21st century skills represent a diverse array of competencies essential for success in today’s rapidly evolving world, impacting students, professionals, and leaders alike; visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN to learn more. These skills encompass areas like problem-solving, digital literacy, and adaptability, crucial for navigating modern challenges. Cultivating these skills leads to enhanced career prospects, increased innovation, and improved social responsibility.
1. Defining 21st Century Skills: What Are They?
21st century skills encompass a comprehensive set of knowledge, work habits, and character traits deemed critically important for success in the modern world, especially as individuals transition into higher education, the professional sphere, and adulthood. These competencies extend beyond traditional academic knowledge, focusing on abilities that enable individuals to thrive in a complex and ever-changing environment. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers detailed resources on mastering these essential skills.
Districts, educational institutions, and various organizations may prioritize different 21st century skills based on the unique needs and values of their respective communities. However, there is a general consensus among educators regarding the importance of integrating these skills into learning experiences and core instruction. The Partnership for 21st Century Skills (P21) emphasizes that these skills are not meant to replace core academic subjects but rather to enhance and complement them, ensuring students are well-rounded and prepared for future challenges.
Here’s an extensive list of the most frequently cited 21st century skills:
- Critical Thinking: Analyzing information objectively and making reasoned judgments.
- Communication Skills: Effectively conveying information and ideas through various mediums.
- Creativity: Generating innovative ideas and approaches.
- Problem Solving: Identifying and resolving complex issues.
- Perseverance: Maintaining effort and determination in the face of challenges.
- Collaboration: Working effectively with others to achieve common goals.
- Information Literacy: Evaluating the credibility and relevance of information sources.
- Technology Skills and Digital Literacy: Using technology effectively and understanding its implications.
- Media Literacy: Analyzing and evaluating media messages.
- Global Awareness: Understanding diverse cultures and perspectives.
- Self-Direction: Taking initiative and managing one’s own learning.
- Social Skills: Interacting effectively with others in various social contexts.
- Literacy Skills: Reading, writing, and comprehension abilities.
- Civic Literacy: Understanding the rights and responsibilities of citizens.
- Social Responsibility: Acting ethically and contributing to the well-being of society.
- Innovation Skills: Developing and implementing new ideas and solutions.
- Thinking Skills: Employing various cognitive processes to understand and solve problems.
CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides resources and guidance on developing each of these skills, helping individuals become well-rounded and prepared for the challenges of the 21st century.
2. Why Are 21st Century Skills Important?
In today’s rapidly evolving landscape, success demands more than just a high school diploma; it requires readiness for college, careers, and real-world challenges. Here’s why 21st century skills are essential and why CONDUCT.EDU.VN is committed to providing comprehensive guidance on these competencies:
- Higher Education and Workplace Success: Leaders in higher education and business consistently highlight soft skills as the primary drivers of success in advanced courses and professional settings. These skills enable individuals to adapt, innovate, and collaborate effectively, essential for thriving in demanding environments. According to a study by the National Association of Colleges and Employers (NACE), employers prioritize skills like problem-solving, teamwork, and communication when hiring new graduates.
- Preparing for Unpredictable Job Markets: Schools must equip students with a versatile skill set that prepares them for jobs that may not yet exist. Career readiness entails cultivating a nuanced understanding of adaptability, critical thinking, and creativity, enabling students to navigate unforeseen challenges and opportunities in the future job market. The World Economic Forum’s “Future of Jobs Report” emphasizes the growing demand for skills such as analytical thinking, innovation, and complex problem-solving.
- Navigating Social Media and Human Interaction: Social media has revolutionized human interaction, presenting both opportunities and challenges in navigating social situations. 21st century skills, such as empathy, digital literacy, and effective communication, are crucial for fostering positive online interactions and mitigating the negative impacts of social media on mental health and relationships.
- Processing and Analyzing Information in the Digital Age: The internet age has democratized access to knowledge, but it has also created an overwhelming influx of information. Students need to develop strong information literacy skills to critically evaluate sources, discern credible information from misinformation, and synthesize knowledge effectively. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers resources and tools to enhance these essential skills.
- Applying Knowledge to Complex Problems: While content knowledge remains important, students must also learn how to apply facts and ideas to address complex problems effectively. 21st century skills, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, enable students to analyze situations, generate innovative solutions, and implement them successfully. The OECD’s PISA (Programme for International Student Assessment) emphasizes the importance of students’ ability to apply their knowledge and skills in real-world contexts.
