360 video offers an immersive viewing experience, and this beginner’s guide provides a comprehensive introduction to capturing and producing this engaging content. CONDUCT.EDU.VN explains everything from the history of 360° visuals to the latest advancements in cameras and techniques. Master 360-degree filming, virtual reality content creation, and immersive storytelling with the help of this resource.
1. Unveiling the World of 360 Video
Before diving into the practical aspects of creating 360 videos, it’s essential to understand the core concepts and terminology that define this exciting medium. Let’s explore the history, key terms, and fundamental ideas that shape the world of immersive 360 content creation.
1.1. A Journey Through Time: The Evolution of Immersive Visuals
The desire to capture and reproduce immersive visual experiences isn’t a recent phenomenon; it’s a pursuit that spans centuries. From ancient art to modern technology, humans have consistently sought ways to create the sensation of being present within a scene.
During the Roman Empire, artists decorated buildings with murals depicting landscapes, court life, and historical events, creating a kind of 360 visual experience. The concept of the panorama, an ultra-wide horizontal perspective, has existed for centuries, with examples found in various cultures, such as the Song Dynasty in China.
Painters and visual artists in late-18th-century Europe explored new methods of showcasing their panorama art. English painter Robert Barker coined the term “panorama” in 1792, inspired by the Greek words for “all” (pan) and “view” (horama). Barker’s interactive presentation, featuring panoramic paintings of cities wrapped around cylindrical displays, created a deeper sense of immersion. These “cycloramas” became popular throughout the 19th century, with purpose-built panorama theaters appearing across Europe and North America.
These 360 exhibits allowed audiences to experience spaces and events they might never have access to otherwise, especially significant in an age when travel was slow and costly. Photographers developed early panoramic cameras, sequencing wide shots together to recreate unbroken views of cities and landscapes. The U.S. Library of Congress has an extensive collection of early panorama photography.
Another unique way to showcase photography immersively was the Kaiserpanorama, patented in 1890. This circular mini-theater used stereoscopic images, presenting slightly different angles to each eye, creating a sense of depth. The stereoscopic technique forms the basis for many modern “3D” experiences.
1.2. The Rise of Digital 360: A Technological Leap
Camera technology advancements, from pressed plates to flexible film, enhanced the ability to create immersive visual experiences. However, throughout much of the early to mid-20th century, 360 photography and video remained expensive and complex, with image quality trailing behind conventional camera technology. The late 20th century introduced smaller, more affordable panoramic cameras, but their use remained largely limited to professionals due to setup, training, and production know-how requirements.
