications is crucial for combating them.
5.1. Complexity of Fake Installs
Fake install methods are more complicated to operate and maintain, requiring a high level of technological skill to generate users and randomize behavior at scale.
5.2. Potential Gain from Fake Installs
Once successful, fake user fraud schemes present unlimited potential scale, as they do not rely on real users or devices. This makes operations potentially limitless and profits much higher.
5.3. Business Implications of Fake Installs
Advertisers receive zero value from fake installs. User interactions are pre-programmed to drain CPA rates, and the advertiser’s data becomes worthless due to the mixture of fake and real users.
Fake installs fraud methods
6. Specific Fraud Techniques
Beyond the broad categories, specific techniques such as SDK hacking and in-app fraud present unique challenges and require specialized detection methods.
6.1. SDK Hacking
SDK hacking involves fraudsters feeding false information into advertiser servers by adding code to an app (the attacker) that generates simulated ad clicks, installs, and engagement signals on behalf of another app (the victim).
How SDK Hacking Works:
- Fraudsters add code to an attacking app.
- The code generates simulated ad clicks, installs, and engagement signals.
- The signals are sent to the advertiser’s attribution provider on behalf of a victim app.
- The advertiser pays for installs that did not occur.
SDK hacking is common with attribution providers that have weaker SDKs or poor security infrastructure. A closed-source, encrypted SDK provides better protection. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers resources to safeguard against SDK hacking.
6.2. In-App (CPA) Fraud
In-app CPA (Cost Per Action) fraud involves fraudsters targeting key in-app events to generate revenue, exploiting the CPA model designed to reward actions beyond installation.
Common In-App Events Targeted:
- Level reached
- Tutorial completed
- In-app purchase made
Fraudsters use sophisticated bots specifically designed to bypass install fraud detection and trigger rewarded in-app events, crushing advertiser in-app economies.
6.3. In-App Purchase Fraud
In-app purchase fraud targets in-app marketplaces, where fraudsters attempt to generate revenue by simulating purchases of merchandise, services, or virtual goods.
Characteristics of In-App Purchase Fraud:
- Targets apps with freemium business models.
- Fraudsters aim for CPS (Cost Per Sale) rates, which are the highest in the market.
- Fraudulent in-app purchase attempts are increasing across major verticals.
Advertisers need robust fraud detection to protect revenue streams generated by legitimate transactions.
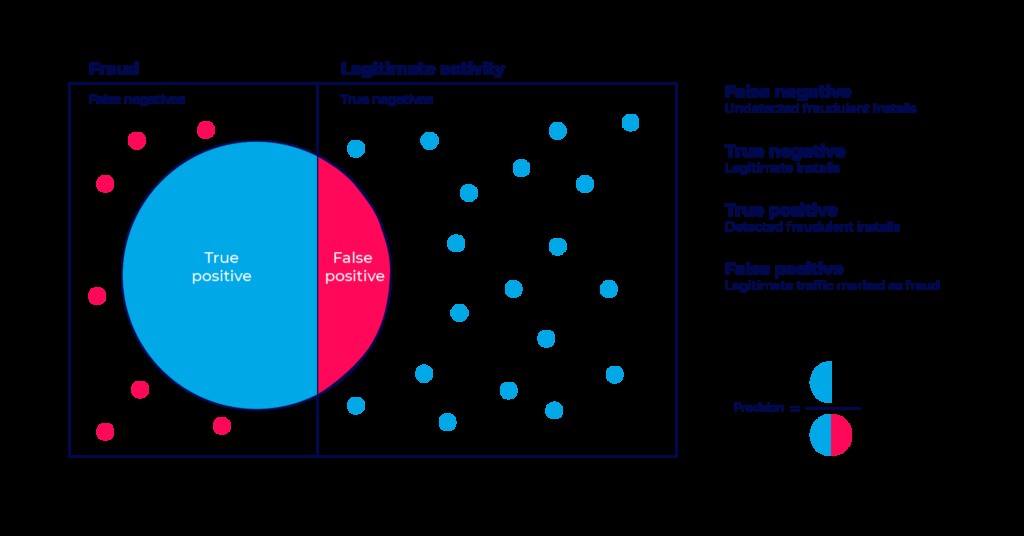
7. Understanding False Positives
A false positive occurs when a legitimate install is incorrectly flagged as fraud. Managing false positives is critical to maintaining trust and accuracy in fraud detection systems.
