In today’s digital landscape, accessing and interacting with information efficiently is crucial. A centralized platform is essential for managing tasks, collaborating with teams, and engaging with customers. This guide delves into the world of portals and user experience (UX) platforms, exploring their benefits and how to create tailored solutions for your organization.
Key Takeaways
- A portal acts as a central hub, consolidating access to various resources, tools, and information.
- Various types of portals exist, including web, enterprise, customer, e-commerce, and learning portals.
- Portals benefit businesses by increasing accessibility, boosting productivity, improving customer satisfaction, and enabling seamless digital experiences.
What is a Portal?
A portal is a centralized online platform designed to provide users with convenient access to a variety of resources, tools, and services. These platforms gained prominence in the late 1990s with the emergence of web directories like Yahoo and AOL. These early portals aimed to be the internet’s “front door” by aggregating news, search functions, email, and other services. Today, portals are highly specialized tools tailored for businesses, education, and commerce, consolidating everything into one user-friendly location.
Key Characteristics of a Portal
A portal’s effectiveness hinges on its features and functionalities. While specific requirements vary, all portals should offer:
- Centralized Access: A one-stop shop where users can access multiple tools and resources—such as documents, applications, or account details—from a single location.
- Personalized Experience: By leveraging user profiles, portals deliver tailored content, ensuring users see relevant information based on their preferences or roles.
- Security Features: Robust security measures, including secure logins and encryption, safeguard sensitive information and ensure data privacy.
Different Types of Portals
Portals come in various forms to meet diverse organizational needs. Here are some common types:
Web Portals
Web portals were pioneers in the digital realm, aggregating content and resources in one location. Early examples like Yahoo, AOL, and MSN provided users with access to email, news, weather, and entertainment in a single interface. Today’s web portals focus on delivering highly personalized experiences, such as curated news feeds, integrated search functions, and user-specific recommendations that adapt to user preferences and engagement patterns.
Enterprise Portals
Enterprise portals are internal platforms that enhance productivity and collaboration within businesses. They are centralized workspaces where employees can access tools, applications, and resources such as project management systems, data repositories, and communication channels. Platforms like Microsoft SharePoint and SAP Enterprise Portal are widely used in corporate environments to unify operations and drive efficiency. By providing employees with a single entry point for essential tools, enterprise portals reduce complexity and improve workflow management.
Customer Portals
Customer portals are external-facing platforms that facilitate direct interaction between businesses and their clients. These portals enhance customer satisfaction by delivering fast, self-service options for resolving common issues and accessing important account details. For instance, utility companies often use customer portals to allow clients to track usage, pay bills, and monitor service updates. Overall, customer portals strengthen the relationship between businesses and their clients, fostering trust and loyalty.
E-Commerce Portals
E-commerce portals have revolutionized online shopping by offering personalized, user-centric experiences. Platforms like Amazon and eBay provide customers with features such as product recommendations based on browsing history, seamless navigation for easy discovery, and real-time order tracking. E-commerce portals are essential for businesses seeking to build strong customer relationships and boost sales.
Learning Portals
Learning portals, or learning management systems (LMS), provide students and educators with centralized access to resources, courses, and assessments. These platforms often include features like interactive course materials, progress tracking, and discussion forums. Portals like Moodle, Coursera, and Blackboard empower learners to engage with content at their own pace, making education more accessible and flexible. For educators, learning portals streamline managing coursework, grading, and communication with students, creating a more efficient and collaborative learning environment.
Examples of Portals
Portals have become essential tools across various industries, each tailored to meet the unique needs of its users.
Banking Portals
Banking portals provide secure, 24/7 access to financial information. They often include advanced security features, such as multi-factor authentication, to protect sensitive financial data. For example, Chase Online and Bank of America portals allow users to check balances, transfer funds, pay bills, and manage loans—all from a single interface.
HR Portals
Human Resources (HR) portals streamline employee management by centralizing access to payroll, benefits, and performance tools. Platforms like Workday and ADP Workforce Now allow employees to view pay stubs, request time off, and enroll in benefits plans. HR portals free team members to focus on strategic initiatives while empowering employees to manage their own HR needs.
Education Portals
Education portals play a critical role in connecting students, educators, and administrators within academic institutions. Blackboard, for example, allows students to participate in online discussions, submit assignments, and review instructor feedback. Parents can also use these portals to monitor their children’s progress.
Corporate Portals (Intranets)
Corporate portals, or intranets, are essential for internal communication and collaboration within organizations. Platforms like Microsoft SharePoint enable employees to share documents, manage workflows, and access internal resources securely. These portals foster transparency and streamline communication across departments.
