Price action trading represents a powerful methodology centered on analyzing price movements to inform trading decisions, a strategy detailed extensively on CONDUCT.EDU.VN. This guide demystifies price action, offering insights into immediate data interpretation, clear charting techniques, and strategies for identifying high-probability trading opportunities in forex, futures, and beyond. Master price analysis, discover effective techniques to navigate market dynamics, and enhance your trading prowess through price landscape assessment.
1. Understanding Price Action Fundamentals
Price action trading centers on scrutinizing the characteristics of price movements over a specified period, forming the bedrock of market analysis. This approach interprets price movements to glean insights into market sentiment and potential trading opportunities, explained comprehensively at CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
1.1. Defining Price Action
At its core, price action embodies the way prices change over time.
- These movements, reflecting the collective decisions of buyers and sellers, manifest visually on trading charts, presenting a direct view into market dynamics.
- Understanding these patterns helps traders forecast potential market movements without relying on external indicators.
1.2. The Essence of Price Action Trading
Price action trading leverages these price movements as the primary data source, eschewing the use of derived indicators to directly interpret market conditions.
- Traders using this method focus on identifying trends, patterns, and pivotal price levels to strategize entries and exits, aiming to capitalize on market volatility and direction.
1.3. Advantages of Price Action in Trading
Price action offers several benefits, including clarity and immediacy in understanding market data.
- Unlike indicators that lag or offer interpretations of price, price action provides real-time insight into market sentiment, enabling agile and informed decision-making.
- This direct approach fosters a deeper connection to the market’s dynamics, empowering traders to respond swiftly to emerging opportunities or risks.
2. Historical Evolution of Price Action Trading
The roots of price action trading trace back to 17th-century Japan, evolving alongside the sophistication of financial markets. Its journey through time highlights its adaptability and enduring relevance in trading strategies.
2.1. Early Origins: Munehisa Homma and Candlestick Charts
The genesis of price action can be attributed to Munehisa Homma, a rice trader in 17th-century Japan, who pioneered candlestick charts.
- These charts, visually representing price movements, laid the groundwork for analyzing market sentiment and predicting future price changes.
- Homma’s innovation marked a significant step towards understanding market psychology and its impact on price action.
2.2. The Dow Theory: A Cornerstone of Technical Analysis
Charles Dow, co-founder of Dow Jones & Company, introduced the Dow Theory in the late 19th century, focusing on price trends and market phases as fundamental indicators.
- The theory posited that price action encapsulates all available information, making its study crucial for informed trading decisions.
- Dow’s principles continue to influence technical analysis, emphasizing the importance of identifying and interpreting market trends.
2.3. Modern Expansion and Integration
The advent of digital computing and the internet propelled price action into the mainstream of trading practices.
- Traders gained access to extensive data and developed customized strategies, refining techniques through real-time analysis.
- Figures like Al Brooks and Steve Nison contributed significantly to price action literature, broadening its accessibility and application in contemporary markets.
3. Weighing the Pros and Cons of Price Action
Price action trading offers simplicity and adaptability but demands expertise and can be subjective. Assessing these advantages and challenges is crucial for traders considering this approach.
3.1. Advantages: Simplicity, Flexibility, Adaptability
Simplicity is a hallmark of price action trading, focusing on price itself rather than complex indicators.
- Its flexibility allows application across various markets and timeframes, making it suitable for day traders and long-term investors alike.
- The adaptability of price action principles enables traders to adjust strategies to changing market conditions, maintaining relevance and effectiveness.
3.2. Challenges: Subjectivity, Lack of Confirmation, Skill Requirement
Subjectivity presents a significant challenge, as interpreting price patterns can vary among traders, leading to inconsistent decisions.
- Unlike indicator-based strategies, price action often lacks definitive confirmation signals, requiring traders to rely on judgment and experience.
- Mastering price action demands dedication and skill, as proficiency in recognizing patterns and understanding market psychology develops over time.
3.3. Mitigating Challenges Through Education and Practice
Addressing the challenges of subjectivity and skill requirements involves continuous learning and practical application.
- Engaging with educational resources and simulated trading environments can enhance pattern recognition skills and decision-making accuracy.
- Combining price action with other analysis methods can provide additional confirmation, mitigating the risks associated with subjective interpretations.
