Drawing hands can be a daunting task for artists of all skill levels. However, with the right guidance and techniques, anyone can master the art of hand drawing. CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive solution, offering expert tips and resources to improve your artistic skills and refine hand drawing techniques. Learn practical methods and elevate your drawing expertise with our illustrative tutorials, drawing reference materials, and educational articles.
1. Understanding Hand Anatomy for Artists
Drawing realistic and expressive hands requires a solid understanding of hand anatomy. The human hand is a complex structure composed of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, all working together to allow a wide range of movements and gestures. Artists who take the time to study and understand this anatomy are better equipped to create accurate and compelling hand drawings.
1.1. The Skeletal Structure of the Hand
The skeletal structure of the hand consists of 27 bones, divided into three main groups: the carpals (wrist bones), the metacarpals (palm bones), and the phalanges (finger bones).
- Carpals: There are eight carpal bones arranged in two rows at the wrist. These bones provide flexibility and support to the wrist joint.
- Metacarpals: Five metacarpal bones form the palm of the hand. Each metacarpal connects to a finger and allows for grasping and gripping actions.
- Phalanges: Each finger has three phalanges (proximal, middle, and distal), except for the thumb, which has only two (proximal and distal). These bones provide the structure and articulation for finger movements.
Understanding the arrangement and proportions of these bones is crucial for accurately depicting hand shapes and gestures.
1.2. Muscles and Tendons in Hand Drawings
Muscles and tendons play a significant role in hand movement and contour. The muscles that control hand and finger movements are located both within the hand (intrinsic muscles) and in the forearm (extrinsic muscles).
- Intrinsic Muscles: These muscles are located within the hand and are responsible for fine motor movements and precise control of the fingers.
- Extrinsic Muscles: These muscles originate in the forearm and have tendons that extend into the hand. They are responsible for powerful gripping and large-scale movements of the hand and fingers.
Tendons connect muscles to bones and transmit the force generated by the muscles to move the hand and fingers. When drawing hands, it’s important to understand how these muscles and tendons create the visible contours and shapes on the surface of the hand.
1.3. Proportions and Landmarks of the Hand
Accurate proportions are essential for creating realistic hand drawings. Here are some key proportions and landmarks to keep in mind:
- Hand Length: The length of the hand is roughly equal to the distance from the wrist to the base of the fingers.
- Finger Lengths: The middle finger is the longest, followed by the index and ring fingers, which are approximately the same length. The little finger is the shortest.
- Thumb Position: The thumb originates from the wrist and extends outwards, allowing for opposition and grasping actions.
- Knuckles: The knuckles (metacarpophalangeal joints) create prominent landmarks on the back of the hand and affect the overall shape and contour.
- Wrist Creases: The wrist creases are important landmarks that indicate the flexibility and movement of the wrist joint.
By paying attention to these proportions and landmarks, artists can create more accurate and convincing hand drawings.
2. Essential Techniques for Drawing Realistic Hands
Drawing realistic hands involves more than just understanding anatomy; it also requires mastering various drawing techniques. These techniques help capture the nuances of hand shapes, gestures, and textures.
2.1. Gesture Drawing and Simplifying Hand Shapes
Gesture drawing is a technique that focuses on capturing the essence of a pose or action quickly and dynamically. When drawing hands, start with a gesture drawing to capture the overall movement and flow of the hand. Simplify the hand into basic shapes, such as rectangles, ovals, and cylinders, to establish the proportions and structure.
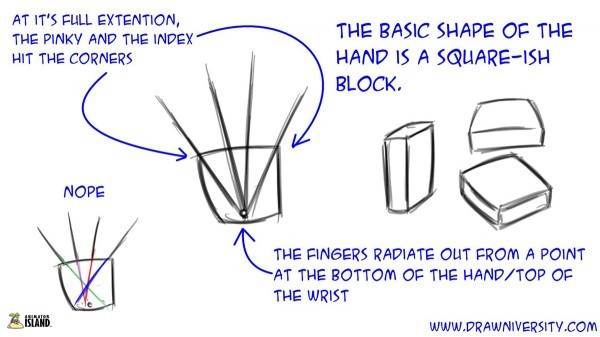
2.2. Using Basic Shapes to Construct Hands
Breaking down the hand into basic shapes is a fundamental technique for creating accurate and well-proportioned drawings. Start by visualizing the palm as a flattened rectangle or square, and then add cylinders for the fingers and a modified triangle for the thumb.
- Palm: Represent the palm as a flattened rectangle or square, paying attention to its proportions and curvature.
- Fingers: Draw the fingers as a series of connected cylinders, with each cylinder representing a phalanx.