The early 2000s marked a turning point with the advent of sophisticated, affordable digital cameras and smartphones. Companies like Nikon and Canon introduced digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) cameras, inspiring new generations of photographers. GoPro popularized affordable action cameras designed for durability and stability in extreme conditions.
GoPro’s action camera became popular by offering a small, robust camera with a very wide lens. While this became popular with extreme sports lovers, it also found a place in 360 shooting.
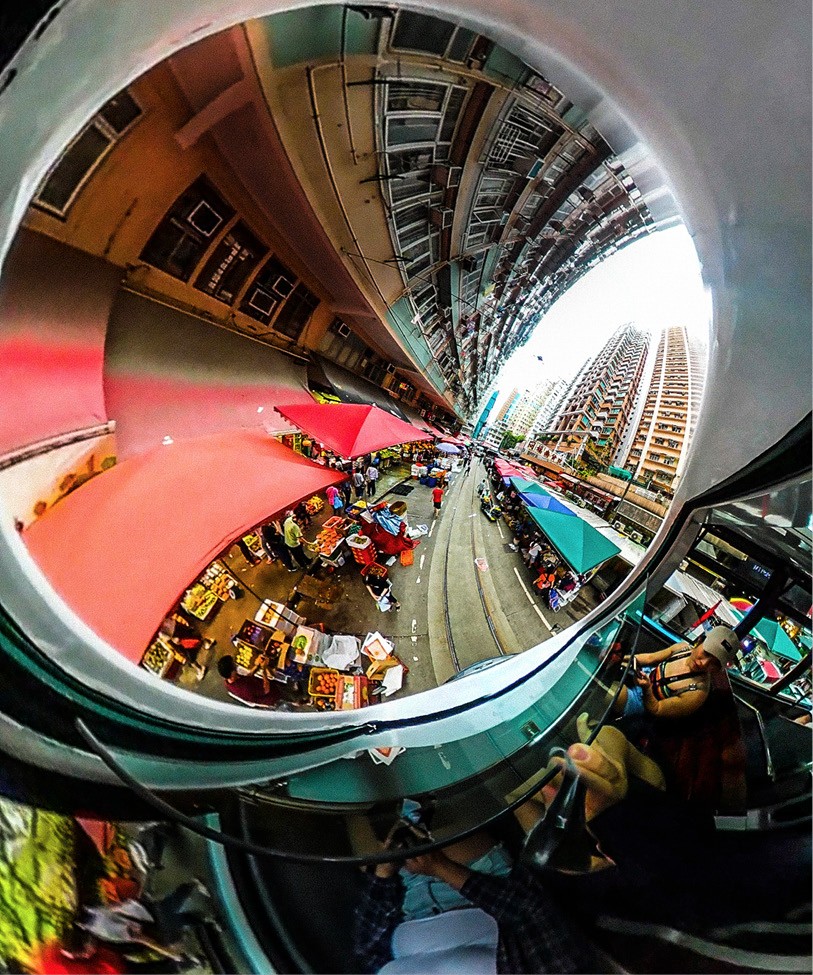
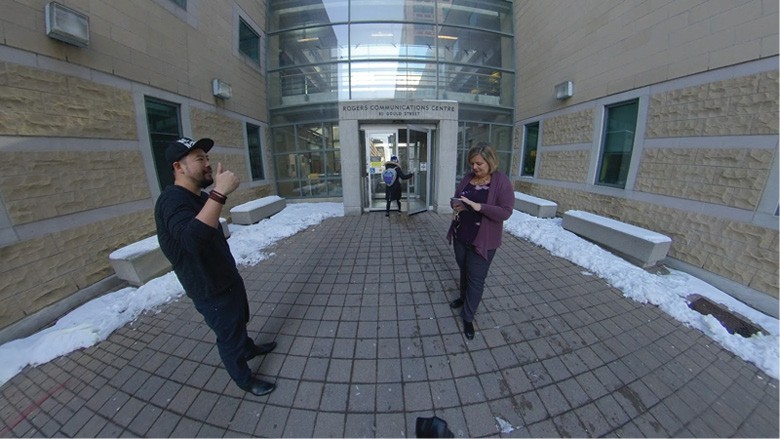
Standard cameras utilize one lens, allowing you to shoot with a narrow field of vision, generally a few degrees up to 180 degrees. In order to create a 360 effect, one would use a computer program to arrange and overlap the separate wide shots together to create an unbroken view of a scene in all directions — essentially, a panorama that covered the entire field of view for a person. This is why 360 video is often referred to as being spherical — spheres have no edges, so you can keep looking around and around — vs. flat video (i.e. 180 degree visuals where the edges are clearly visible).
The ability to shoot and edit digital files and the higher optical quality of these new digital cameras made 360 content production far easier. One could now position a few digital cameras together in a custom rig, covering every angle. Each camera would shoot video simultaneously, giving the shooter high-quality videos and photos from each angle. Several rigs were developed using multiple GoPro cameras, which were quite clunky and hard to manage.
There were several other major disadvantages with these rigs. One was the cost. At about $500 per GoPro camera the price quickly escalated (and don’t forget the SD cards needed as well!). The other issue was that if one of the cameras stopped working (battery issues for example), then there would be a piece of the 360 scene missing.
The other disadvantage with these rigs was that they required tremendous computing power (and time!) to sequence all the footage together. Clearly this was not technology aimed at main street.
There were other attempts to create 360 photos. One involved placing a single GoPro camera on a motorized tilt pan head which would automatically rotate and take the photos needed to create a 360 photo. It would then stitch the photos together using software. The issue with this set up was that if there were people in the scene they had to stand completely still (sort of a throw back to the early days of photography!). Again, this was not a technology that would work for most people and was only photos, not video.
Over the past decade, rapid advances in 360 shooting technology have reduced the need for elaborate rigs. High-definition video became a standard feature on digital cameras, including smartphones. Affordable 360 cameras capable of shooting 4K resolution video emerged, with 6K and 8K cameras becoming increasingly accessible.
1.3. Stitching: The Art of Seamless Immersion
Significant progress has been made in creating cameras and programs that simplify the process of sequencing footage. Stitching, the act of combining separate shots to produce a 360 effect, is a crucial aspect of 360 video production. A seamless stitch helps create a smooth and convincing 360 “illusion.” Challenges can arise due to distortions, blurring, or lighting differences along stitch lines.