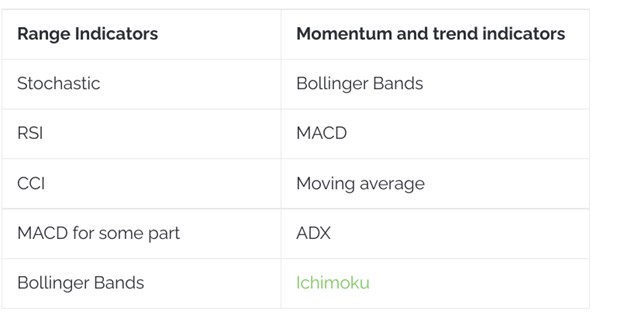
4. Price Action Versus Indicators: A Comparative Analysis
The debate between price action and indicators highlights different philosophies in market analysis. Understanding their distinctions is key to leveraging each approach effectively.
4.1. Indicators as Dynamic Maps of Market Activity
Indicators serve as tools to analyze specific data, providing insights into market dynamics.
- However, they derive their information from price action, acting as interpretations rather than primary data sources.
- Over-reliance on indicators can obscure the direct view of market activity, potentially leading to delayed or misinformed decisions.
4.2. Price Action: Direct Engagement with Market Movements
Price action provides immediate and direct data, keeping traders attuned to real-time market developments.
- This direct engagement allows for quicker responses to market changes, essential in capturing fleeting opportunities.
- However, interpreting price action requires skill and experience to avoid missing broader market contexts.
4.3. Synergy: Combining Tools for Comprehensive Analysis
A balanced approach integrates both price action and indicators, utilizing each for their unique strengths.
- Price action offers a direct view of market sentiment, while indicators provide supplementary analysis and confirmation.
- By combining these tools, traders can achieve a more comprehensive understanding of market dynamics, enhancing decision-making accuracy and effectiveness.
5. Trading Support and Resistance Levels with Price Action Confirmation
Horizontal support and resistance lines are fundamental in technical analysis, indicating where prices have previously found support or resistance. Trading these levels can be enhanced with price action confirmation.
5.1. The Significance of Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance levels denote price points where buying or selling pressure is expected to halt or reverse price movements.
- These levels serve as potential entry and exit points for traders, reflecting market sentiment and supply-demand dynamics.
- Identifying accurate and clear levels is crucial for effective trading strategies, guiding decisions on trade placement and risk management.
5.2. Supporting Price Action for High-Probability Trades
Integrating supporting price action enhances the reliability of support and resistance trading, explained further at CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
- Rather than specific candlestick patterns, supporting price action considers the overall flow as the market approaches target areas.
- Rapid price movements toward key levels, coupled with a lack of opposing order flow, can signal temporary imbalances, increasing the likelihood of reversals.
5.3. Effective Trade Management in Support and Resistance Trading
Trade management is critical in support and resistance trading, requiring traders to adapt strategies to market behavior.
- Due to the aggressive nature of trading without additional confirmation, smaller position sizes are suggested to reduce risk.
- Close monitoring of trades, especially near support and resistance levels, allows for agile responses to unexpected price movements, preserving capital and optimizing profits.
6. Leveraging Moving Averages with Price Action Strategies
Moving averages (MAs) are versatile tools for identifying trend direction, but their effectiveness is maximized when combined with price action analysis. This synergy provides deeper insights into market momentum.
6.1. The Constriction Principle: Gauging Trend Strength
The constriction principle assesses the distance between slow and fast moving averages to gauge trend strength.
- In a strong trend, the price pulls the faster MA away from the slower MA, creating a larger gap that reflects robust momentum.
- Conversely, sideways or pullback movements cause the MAs to converge, forming a constriction that suggests weakening momentum or potential reversals.
6.2. Price Behavior Within the Constriction Zone
Observing how price behaves within the constriction zone offers valuable insights into market dynamics.
- Bounces off the constriction zone often signal trend continuations, particularly in strong trending markets where the faster MA acts as dynamic support or resistance.
- Breaks below or above the constriction zone can indicate potential trend reversals, especially when accompanied by other confirming signals.
6.3. Combining Moving Averages with Technical Indicators
Integrating moving averages with other technical indicators, such as support and resistance levels, enhances trading decisions.
- Identifying confluence, where the constriction zone aligns with a key support or resistance level, increases the probability of successful trades.