- Thumb: Represent the thumb as a modified triangle or teardrop shape, considering its unique range of motion and position relative to the palm.
By constructing the hand from these basic shapes, you can create a solid foundation for adding details and refining the drawing.
2.3. Line of Action and Flow in Hand Drawings
The line of action is an imaginary line that runs through the center of a form, indicating its direction and movement. When drawing hands, identify the line of action to create a sense of flow and dynamism. The line of action can run through the palm, fingers, or thumb, depending on the gesture.
2.4. Contouring and Shading Techniques
Contouring and shading are essential for adding depth and realism to hand drawings. Use contour lines to define the edges and shapes of the hand, and then apply shading to create volume and form.
- Contour Lines: Use varying line weights to emphasize different parts of the hand. Thicker lines can indicate areas in shadow, while thinner lines can suggest highlights.
- Shading: Apply shading to create the illusion of light and shadow on the hand. Consider the direction of the light source and how it affects the planes and surfaces of the hand. Use techniques such as hatching, cross-hatching, and blending to create smooth gradations of tone.
2.5. Capturing Hand Gestures and Expressions
Hands are incredibly expressive and can convey a wide range of emotions and intentions. When drawing hands, pay attention to the gesture and expression you want to communicate.
- Observe Real Hands: Study real hands in different poses and gestures to understand how they move and change shape.
- Exaggerate Poses: Exaggerate poses and expressions to emphasize the emotion or intention you want to convey.
- Consider the Context: Consider the context of the drawing and how the hands interact with other elements in the composition.
3. Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Drawing hands can be challenging, and it’s easy to make mistakes. However, by being aware of these common pitfalls and learning how to avoid them, you can improve the accuracy and realism of your hand drawings.
3.1. Proportional Errors in Drawings
One of the most common mistakes is getting the proportions wrong. Fingers that are too long or too short, a palm that is too big or too small, or a thumb that is out of proportion can all detract from the realism of a hand drawing.
- Measure and Compare: Use your pencil or a ruler to measure the proportions of real hands and compare them to your drawing.
- Use Reference Photos: Use reference photos to check the proportions and shapes of hands in different poses.
- Step Back and Evaluate: Step back from your drawing periodically to evaluate the overall proportions and make adjustments as needed.
3.2. Stiffness and Lack of Natural Flow
Hands should appear natural and relaxed, not stiff and rigid. Avoid drawing fingers that are perfectly straight or evenly spaced, as this can create an unnatural look.
- Study Hand Gestures: Study the natural curves and movements of real hands to understand how they flow and bend.
- Use a Line of Action: Use a line of action to guide the flow of the hand and create a sense of movement.
- Vary Finger Positions: Vary the positions of the fingers to create a more natural and dynamic look.
3.3. Over-Reliance on Outlines
Relying too heavily on outlines can flatten the hand and make it appear two-dimensional. Avoid drawing thick, dark outlines around the entire hand.
- Use Contour Lines: Use contour lines to define the edges and shapes of the hand, but vary the line weight to create depth and volume.
- Shading: Use shading to create the illusion of form and volume on the hand.
- Lost and Found Edges: Use lost and found edges to create a more natural and organic look.
3.4. Ignoring Anatomical Details
Ignoring anatomical details can result in a hand that looks generic and unconvincing. Pay attention to the underlying bone structure, muscles, and tendons that create the visible forms and shapes on the hand.
- Study Anatomy: Study hand anatomy to understand the underlying structure and how it affects the surface forms.
- Observe Real Hands: Observe real hands closely to see how the bones, muscles, and tendons create the visible contours and shapes.
- Use Reference Photos: Use reference photos to capture the anatomical details of hands in different poses.
3.5. Inconsistent Shading and Lighting
Inconsistent shading and lighting can create a confusing and unrealistic effect. Pay attention to the direction of the light source and how it affects the planes and surfaces of the hand.
- Establish a Light Source: Establish a clear light source and use it consistently throughout the drawing.
- Understand Planes: Understand how the planes and surfaces of the hand interact with the light source to create highlights, shadows, and midtones.
- Use Gradations of Tone: Use smooth gradations of tone to create a realistic illusion of form and volume.
4. Advanced Tips for Drawing Hands
Once you have mastered the basic techniques, you can move on to more advanced tips and tricks for drawing hands. These tips will help you create even more realistic and expressive hand drawings.
4.1. Drawing Hands from Different Angles and Perspectives
Drawing hands from different angles and perspectives can be challenging, but it’s essential for creating dynamic and engaging compositions.
- Foreshortening: Understand the principles of foreshortening and how it affects the appearance of hands and fingers.