The primary method for shooting high-quality 360 video involved rigging multiple cameras and stitching the footage together using computer software. However, the development of affordable, user-friendly digital cameras specifically designed to capture 360 content has revolutionized the field. Companies like Samsung, GoPro, and Insta360 have introduced various 360 camera options for hobbyists and professional filmmakers alike. These cameras typically feature multiple lenses on a single body, capturing a 180-degree field of view on each side.
1.4. Immersive Viewing: From Theaters to Headsets
Innovations in how we view 360 content are as important as advancements in 360 cameras. 360 video was once limited to specialized theater experiences. Walt Disney explored 360 cinema with “Circarama” (later called Circlevision) in 1955, using multiple projectors to create a panoramic experience. Space 360 in Gwangju, South Korea, offers a true 360 experience with projected images surrounding viewers on a glass bridge.
However, theater-based 360 experiences are limited by the need for special buildings and audience size. Today, 360 video content can be easily viewed on computers and smartphones. For a more immersive experience, headsets or head-mounted devices (HMDs) block out distractions and enhance the sensation of presence. Headsets like Google Cardboard, Oculus, and HTC Vive offer varying levels of immersion and control.
1.5. Demystifying the Terminology: 360, 3D-360, and VR Video
360 video, 3D video, and virtual reality (VR) are often used interchangeably, but they are distinct in their own rights.
- 360 Video: Allows viewers to choose their viewing angle using a mouse, trackpad, or by moving their phone.
- 3D-360 Video: Employs stereoscopic techniques to create the illusion of depth.
- Virtual Reality (VR): An immersive media experience that replicates a real or imagined environment, allowing users to interact with the world in a way that feels as if they are there. VR emphasizes presence, the sensation of feeling physically part of the scene.
1.6. Degrees of Freedom: Exploring Virtual Worlds
Degrees of freedom (DoF) refer to the ways a user can move and interact within a virtual environment.
- 3DoF: Allows rotational movements around the x, y, and z axes (pitch, yaw, and roll). Users can look around but are tethered to a single spot.
- 6DoF: Allows movement within a scene, including elevating, strafing, and surging. Users can explore a scene more freely with natural movements like walking and crouching.
YouTube and Facebook typically offer 3DoF experiences, while premium VR headsets like Oculus and HTC Vive support 6DoF games and video content.
CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides comprehensive information on the latest advancements in 360 video technology and techniques. For inquiries, contact us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (707) 555-1234. Visit our website: CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
2. Mastering the Art of 360 Video Production
Now that we’ve explored the history and fundamental concepts of 360 video, let’s delve into the practical aspects of capturing and producing immersive content. This section will guide you through the essential steps and techniques for creating compelling 360 videos that captivate your audience.
2.1. Selecting the Right Equipment: Choosing Your 360 Camera
The first step in your 360 video journey is selecting the right camera. Various options are available, ranging from affordable consumer models to high-end professional cameras. Consider your budget, intended use, and desired level of quality when making your decision.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a 360 Camera:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Resolution | Higher resolution captures more detail, resulting in sharper and more immersive videos. Look for cameras that can shoot at least 4K resolution. |
| Lenses | Most 360 cameras feature two or more lenses that capture a wide field of view. The number and quality of lenses affect the overall image quality and stitching. |
| Stitching | Some cameras offer automatic in-camera stitching, while others require manual stitching using software. Consider your comfort level with post-processing. |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly cameras with intuitive controls and software can make the production process smoother and more enjoyable. |
| Price | 360 cameras range in price from a few hundred dollars to several thousand. Determine your budget and find a camera that meets your needs. |


2.2. Planning Your Shoot: Storyboarding and Composition
Effective 360 video requires careful planning and attention to composition. Unlike traditional video, where you control the viewer’s perspective, 360 video allows viewers to explore the scene at their own pace.
Tips for Planning Your 360 Video Shoot:
- Develop a Storyboard: Plan out the key scenes and shots you want to capture. Consider how viewers will navigate the scene and what they will focus on.
- Consider Composition: Pay attention to the placement of subjects and objects within the 360-degree frame. Guide viewers’ attention with leading lines, framing, and visual cues.
- Minimize Camera Movement: Excessive camera movement can be disorienting in 360 video. Use smooth, deliberate movements or keep the camera stationary.
- Think About Audio: Immersive audio is essential for creating a sense of presence. Use spatial audio techniques to create a realistic soundscape that matches the visuals.