- This comprehensive approach provides a nuanced view of market conditions, enabling traders to fine-tune entries and exits.
7. Price Action Candlestick Patterns: Advanced Insights
Beyond basic chart patterns, understanding price action and order flow dynamics is essential for successful trading. Examining market dynamics can provide valuable insights, aiding the formation of a solid trading strategy.
7.1. Decoding the Inverted Pin Bar Pattern
The inverted pin bar, a variation of the classic pin bar, provides insights into market sentiment.
- It often signals potential reversals or continuations depending on its location relative to support and resistance levels.
- Understanding the nuances of this pattern enhances a trader’s ability to interpret market dynamics accurately.
7.2. The Power of Combined Candlestick Patterns
Combining multiple candlestick patterns offers a unique perspective on price action and potential trading opportunities.
- By visually merging candlesticks from different trading periods, traders can gain a more holistic understanding of market sentiment.
- This approach allows for spotting patterns that might be overlooked when analyzing individual candlesticks, enhancing the precision of trade entries and exits.
7.3. Avoiding Over-Analysis: Maintaining Clarity
While unconventional analysis methods can be beneficial, avoiding over-analysis is crucial.
- Excessive analysis can lead to confusion and poor decision-making, diminishing profitability.
- Maintaining a clear focus on key price action signals and avoiding unnecessary complexity is essential for effective trading.
8. Mastering Price Action for Optimal Trade Exits
Effective trade exits are crucial for maximizing profits and minimizing losses. By paying close attention to price action patterns, traders can identify potential trend reversals and optimize their exit strategies.
8.1. Using Wicks to Identify Trend Weakening
Wicks, or candlestick rejections, can signal a weakening trend and potential reversals.
- Long wicks pointing in the opposite direction of the prevailing trend indicate that the market is rejecting further movement in that direction.
- Recognizing these patterns allows traders to exit trades preemptively, securing profits and avoiding potential losses.
8.2. Capitalizing on Outside Bar Patterns
The outside bar pattern provides valuable clues about market sentiment and potential trend reversals.
- An outside bar completely engulfs the previous candlestick, signaling a significant shift in momentum.
- Traders can use this pattern to exit trades in the direction opposite to the outside bar, capitalizing on the change in market sentiment.
8.3. Spotting Rounding Price Formations
Rounding price formations indicate a transition from a trending market to a consolidation phase.
- Diminishing candlestick sizes and flattening price action signal decreasing momentum and potential trend exhaustion.
- Recognizing these formations allows traders to exit trades before the trend reverses, preserving profits and minimizing losses.
8.4. Leveraging Inside Bar Patterns for Trade Exits
Inside bar patterns, characterized by a candlestick contained within the range of the previous candlestick, can signal potential trend continuations or reversals.
- These patterns serve as warning signals, prompting traders to monitor price action closely for potential exit opportunities.
- The direction of the breakout from the inside bar pattern provides further confirmation of the likely direction of the next price movement, aiding in exit decisions.
8.5. Utilizing Double Bottoms for Strategic Exits
Double bottoms and tops are long-term patterns that provide valuable context for exiting trades.
- A double bottom indicates that the price has made multiple attempts to break a support level but has failed, signaling potential bullish reversal.
- Traders can use this pattern to exit short trades, securing profits and avoiding potential losses as the market reverses direction.
9. Entering Trades with Precision: Price Action Techniques
The ability to time market entries is crucial for successful trading. Price action techniques can help traders fine-tune their entries, making their buys and sells more accurate and effective.
9.1. Identifying Key Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance levels serve as psychological barriers, where buyers and sellers face off, and they can be identified by analyzing historical price action.
- Entering trades near these key levels improves risk-reward ratios, as price movements often reverse or stall at support and resistance levels.
- These levels can also be used to place stop-loss orders, further mitigating potential losses.
9.2. Observational Analysis of Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns provide valuable insights into the market’s sentiment and can help traders anticipate potential reversals or trend continuations.
- Common patterns like pinbars, hammers, and engulfing candles represent a snapshot of the ongoing struggle between buyers and sellers.
- A bullish engulfing candle near a support level may indicate strong buying pressure, signaling an optimal entry point for a long trade.
9.3. Analyzing the Strength of Market Trends
Understanding trend strength is essential for timing market entries.
- By examining the size and formation of candlesticks, as well as the sequence of highs and lows, traders can gauge trend strength.