- Use Reference Photos: Use reference photos to study how hands look from different angles and perspectives.
- Visualize in 3D: Visualize the hand in 3D space to understand how the forms and shapes change as the viewing angle shifts.
4.2. Drawing Hands in Motion and Action
Drawing hands in motion requires capturing the energy and flow of the movement.
- Gesture Drawing: Start with a gesture drawing to capture the overall movement and flow of the hand.
- Exaggerate Poses: Exaggerate poses to emphasize the energy and dynamism of the movement.
- Use Blur: Use blur or motion lines to suggest movement and speed.
4.3. Drawing Hands with Different Skin Tones and Textures
Drawing hands with different skin tones and textures requires careful attention to detail and nuance.
- Study Skin Tones: Study the different skin tones and undertones of real hands to understand how they vary.
- Use Color: Use color to capture the subtle variations in skin tone and create a realistic effect.
- Add Texture: Add texture to the skin using techniques such as stippling, hatching, or cross-hatching.
4.4. Drawing Hands with Details: Wrinkles, Veins, and Nails
Adding details such as wrinkles, veins, and nails can enhance the realism and character of your hand drawings.
- Observe Real Hands: Observe real hands closely to see how wrinkles, veins, and nails appear in different poses and lighting conditions.
- Use Subtle Lines: Use subtle lines to indicate wrinkles and veins, avoiding heavy or harsh lines.
- Shape Nails: Shape the nails carefully to match the contours of the fingers and create a realistic effect.
4.5. Developing a Personal Style in Drawing Hands
Developing a personal style is an essential part of artistic growth. Experiment with different techniques, materials, and approaches to find what works best for you.
- Study Other Artists: Study the work of other artists to see how they draw hands and develop their own unique styles.
- Experiment: Experiment with different techniques and materials to find what you enjoy and what suits your artistic vision.
- Practice: Practice regularly to refine your skills and develop your own unique style.
5. Drawing Hands for Different Characters and Styles
The way you draw hands can vary depending on the character and style you are trying to create. Consider the age, gender, and personality of the character when drawing their hands.
5.1. Drawing Male vs. Female Hands
Male and female hands have distinct characteristics that can be emphasized in your drawings.
- Male Hands: Male hands tend to be larger, more muscular, and have more prominent knuckles and veins.
- Female Hands: Female hands tend to be smaller, more delicate, and have smoother contours.
5.2. Drawing Hands for Different Age Groups
The appearance of hands changes with age.
- Young Hands: Young hands are typically soft, smooth, and have fewer wrinkles.
- Elderly Hands: Elderly hands have more wrinkles, thinner skin, and more prominent veins and bones.
5.3. Drawing Cartoon Hands
Cartoon hands are often simplified and exaggerated for comedic effect.
- Simplify Shapes: Simplify the shapes of the hands and fingers to create a more cartoonish look.
- Exaggerate Poses: Exaggerate poses and expressions to emphasize the humor and personality of the character.
- Use Bold Lines: Use bold lines and bright colors to create a visually striking effect.
5.4. Drawing Stylized Hands
Stylized hands can be used to create a unique and distinctive look.
- Experiment with Proportions: Experiment with different proportions and shapes to create a stylized effect.
- Use Texture: Use texture and patterns to add visual interest and create a unique look.
- Combine Elements: Combine elements from different styles and approaches to create your own unique style.
5.5. Integrating Hands into Character Design
Hands should be an integral part of character design, reflecting the personality, occupation, and lifestyle of the character.
- Consider the Context: Consider the context of the character and how their hands interact with their environment.
- Use Props: Use props to emphasize the character’s personality and occupation.
- Tell a Story: Use the hands to tell a story and convey the character’s emotions and intentions.
6. Practice Exercises and Resources
To improve your hand drawing skills, it’s important to practice regularly and use a variety of resources.
6.1. Daily Hand Drawing Exercises
Set aside time each day to practice drawing hands.
- Gesture Drawings: Do quick gesture drawings to capture the overall movement and flow of the hand.
- Anatomy Studies: Do anatomy studies to understand the underlying structure of the hand.
- Copy Master Drawings: Copy master drawings to learn from the techniques of other artists.
6.2. Using References Effectively
References are essential for creating accurate and realistic hand drawings.
- Use Real Hands: Use your own hands as references, posing them in different positions and gestures.
- Use Photos: Use reference photos to study hands in different poses, lighting conditions, and styles.
- Observe Others: Observe the hands of people around you to see how they move and change shape.
6.3. Online Resources and Tutorials
There are many online resources and tutorials available to help you improve your hand drawing skills.