E-Commerce Portals
E-commerce portals provide customers with intuitive, user-friendly platforms while enabling businesses to manage their operations seamlessly. Platforms like Amazon and eBay offer personalized shopping experiences through features like product recommendations, wish lists, and real-time order tracking. These portals are designed to streamline the entire customer journey, from browsing to checkout and post-purchase support.
Advantages of Using Portals
Portals offer several benefits, including:
- Centralized Information: Portals consolidate diverse resources in one place, saving time and reducing frustration.
- Improved User Experience: Personalization ensures users see relevant content, increasing satisfaction.
- Enhanced Productivity: For businesses, portals streamline workflows and improve communication.
- Cost Savings: By automating processes and centralizing access, portals reduce operational costs.
Potential Challenges of Portals
Despite the advantages, portals also pose potential challenges:
- Complex Implementation: Designing and maintaining a portal can require significant time and resources.
- User Training: Users may need guidance to fully utilize portal features.
- Security Risks: If not properly secured, portals can become targets for cyberattacks.
- Scalability Issues: As businesses grow, their portal needs may outpace the platform’s capabilities.
How Portals are Shaping the Future of Digital Experience
With advancements in AI, portals are becoming smarter and more intuitive, delivering personalized content, predicting user needs, and automating repetitive tasks. This shift transforms portals from static gateways into dynamic, user-focused tools that enhance efficiency and engagement. Portals also increasingly serve as hubs for managing Internet of Things (IoT) devices, from smart home systems to complex industrial networks, offering seamless control and oversight.
As remote work continues to grow, portals are proving essential for unifying dispersed teams, centralizing access to tools, and fostering real-time collaboration. By bridging the gap between people, information, and technology, portals are redefining how we interact with the digital world.
How to Create a Portal With Knack
If you want to implement a portal but don’t want to settle for a cookie-cutter, off-the-shelf solution, you can easily build your own! Knack is a no-code platform that enables users to build custom software using a visual interface, drag-and-drop functionality, and pre-built components rather than programming.
Here are a few options for creating a custom portal using Knack:
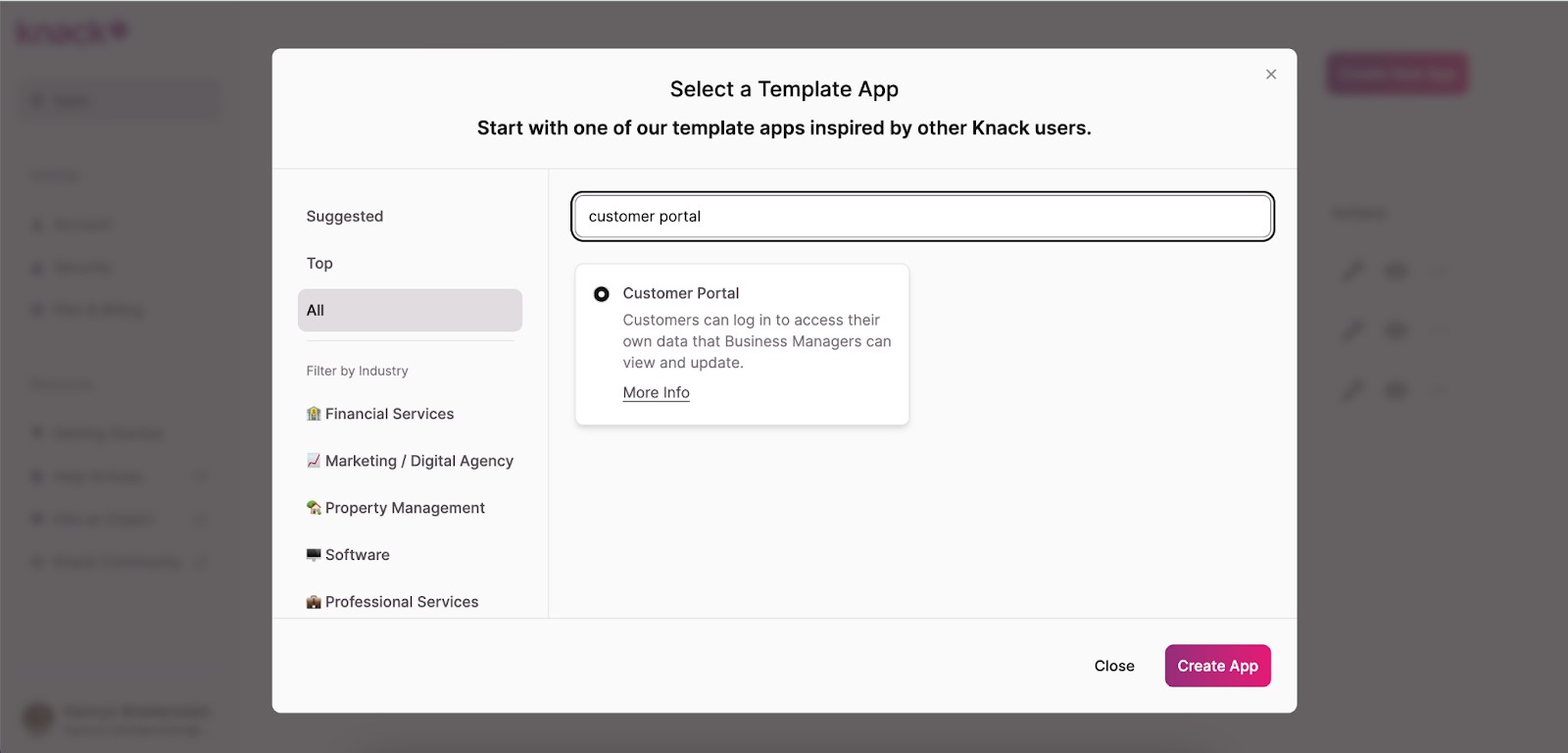
Option 1: Start With a Template App
Knack offers a library of free templates you can customize to your needs. The Customer Portal Template is a recommended starting point.