7.1. False Positive Test
The false positive test sets the allowed precision level for fraud detection algorithms. A higher precision level means a lower false positive rate.
Impact of False Positives:
- Penalize legitimate sources.
- Harm the advertiser’s relationship with quality media partners.
- Compromise the integrity and credibility of the fraud solution.
Responsible fraud solutions minimize false positive rates to protect client interests and maintain the credibility of media partnerships.
False positive test diagram
8. Fraud Prevention Strategies
Implementing robust fraud prevention strategies is essential to safeguard advertising investments and maintain the integrity of user acquisition data.
8.1. Real-Time Monitoring
Implementing real-time monitoring of key metrics such as CTIT, conversion rates, and new device rates allows for immediate detection of suspicious activities. Real-time analysis enables prompt responses to potential fraud attempts, reducing their impact.
8.2. Advanced Analytics
Employing advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms can detect patterns and anomalies indicative of fraudulent behavior. These technologies can identify sophisticated fraud tactics that may evade traditional detection methods.
8.3. Collaboration with Industry Partners
Collaborating with industry partners and sharing threat intelligence can enhance fraud detection capabilities. Collective knowledge sharing helps identify emerging fraud trends and develop coordinated prevention strategies.
8.4. Continuous SDK Updates
Regularly updating SDKs with the latest security patches and encryption technologies is crucial to prevent SDK hacking and other forms of code manipulation. Keeping the SDK secure minimizes vulnerabilities that fraudsters can exploit.
8.5. Verification of Attribution Data
Implementing methods to verify the accuracy of attribution data ensures that credit is accurately assigned to legitimate sources. This can include validating click timestamps and cross-referencing data with trusted partners.
8.6. Training and Education
Educating internal teams and media partners about fraud prevention best practices fosters a culture of vigilance and compliance. Training can equip stakeholders with the knowledge and skills to identify and report suspicious activities. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training materials and guidelines.
9. Case Studies: Successful Fraud Prevention
Examining real-world case studies demonstrates the effectiveness of various fraud prevention strategies and provides practical insights for implementation.
9.1. Gaming App: Preventing In-App Purchase Fraud
A gaming app detected a sudden surge in in-app purchases originating from suspicious sources. By implementing real-time monitoring and advanced analytics, the app identified patterns indicative of bot activity. The app blocked these sources and verified legitimate transactions, resulting in a significant reduction in fraudulent in-app purchases and increased revenue.
9.2. E-Commerce App: Combating Click Flooding
An e-commerce app experienced high volumes of click flooding, leading to inaccurate attribution and wasted ad spend. By collaborating with industry partners and sharing threat intelligence, the app identified and blocked the fraudulent sources. This resulted in improved attribution accuracy and more efficient marketing budget allocation.
9.3. Travel App: Mitigating SDK Hacking
A travel app discovered instances of SDK hacking, where fraudsters were generating simulated installs to claim attribution credit. By implementing continuous SDK updates and enhancing encryption technologies, the app mitigated the risk of code manipulation. This led to better protection of user data and accurate attribution reporting.
10. Future Trends in Mobile Ad Fraud
Staying ahead of emerging fraud trends is crucial for proactive fraud prevention. Understanding the evolving landscape allows advertisers to prepare and adapt their strategies accordingly.
10.1. AI-Driven Fraud
Fraudsters are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to create more sophisticated and evasive fraud tactics. AI-driven bots can mimic real user behavior with greater accuracy, making them harder to detect.