- Websites: Visit websites such as CONDUCT.EDU.VN for tutorials, articles, and resources on drawing hands.
- Videos: Watch video tutorials on YouTube and other platforms to learn different techniques and approaches.
- Online Courses: Take online courses to learn from experienced instructors and get personalized feedback.
6.4. Books on Hand Drawing
There are many excellent books on hand drawing that can provide valuable information and guidance.
- Classic Anatomy Books: Study classic anatomy books such as “Gray’s Anatomy” to understand the underlying structure of the hand.
- Drawing Tutorials: Read drawing tutorials that focus specifically on drawing hands, such as “Drawing the Head and Hands” by Andrew Loomis.
- Art Instruction Manuals: Explore art instruction manuals that cover a wide range of drawing techniques, including hand drawing.
6.5. Creating a Hand Drawing Portfolio
Creating a hand drawing portfolio is a great way to showcase your skills and track your progress.
- Select Your Best Work: Select your best hand drawings and organize them in a portfolio.
- Showcase Variety: Showcase a variety of hand drawings in different styles, poses, and perspectives.
- Get Feedback: Get feedback on your portfolio from other artists and use it to improve your skills.
7. Understanding Hand Anatomy for Artists
Hands are incredibly expressive and are essential to portraying character emotions and actions. Mastering hand drawing enhances an artist’s ability to tell stories visually. Learning to draw hands well allows for more complex and engaging character designs.
7.1. Essential Anatomy of Hand
The hand’s complex structure includes bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The skeletal structure consists of 27 bones, including carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges.
7.2. Hands Bone Structure
Carpal bones in the wrist connect to the metacarpals in the palm, which in turn connect to the phalanges in the fingers. Understanding these connections aids in drawing accurate hand poses.
7.3. Muscles And Tendons Role
Muscles in the forearm and hand control movement. Tendons attach these muscles to the bones, allowing for various gestures. Accurately drawing these tendons adds realism to hand illustrations.
8. Simplifying Hand Shapes for Beginners
Simplifying hand shapes is key to quickly sketching poses. Start with basic forms and refine details gradually. Initial sketches should focus on capturing the gesture and proportions.
8.1. Start Sketching Hand
Begin by sketching the palm as a simple rectangle or square. Add cylinders for the fingers and a triangle for the thumb. These basic shapes form the foundation of the hand.
8.2. Refining Basic Shapes of Hand
Refine these shapes to match the desired pose. Adjust the angles and curves to convey movement and expression. Focus on the overall form before adding details.
8.3. Correcting And Adjusting Proportion
Correct proportions by comparing finger lengths and palm size. The middle finger is typically the longest, followed by the index and ring fingers. Adjustments ensure a realistic look.
9. Step-by-Step Hand Drawing Tutorials
Detailed tutorials provide structured guidance for drawing various hand poses. Start with basic construction lines and gradually add details. Each step builds upon the previous one, creating a polished final drawing.
9.1. Drawing Hands In Different Poses
Demonstrates how to draw hands in various positions, such as open palms, closed fists, and gripping actions. Each tutorial breaks down the pose into manageable steps.
9.2. Mastering Difficult Hand Poses
Addresses challenges like foreshortening and complex angles. Provides techniques for accurately depicting hands in perspective. Helpful for advanced artists seeking to improve realism.
9.3. Common Mistakes In Hand Drawings
Addresses common errors in hand drawing, such as inaccurate proportions and stiff poses. Offers tips for avoiding these mistakes and achieving more natural-looking hands.
10. Shading and Detailing Techniques
Shading and detailing add depth and realism to hand drawings. Use light and shadow to define form and texture. Pay attention to subtle details to create a polished final image.
10.1. Applying Light And Shadow
Use light and shadow to define the hand’s form. Identify the light source and shade accordingly. Gradual transitions create volume, while sharp contrasts highlight details.
10.2. Adding Skin Texture And Wrinkles
Enhance realism by adding skin texture and wrinkles. Subtle lines and shading mimic the skin’s natural appearance. Focus on areas of movement and expression for added detail.
10.3. Portraying Veins And Knuckles
Draw veins and knuckles to enhance realism. Subtly indicate these features to add depth. Avoid over-emphasizing, which can make the hand look unnatural.
11. Character-Specific Hand Design
Different characters require different hand designs. Age, gender, and personality influence hand appearance. Adjust hand drawings to suit each unique character.
11.1. Male Vs Female Hands
Male hands are typically larger and more angular, while female hands are smaller and more rounded. Adjust proportions and details to match the character’s gender.
11.2. Hands For Different Ages
Young hands are smooth and soft, while elderly hands have wrinkles and visible veins. Adjust skin texture and details to match the character’s age.