2.3. Capturing the Footage: Shooting Techniques for 360 Video
Shooting 360 video requires different techniques than traditional video. Here are some tips for capturing high-quality 360 footage:
Essential Shooting Techniques:
- Keep the Camera Level: Ensure the camera is level to avoid distortion and maintain a natural perspective.
- Minimize Obstructions: Avoid placing objects too close to the camera, as they can cause parallax errors and stitching issues.
- Control Lighting: Pay attention to lighting conditions and avoid extreme contrast. Use natural light or external lights to illuminate the scene evenly.
- Monitor Audio Levels: Use an external microphone to capture clear and immersive audio. Monitor audio levels to avoid clipping and distortion.
2.4. Stitching and Editing: Assembling Your 360 Masterpiece
Once you’ve captured your 360 footage, the next step is to stitch and edit it together. Stitching software combines the footage from multiple lenses into a single 360-degree video. Editing software allows you to refine your video, add effects, and create a compelling narrative.
Key Steps in Stitching and Editing:
- Import Footage: Import the footage from your 360 camera into your stitching software.
- Stitch the Footage: Use the software’s stitching tools to combine the footage from multiple lenses into a seamless 360-degree video.
- Stabilize the Footage: Stabilize the footage to remove any unwanted camera movement.
- Color Correct the Footage: Adjust the color and brightness of the footage to create a consistent look.
- Add Effects and Transitions: Add visual effects, transitions, and text to enhance your video.
- Edit Audio: Edit the audio to create an immersive soundscape.
- Export the Video: Export the video in a format compatible with 360 video platforms like YouTube and Facebook.
CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides detailed guidance on ethical video production and distribution. For assistance, reach out to us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (707) 555-1234. Visit our website: CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
3. Optimizing and Sharing Your 360 Video
With your 360 video masterpiece complete, it’s time to optimize it for viewing and share it with the world. This section will guide you through the process of optimizing your video for different platforms and promoting it to reach a wider audience.
3.1. Choosing the Right Platform: YouTube, Facebook, and Beyond
360 videos can be shared on various platforms, each with its own unique features and audience. YouTube and Facebook are the most popular platforms for sharing 360 videos, but other options exist, such as Vimeo, Littlstar, and Veer.
Comparing 360 Video Platforms:
| Platform | Features | Audience |
|---|---|---|
| YouTube | Wide reach, supports 360 and VR video, monetization options, analytics, integration with Google Cardboard and Daydream. | Broad audience, diverse interests. |
| Large user base, supports 360 video, social sharing, integration with Oculus VR, live 360 video. | Socially connected audience, diverse demographics. | |
| Vimeo | High-quality video, ad-free experience, customizable player, advanced analytics, professional community. | Creative professionals, filmmakers, and video enthusiasts. |
| Littlstar | Dedicated 360 and VR platform, curated content, supports various VR headsets, monetization options. | VR enthusiasts, early adopters. |
| Veer | Focus on high-quality 360 content, curated selection, supports various VR headsets, monetization options. | VR enthusiasts, professional creators. |
3.2. Optimizing for Viewing: Resolution, Bitrate, and Format
To ensure a smooth and immersive viewing experience, it’s essential to optimize your 360 video for the platform you’re using. This involves selecting the right resolution, bitrate, and format.
Recommended Settings for 360 Video:
| Setting | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Resolution | Minimum 4K (3840×2160), 5.6K (5760×2880) or 8K (7680×3840) for higher quality. |
| Bitrate | 50-80 Mbps for 4K, 80-120 Mbps for 5.6K, 120-150 Mbps for 8K. |
| Format | MP4 with H.264 or H.265 codec. |
| Frame Rate | 24, 25, 30, or 60 fps. |
| Audio | AAC codec, 48kHz sample rate, 192-320 kbps bitrate. |
| Metadata | Inject 360 metadata into the video file using tools like Spatial Media Metadata Injector or platform-specific settings. This tells the platform that the video is in 360 format and enables interactive viewing. |
3.3. Promoting Your Video: Reaching a Wider Audience
Creating a great 360 video is only half the battle. To reach a wider audience, you need to promote your video effectively.
Strategies for Promoting Your 360 Video:
- Optimize Your Video Title and Description: Use relevant keywords to help people find your video.
- Create a Compelling Thumbnail: Choose a thumbnail that grabs attention and accurately represents your video.
- Share Your Video on Social Media: Promote your video on social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
- Engage with Your Audience: Respond to comments and questions to build a community around your video.
- Collaborate with Other Creators: Partner with other 360 video creators to cross-promote your videos.