10.2. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers potential solutions for enhancing transparency and accountability in advertising attribution. Blockchain can create a secure and immutable ledger of ad interactions, reducing the risk of fraud.
10.3. Enhanced Biometric Verification
Enhanced biometric verification methods can provide more accurate user authentication, reducing the likelihood of fraudulent installs and in-app activities. Biometric data can confirm user identity and validate the legitimacy of interactions.
10.4. Privacy-Centric Fraud Detection
Privacy-centric fraud detection methods prioritize user privacy while still providing effective fraud prevention. These methods use anonymized data and privacy-enhancing technologies to detect fraud without compromising user information.
11. Importance of Compliance and Ethics
Compliance with industry regulations and ethical standards is essential for maintaining integrity and building trust with users and partners.
11.1. GDPR Compliance
Complying with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) ensures that user data is handled responsibly and transparently. GDPR compliance requires obtaining user consent for data collection and providing users with control over their data.
11.2. CCPA Compliance
Complying with the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) ensures that California residents have the right to know what personal information is collected about them and the right to opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
11.3. Ethical Advertising Practices
Adhering to ethical advertising practices ensures that advertisements are truthful, non-deceptive, and fair. Ethical advertising builds trust with users and promotes a positive brand image.
12. The Role of CONDUCT.EDU.VN
CONDUCT.EDU.VN serves as a valuable resource for individuals and organizations seeking to understand and combat fraud. We offer comprehensive information, guidelines, and training materials to promote ethical conduct and compliance.
12.1. Comprehensive Resources
CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides a wide range of resources, including articles, case studies, and best practices, to help users understand and prevent fraud. Our resources are regularly updated to reflect the latest trends and techniques in fraud prevention.
12.2. Expert Guidance
Our team of experts offers guidance and support to organizations seeking to implement effective fraud prevention strategies. We provide tailored solutions to meet the unique needs of our clients.
12.3. Training Programs
CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers training programs to equip internal teams and media partners with the knowledge and skills to identify and report suspicious activities. Our training programs promote a culture of vigilance and compliance.
13. FAQ: Common Questions About Fraud
Here are some frequently asked questions about fraud and how to combat it:
- What is mobile ad fraud? Mobile ad fraud refers to deceptive practices in mobile advertising aimed at generating fraudulent revenue.
- How can I identify attribution hijacking? Look for anomalies in CTIT measurements and conversion rates.
- What are the key indicators of fake installs? High NDRs and unusual in-app activity are common indicators.
- How does SDK hacking work? Fraudsters add code to an app that generates simulated ad clicks and installs.
- What is in-app (CPA) fraud? Fraudsters target key in-app events to generate revenue.
- What are false positives, and how can I minimize them? False positives are legitimate installs flagged as fraud. Minimize them by setting a higher precision level in fraud detection algorithms.
- What steps can I take to prevent mobile ad fraud? Implement real-time monitoring, advanced analytics, and collaboration with industry partners.
- How can CONDUCT.EDU.VN help with fraud prevention? We provide comprehensive resources, expert guidance, and training programs.
- Why is compliance with regulations like GDPR important? Compliance ensures responsible and transparent handling of user data.
- What are some future trends in mobile ad fraud? AI-driven fraud and blockchain technology are emerging trends.
14. Final Thoughts: Protecting Your Interests
Protecting your advertising investments and maintaining the integrity of user data requires vigilance, proactive strategies, and a commitment to ethical practices. By understanding the methods of mobile ad fraud and implementing effective prevention strategies, you can safeguard your interests and build trust with users and partners.
Remember, staying informed and continuously adapting to the evolving fraud landscape is essential for maintaining a robust defense. Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 555-1234 for more resources and expert guidance on fraud prevention.
Don’t let fraud compromise your success. Take action today to safeguard your business and build a secure and trustworthy future. Explore conduct.edu.vn for detailed insights and actionable strategies that will empower you to detect, prevent, and mitigate fraud effectively.