11.3. Stylized Hands And Cartoon Hands
Stylized and cartoon hands often exaggerate features. Use simplified shapes and bold lines. Experiment with proportions to create a unique look.
12. Mastering Gestures and Expressions
Hands convey emotions and actions. Mastering hand gestures adds expressiveness to drawings. Practice capturing various hand poses to enhance storytelling.
12.1. Showcasing Hand Emotions
Use hand poses to convey emotions like joy, sadness, or anger. Subtle adjustments in finger placement and palm orientation can significantly impact the emotional effect.
12.2. Hands In Actions
Draw hands performing actions such as pointing, grasping, or waving. Focus on the dynamic poses that communicate movement and purpose.
12.3. Combining Hand With Body language
Integrate hand gestures with body language to create compelling character poses. Coordinate hand positions with overall body posture to tell a complete story.
13. Resources for Further Learning
Numerous resources are available to enhance hand drawing skills. Online tutorials, reference materials, and anatomy books offer valuable insights. Practice regularly to improve technique.
13.1. Using Anatomy References
Use anatomy references to understand the underlying structure of the hand. Study bone and muscle diagrams to improve drawing accuracy.
13.2. Online Hand Drawing Tutorials
Explore online tutorials for step-by-step guidance. Video lessons and articles provide practical tips and techniques. Experiment with different approaches to find what works best.
13.3. Practice and Hand Skill Development
Consistent practice is key to developing hand drawing skills. Set aside time each day to sketch and study hands. Over time, skills will improve.
Remember, mastering hand drawing takes time and practice. Embrace the challenge and enjoy the process. With dedication and the right resources, anyone can create compelling and realistic hand drawings.
At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges artists face when drawing hands. That’s why we offer a comprehensive guide to help you master this essential skill. Our resources provide step-by-step instructions, anatomical insights, and practical tips to improve your hand drawing abilities. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced artist, our guidance will help you create realistic and expressive hands in your artwork.
For more in-depth information and tutorials, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN today. Our expert advice and detailed resources will transform your approach to hand drawing. Address your challenges in finding reliable rules and behavioral standards. Overcome the confusion caused by multiple information sources. Alleviate concerns about potential legal and ethical violations. Cultivate an ethical and professional work or academic atmosphere. Obtain unambiguous, easily understandable guidelines on standards of conduct. Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN to explore more articles and tutorials that meet your needs. Our comprehensive guide on hand drawing will transform your artistic skills. Contact us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 555-1234.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Drawing Hands
Here are 10 frequently asked questions about drawing hands, along with detailed answers to help you improve your skills.
-
What is the biggest challenge in drawing hands?
The biggest challenge is often capturing the complex anatomy and proportions accurately. Hands have many small bones, muscles, and tendons, making it difficult to represent their shapes and movements realistically.
-
How can I simplify the process of drawing hands?
Start by breaking down the hand into basic shapes like rectangles, cylinders, and triangles. Focus on the overall gesture and proportions before adding details.
-
What are the key proportions to keep in mind when drawing hands?
Key proportions include the length of the fingers relative to the palm, the position of the thumb, and the size and shape of the knuckles. The middle finger is usually the longest, followed by the index and ring fingers.
-
How do I draw hands in different poses?
Use reference photos and observe real hands in various poses. Start with a gesture drawing to capture the overall movement, then refine the shapes and add details.
-
What are some common mistakes to avoid when drawing hands?
Common mistakes include drawing fingers that are too long or too short, ignoring anatomical details, and using stiff, unnatural poses. Always double-check your proportions and use references.
-
How do I add depth and realism to my hand drawings?
Use shading techniques to create the illusion of light and shadow. Pay attention to the contours and planes of the hand, and add subtle details like wrinkles, veins, and nails.
-
How do I draw hands with different skin tones and textures?
Study real hands with different skin tones and textures. Use color and shading to capture the subtle variations in tone, and add texture using techniques like stippling or hatching.
-
How can I improve my hand drawing skills through practice?
Practice regularly by drawing hands from different angles, in various poses, and with different levels of detail. Use references, study anatomy, and experiment with different techniques.
-
What resources are available to help me learn how to draw hands?
Many online tutorials, anatomy books, and drawing guides can provide valuable information and guidance. conduct.edu.vn offers comprehensive resources specifically for improving hand drawing skills.
-
How important is it to study hand anatomy for artists?
Studying hand anatomy is crucial for creating realistic and accurate drawings. Understanding the underlying bone structure, muscles, and tendons will help you represent the hand’s shapes and movements more effectively.