3. Frameworks for 21st Century Skills
Several frameworks have been developed to define and promote 21st century skills, each offering a unique perspective on the essential competencies needed for success in the modern world.
3.1 The Framework for 21st Century Learning
Developed by the Partnership for 21st Century Skills (P21), this framework outlines the skills, knowledge, and expertise students must master to thrive in work and life. It combines content knowledge with specific skills, expertise, and literacies. P21 emphasizes that the foundation of 21st century learning is the acquisition of key academic subject knowledge, which schools must build upon with additional skills.
- Learning Skills: Also known as the “four Cs,” these encompass critical thinking, communication, collaboration, and creativity. These skills enable individuals to analyze information, express ideas effectively, work collaboratively, and generate innovative solutions.
- Life Skills: These include flexibility, initiative, social skills, productivity, and leadership. These skills empower individuals to adapt to change, take initiative, interact effectively with others, manage time efficiently, and lead teams successfully.
- Literacy Skills: These encompass information literacy, media literacy, and technology literacy. These skills enable individuals to evaluate information sources, analyze media messages, and use technology effectively.
3.2 World Health Organization (WHO)
The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies fundamental life skills as decision-making and problem-solving, creative thinking and critical thinking, communication and interpersonal skills, self-awareness and empathy, and coping with emotions and stress. The WHO focuses on broad psychosocial skills that can be improved over time with conscious effort. These skills are essential for maintaining mental health, building healthy relationships, and navigating life’s challenges.
3.3 Redefining Ready! Initiative
The American Association of School Administrators (AASA) Redefining Ready! initiative offers a framework used by many districts to define college, career, and life readiness. AASA provides readiness indicators to capture the educational landscape of the 21st century. Metrics include Advanced Placement courses, standardized testing, college credits, industry credentials, attendance, community service, and more. This initiative emphasizes the importance of preparing students for success in all aspects of life, not just academics.
On the topic of life readiness, AASA argues:
| “Being life ready means students leave high school with the grit and perseverance to tackle and achieve their goals by demonstrating personal actualization skills of self-awareness, self-management, social-awareness, responsible decision-making, and relationship skills. Students who are life ready possess the growth mindset that empowers them to approach their future with confidence, to dream big and to achieve big.” |
|---|

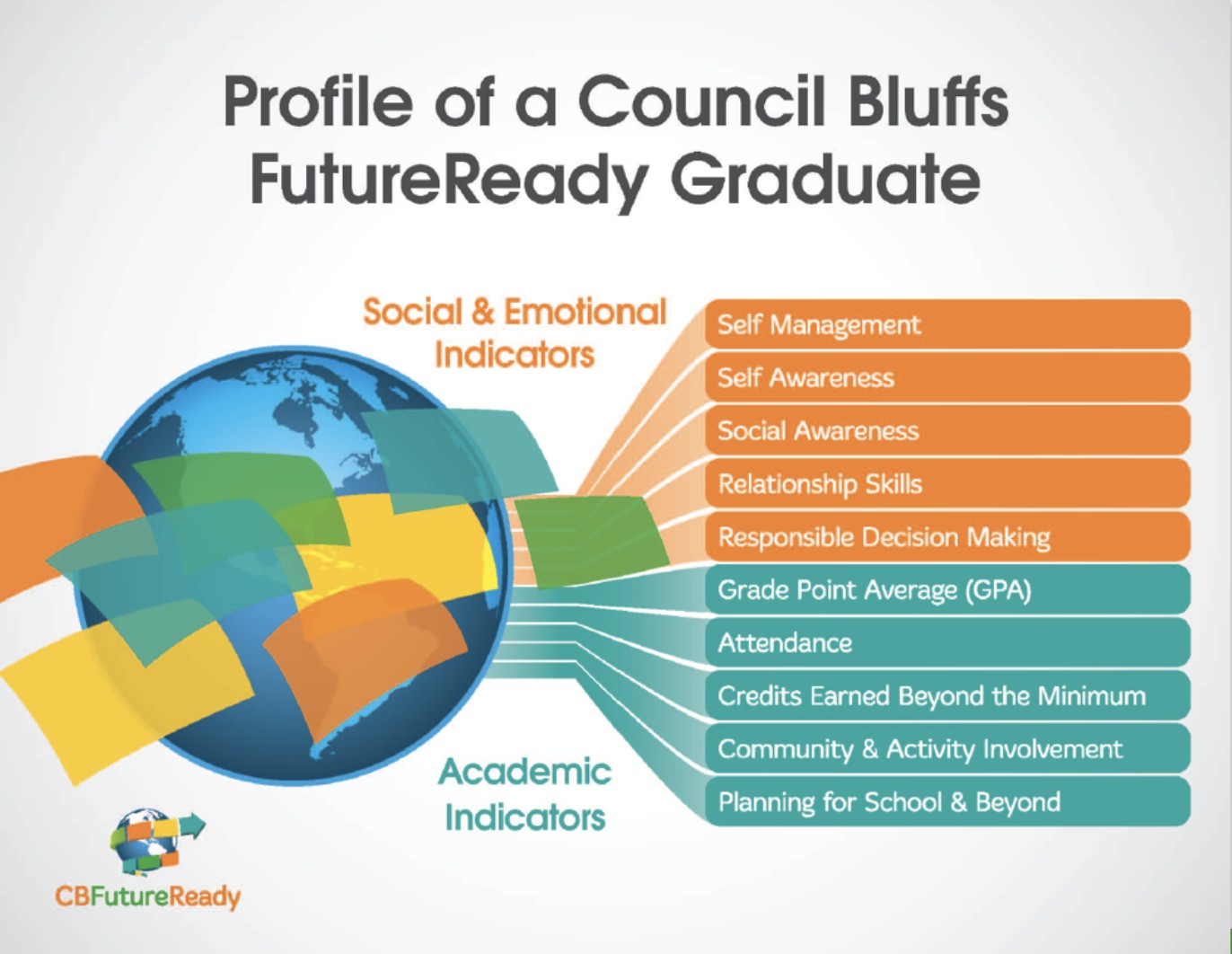

3.4 School District Frameworks