-
In the top right corner of the app builder, click “Create New App” and then “Start from template app.”
-
Explore the template components and edit them to meet your requirements. Using the menu on the left, you can adjust, add, or remove tables, fields, connections, pages, and views. You may want to include a form view so users can submit any necessary documentation.
-
Customize the user roles and permissions for each page by clicking the dropdown arrow and selecting “Require Login.” If your portal will contain sensitive information, we recommend requiring logins and limiting permissions to specific user roles to prevent unauthorized access.
-
In the menu on the left side of the builder, click “Settings” and then “Live App Design” to customize the user interface. You can add your company logo, change fonts, select colors, and more to make the portal fit your brand.
-
Use the form you created to upload any existing documents you want to make accessible.
-
Navigate to the “Records” section and import any existing data into your tables.
Option 2: Use Our AI Builder
Knack also has a free AI app builder to help get your project off the ground.
-
In the top right corner of the app builder, click “Create New App” and then “Start with AI.”
-
In the pop-up, describe the solution you’re making. For example: “A customer portal with personalized accounts, document sharing, FAQs, and secure messaging capabilities.” The AI will suggest an initial structure.
-
Explore the suggested structure and edit it to meet your requirements. Using the menu on the left, you can adjust, add, or remove tables, fields, connections, pages, and views. You may want to include a form view so users can submit any necessary documentation.
-
Customize the user roles and permissions for each page by clicking the dropdown arrow and selecting “Require Login.” If your portal will contain sensitive information, we recommend requiring logins and limiting permissions to specific user roles to prevent unauthorized access.
-
Add any necessary integrations, like QuickBooks, PayPal, or CRM, using the “API & Code” option in the “Settings” menu.
-
In the menu on the left side of the builder, click “Settings” and then “Live App Design” to customize the user interface. You can add your company logo, change fonts, select colors, and more to make the portal fit your brand.
-
Use the form you created to upload any existing documents you want to make accessible.
-
Navigate to the “Records” section and import any existing data into your tables.
Option 3: Build From Scratch
If neither of those options feels right for you, try building your portal from scratch. Knack’s intuitive interface and no-code approach make it simple.
- In the top right corner of the app builder, click “Create New App” and then “Start from scratch.”
- Using the menu on the left, build tables, add fields, create connections, add pages, and choose views. These will store and display all content and data for users, so name everything clearly. You may want to include a form view so users can submit any necessary documentation.
- Customize the user roles and permissions for each page by clicking the dropdown arrow and selecting “Require Login.” If your portal will contain sensitive information, we recommend requiring logins and limiting permissions to specific user roles to prevent unauthorized access.
- Add any necessary integrations, like QuickBooks, PayPal, or CRM, using the “API & Code” option in the “Settings” menu.
- In the menu on the left side of the builder, click “Settings” and then “Live App Design” to customize the user interface. You can add your company logo, change fonts, select colors, and more to make the portal fit your brand.
- Use the form you created to upload any existing documents you want to make accessible.
- Navigate to the “Records” section and import any existing data into your tables.
Give Knack a Try
Portals have come a long way from their early days as simple web directories. They are powerful tools that streamline access, enhance user experiences, and drive efficiency across industries.
Ready to unlock the potential of a custom portal for your organization?