- Submit Your Video to 360 Video Festivals and Competitions: Gain recognition and exposure for your work.
- Use Paid Advertising: Consider using paid advertising on platforms like YouTube and Facebook to reach a wider audience.
3.4. Ethical Considerations: Responsible 360 Video Creation
As a 360 video creator, it’s essential to be mindful of ethical considerations. This includes respecting privacy, avoiding misinformation, and promoting responsible use of the technology.
Ethical Guidelines for 360 Video Creation:
- Obtain Consent: Obtain informed consent from individuals before recording them in 360 video.
- Protect Privacy: Avoid capturing sensitive or private information without permission.
- Be Transparent: Disclose any potential biases or conflicts of interest.
- Avoid Misinformation: Ensure your video is accurate and does not mislead viewers.
- Promote Responsible Use: Encourage viewers to use 360 video technology responsibly and ethically.
CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides resources and guidance on ethical content creation. For support, contact us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (707) 555-1234. Visit our website: CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
4. The Future of 360 Video
360 video technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations and applications emerging all the time. Let’s explore some of the exciting trends shaping the future of 360 video.
4.1. Emerging Technologies: Volumetric Video and Light Field Capture
Volumetric video and light field capture are emerging technologies that promise to revolutionize 360 video. Volumetric video captures a 3D representation of a scene, allowing viewers to move around and interact with the environment in a more realistic way. Light field capture captures the direction and intensity of light rays, creating a more immersive and photorealistic experience.
Benefits of Volumetric Video and Light Field Capture:
- Enhanced Immersion: Creates a more realistic and engaging experience for viewers.
- Increased Interactivity: Allows viewers to move around and interact with the environment.
- Improved Photorealism: Captures more detail and accurately represents the real world.
4.2. New Applications: Education, Training, and Entertainment
360 video is finding new applications in various fields, including education, training, and entertainment.
Examples of 360 Video Applications:
- Education: Virtual field trips, immersive learning experiences.
- Training: Simulated environments for training professionals in high-risk industries.
- Entertainment: Immersive storytelling, virtual concerts, live events.
- Real Estate: Virtual tours of properties.
- Tourism: Immersive travel experiences.
- Healthcare: Virtual reality therapy, medical training.
4.3. The Convergence of 360 Video and VR: A Seamless Immersive Experience
The convergence of 360 video and VR is creating a seamless immersive experience that blurs the lines between the real and virtual worlds. VR headsets are becoming more affordable and accessible, making it easier for people to experience 360 video in a fully immersive way.
Benefits of the Convergence of 360 Video and VR:
- Enhanced Immersion: Creates a more realistic and engaging experience for viewers.
- Increased Interactivity: Allows viewers to interact with the environment in a more natural way.
- New Storytelling Possibilities: Opens up new avenues for storytelling and creative expression.
CONDUCT.EDU.VN is committed to providing the latest insights on emerging technologies and ethical considerations in the field of immersive media. For more information, contact us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (707) 555-1234. Visit our website: CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
5. FAQ: Your Questions Answered About 360 Video
Here are some frequently asked questions about 360 video:
- What is 360 video? 360 video is a video format that allows viewers to explore a scene from any angle, creating an immersive viewing experience.
- What equipment do I need to create 360 video? You’ll need a 360 camera, a tripod, and editing software.
- How do I stitch 360 video footage? Use stitching software to combine the footage from multiple lenses into a seamless 360-degree video.
- What is the best resolution for 360 video? A minimum of 4K (3840×2160) is recommended, but 5.6K (5760×2880) or 8K (7680×3840) provides higher quality.
- How do I optimize 360 video for YouTube and Facebook? Use the recommended resolution, bitrate, and format for each platform. Inject 360 metadata into the video file.
- What are the ethical considerations for 360 video creation? Obtain consent, protect privacy, be transparent, avoid misinformation, and promote responsible use.
- What is volumetric video? Volumetric video captures a 3D representation of a scene, allowing viewers to move around and interact with the environment.
- What are the applications of 360 video? 360 video is used in education, training, entertainment, real estate, tourism, and healthcare.
- How is 360 video related to virtual reality? The convergence of 360 video and VR creates a seamless immersive experience that blurs the lines between the real and virtual worlds.
- Where can I learn more about 360 video? CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides comprehensive resources and guidance on 360 video production and ethical considerations.
By following the guidance provided by conduct.edu.vn, you can easily navigate the world of 360 video and contribute to a more ethical and immersive digital landscape.