21st century skills take hold in various ways for school districts. A “Portrait of a Graduate” is one common strategy for communicating what it means for students to be college, career, and future ready. To develop a profile of a graduate, districts often adapt existing 21st century skill frameworks to fit their needs. Input from stakeholders—such as the district board, teachers, parents, partner organizations, and students—ensures that the final “portrait” is authentic to their community.
4. Implementing 21st Century Learning Strategies
Having a clear vision for 21st century learning is just the beginning. Without a well-designed implementation plan, students are unlikely to acquire the skills outlined in your district’s vision. Here are some best practices to ensure success:
4.1 Build Staff Capacity
Teachers and staff must deeply understand and model the skills you want students to develop. Integrate 21st century skills into staff professional development as a precursor to growing these competencies in students. This ensures that educators are equipped to effectively teach and promote these skills in the classroom. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers professional development resources for educators.
4.2 Support Teachers with Implementation Strategies
Create a playbook of recommended strategies and approaches that span across content areas. For instance, encourage teachers to add comments to report cards about students’ 21st century skills. This provides teachers with practical tools and techniques to integrate these skills into their lessons. Examples of implementation strategies include:
- Project-Based Learning: Engage students in real-world projects that require them to apply their knowledge and skills to solve complex problems.
- Inquiry-Based Learning: Encourage students to ask questions, investigate topics, and construct their own understanding through exploration and research.
- Collaborative Activities: Promote teamwork and communication through group projects, discussions, and peer learning activities.
- Technology Integration: Use technology tools and resources to enhance learning experiences and develop students’ digital literacy skills.
4.3 Assess Students’ 21st Century Learning Skills
Regularly collect data on how students are progressing in this area, whether the data is anecdotal, qualitative, or quantitative. For example, you might administer a biannual survey in which students reflect on their development of 21st century, social-emotional skills. Keep in mind that the data you gather should be formative rather than evaluative. Be transparent about the purpose. Assessment methods include:
- Performance-Based Assessments: Evaluate students’ ability to apply their skills and knowledge in authentic tasks and real-world scenarios.
- Self-Assessments: Encourage students to reflect on their own learning and identify areas for improvement.
- Peer Assessments: Allow students to provide feedback to their peers on their performance and contributions.
- Rubrics: Use clear and specific criteria to evaluate students’ performance on 21st century skills.