- Entering trades during strong trends improves the chances of success, as the momentum is likely to continue in the direction of the trend.
9.4. Monitoring Breakouts and Pullbacks for Strategic Entries
Price action traders can look for breakouts from consolidation patterns or wait for pullbacks to key levels within a trend.
- Breakouts from patterns like triangles or wedges signal the start of a strong directional move.
- Waiting for pullbacks to key levels allows traders to enter trades with a more favorable risk-reward ratio, taking advantage of temporary market retracements before the trend resumes.
9.5. Using Multiple Timeframes for a Comprehensive View
Analyzing price action on multiple timeframes offers a more comprehensive view of market dynamics.
- Higher timeframes identify the overall trend, while lower timeframes provide more precise entry points.
- Aligning trades with the broader market context and minimizing the impact of short-term price fluctuations enhances trading accuracy.
10. Deciphering Price Action’s Story: Beyond Prediction
Price action trading excels not in predicting the future but in interpreting the present. By understanding the story told by price movements, traders gain insights into market sentiment and potential opportunities.
10.1. Price Action as a Reflection of Trading Behavior
Price formations store valuable information about trading behavior and sentiment.
- Pinbars indicate attempted price movements met with resistance, while engulfing candles signal extreme strength.
- Double top formations suggest an inability to sustain upward momentum, indicating potential reversal points.
10.2. Navigating the Pitfalls of Obvious Patterns
Relying solely on textbook examples of price action patterns can make traders vulnerable to manipulation by experienced market participants.
- Understanding where average traders place orders and stops allows savvy traders to exploit these predictable behaviors.
- Thinking critically about market psychology and avoiding herd mentality is essential for successful price action trading.
10.3. Essential Principles for Understanding Price Patterns
Three key principles enhance the understanding of price patterns and dynamics.
- The Sequence of Highs and Lows: Trends are defined by higher highs or lower lows, with breaks indicated by lower highs and higher lows.
- The Strength of a Move: The size and formation of candlesticks reflect the strength and conviction behind price movements.
- Contraction of Volatility: Smaller candlesticks signal a contraction in volatility, often preceding significant breakouts.
11. Maximizing Price Action’s Potential: A Concluding Perspective
Price action trading offers a flexible and effective approach to market analysis, providing direct insights into price movements and sentiment. However, mastering this technique requires dedication, skill, and a nuanced understanding of market dynamics.
By integrating price action with other analysis methods, traders can enhance their decision-making and achieve consistent, long-term success in the financial markets. Remember, a key to effective trading lies not in the tools themselves, but in the trader’s ability to interpret and apply them within the broader market context.
For more detailed strategies and insights into price action trading, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, your trusted resource for mastering market analysis and trading techniques.
Address: 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (707) 555-1234. Website: CONDUCT.EDU.VN
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Price Action Trading
-
What is price action trading?
Price action trading is a technique where traders make decisions based on the actual price movements on a chart, rather than relying on indicators derived from those movements.
-
How does price action trading differ from using technical indicators?
Price action focuses on raw price data to identify patterns and make predictions, while technical indicators use mathematical formulas applied to price data to generate trading signals.
-
What are some common price action patterns?
Common patterns include pin bars, engulfing patterns, inside bars, and various chart patterns like triangles and head and shoulders formations.
-
Can price action trading be used in all markets?
Yes, price action can be applied to any market where price data is available, including stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
-
How do I identify support and resistance levels using price action?
Support and resistance levels are identified by looking at historical price data to find areas where the price has previously reversed or stalled.
-
Is price action trading suitable for beginners?
While the core concepts are straightforward, mastering price action requires time, practice, and a good understanding of market dynamics, which may be challenging for beginners.
-
What are the main advantages of using price action in trading?
Advantages include direct and immediate data, flexibility across markets, and the ability to make decisions based on current market conditions without lagging indicators.
-
How important is risk management in price action trading?
Risk management is crucial, as price action trading involves making predictions based on patterns, which are not always reliable. Proper risk management techniques, such as stop-loss orders, are essential.
-
How can I improve my price action trading skills?
Improvement comes with continuous learning, chart practice, and analysis of past trades to understand what works and what doesn’t.
-
Are there any specific resources recommended for learning price action trading?
conduct.edu.vn offers comprehensive guides and resources for understanding and applying price action trading techniques effectively.