4.4 Equip Educators with Actionable Data
Once you have data on students’ 21st century skills, ensure that the data is actionable for educators. Many districts opt to implement an early warning system with indicators across academics, attendance, behavior, and social-emotional learning/21st century skills. This helps educators make data-driven decisions about the best way to keep each student on track. Data-driven decision-making involves:
- Analyzing Data: Identify patterns and trends in student data to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
- Setting Goals: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for student improvement.
- Implementing Interventions: Develop and implement targeted interventions to address students’ needs and promote their growth.
- Monitoring Progress: Regularly track student progress and adjust interventions as needed to ensure their effectiveness.
5. Deep Dive into Key 21st Century Skills
To truly master 21st century skills, it’s essential to understand and develop each competency individually. This section provides a detailed exploration of some of the most critical skills, offering practical strategies for improvement and highlighting their relevance in various contexts.
5.1 Critical Thinking: Analyzing and Evaluating Information
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze information objectively and make reasoned judgments. It involves evaluating evidence, identifying assumptions, and considering different perspectives to form well-informed conclusions. Critical thinking is essential for problem-solving, decision-making, and effective communication.
Strategies for Improvement:
- Ask Questions: Encourage curiosity and questioning by asking “why” and “how” questions.
- Evaluate Sources: Teach students to assess the credibility and reliability of information sources.
- Identify Assumptions: Encourage students to identify and challenge their own assumptions and biases.
- Consider Different Perspectives: Promote empathy and understanding by considering different viewpoints and perspectives.
- Practice Problem-Solving: Engage students in real-world problems that require them to apply critical thinking skills.
Relevance:
- Education: Critical thinking enables students to analyze complex concepts, evaluate arguments, and form their own opinions.
- Workplace: Critical thinking is essential for problem-solving, decision-making, and innovation in the workplace.
- Civic Life: Critical thinking enables citizens to make informed decisions about public issues and participate effectively in democratic processes.
5.2 Communication Skills: Expressing Ideas Effectively
Communication skills involve effectively conveying information and ideas through various mediums, including verbal, written, and visual communication. Strong communication skills are essential for building relationships, collaborating with others, and achieving goals.
Strategies for Improvement:
- Practice Active Listening: Encourage students to listen attentively and empathetically to others.
- Develop Clear and Concise Writing: Teach students to write clearly, concisely, and effectively for different audiences.
- Enhance Public Speaking Skills: Provide opportunities for students to practice public speaking and presentation skills.
- Use Visual Aids: Incorporate visual aids, such as charts, graphs, and images, to enhance communication.
- Seek Feedback: Encourage students to seek feedback on their communication skills and make improvements.
Relevance:
- Education: Communication skills are essential for expressing ideas, participating in discussions, and collaborating with peers.
- Workplace: Communication skills are crucial for building relationships, working in teams, and leading effectively.
- Personal Life: Communication skills enable individuals to build strong relationships, resolve conflicts, and express their needs and desires.
5.3 Collaboration: Working Effectively with Others
Collaboration involves working effectively with others to achieve common goals. It requires strong communication skills, empathy, and the ability to compromise and negotiate. Collaboration is essential for teamwork, problem-solving, and innovation.
Strategies for Improvement:
- Establish Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Define roles and responsibilities for each team member to ensure accountability.
- Promote Open Communication: Encourage team members to communicate openly and honestly with each other.
- Foster a Culture of Respect: Create a safe and supportive environment where team members feel valued and respected.
- Practice Conflict Resolution: Teach team members how to resolve conflicts constructively and respectfully.
- Celebrate Successes: Recognize and celebrate team accomplishments to build morale and motivation.
Relevance:
- Education: Collaboration enables students to learn from each other, share ideas, and work together to achieve common goals.
- Workplace: Collaboration is essential for teamwork, problem-solving, and innovation in the workplace.
- Community Life: Collaboration enables individuals to work together to address community issues and improve the quality of life.
5.4 Adaptability: Embracing Change and Innovation
Adaptability is the ability to adjust to new conditions and thrive in changing environments. It involves being open to new ideas, willing to take risks, and able to learn from mistakes. Adaptability is essential for success in today’s rapidly evolving world.
Strategies for Improvement:
- Embrace Change: Encourage students to view change as an opportunity for growth and learning.
- Develop a Growth Mindset: Teach students to believe that their abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work.
- Take Risks: Encourage students to step outside their comfort zones and try new things.
- Learn from Mistakes: Teach students to view mistakes as learning opportunities and use them to improve.
- Stay Informed: Encourage students to stay up-to-date on current events and emerging trends.
Relevance:
- Education: Adaptability enables students to thrive in new learning environments and adapt to changing curriculum and teaching methods.
- Workplace: Adaptability is essential for navigating changing job markets and adapting to new technologies and work processes.
- Personal Life: Adaptability enables individuals to cope with life’s challenges and thrive in changing circumstances.
6. Additional Resources
Looking for more information on 21st century skills? CONDUCT.EDU.VN is your go-to resource. Here are some other resources to explore:
| Frequently Asked Questions: |
|---|
| 1. What are some specific examples of 21st century skills in action in educational settings? Examples include students collaborating on a group project to solve a real-world problem, using technology to research and present information, critically analyzing media sources, and demonstrating empathy and social responsibility through service-learning projects. |
| 2. How can educators effectively integrate 21st century skills into their existing curriculum? Educators can integrate 21st century skills by designing learning experiences that encourage critical thinking, communication, collaboration, and creativity. This can involve incorporating project-based learning, inquiry-based activities, and opportunities for student choice and reflection into their teaching practices. |
| 3. What are some challenges educators might face when trying to implement 21st century skills in their classrooms? Challenges may include lack of resources or training in integrating 21st century skills, difficulty in assessing these skills effectively, and addressing the diverse needs and backgrounds of students while fostering collaboration and creativity in the classroom. |
| 4. Can parents play a role in supporting the development of 21st century skills at home, and if so, how? Yes, parents can support the development of 21st century skills by encouraging their children to engage in activities that promote critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving, such as discussing current events, working on creative projects together, or volunteering in the community. Additionally, parents can model these skills in their own behavior and provide opportunities for their children to practice them in everyday situations. |
| 5. How do 21st century skills relate to social-emotional learning (SEL)? 21st century skills and SEL are closely related, as many of the skills encompassed by each framework overlap. For example, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making—all components of SEL—are also essential 21st century skills that contribute to students’ success in school, work, and life. |
| 6. What is the role of technology in developing 21st century skills? Technology plays a critical role in developing 21st century skills by providing students with access to vast amounts of information, tools for collaboration and communication, and opportunities for creativity and innovation. However, it’s important to use technology intentionally and purposefully, ensuring that it enhances learning experiences and promotes the development of essential skills rather than simply being used for its own sake. |
| 7. How can schools create a culture that supports the development of 21st century skills? Schools can create a culture that supports the development of 21st century skills by prioritizing these skills in their mission and vision, providing professional development for teachers on how to integrate these skills into their teaching practices, creating opportunities for students to practice these skills in various contexts, and recognizing and celebrating students’ achievements in these areas. |
| 8. What are some strategies for assessing 21st century skills effectively? Strategies for assessing 21st century skills effectively include using performance-based assessments, such as projects and presentations, that require students to apply their skills in authentic contexts; using rubrics to evaluate students’ performance based on clear and specific criteria; and providing students with opportunities to reflect on their own learning and identify areas for improvement. |
| 9. How can communities support the development of 21st century skills in their local schools? Communities can support the development of 21st century skills in their local schools by providing resources and funding for programs and initiatives that promote these skills; partnering with schools to offer internships and mentorship opportunities for students; and advocating for policies that prioritize 21st century skills in education. |
| 10. What are the long-term benefits of developing 21st century skills? The long-term benefits of developing 21st century skills include increased opportunities for success in education, work, and life; improved problem-solving and decision-making abilities; enhanced communication and collaboration skills; and a greater ability to adapt to change and thrive in a rapidly evolving world. |
7. Conclusion
Focusing on 21st century skills is crucial for ensuring that students are ready for college, careers, and civic life. While there is no single “right” way to approach this, we hope that the information in this guide inspires you to explore what 21st century learning could look like in your district. CONDUCT.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing you with the resources and support you need to succeed.
To learn more about how to enhance your skills and prepare for the future, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 555-1234. Our website, CONDUCT.EDU.VN, offers a wealth of information and guidance on mastering 21st century skills. Don’t wait – start your journey to success today by exploring our resources and connecting with our expert community.
Call to Action:
Are you ready to equip yourself or your students with the essential skills for success in the 21st century? Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN today to access our comprehensive resources, expert guidance, and practical tools. Whether you’re an educator, a student, or a professional, we have everything you need to thrive in today’s rapidly evolving world. Don’t miss out – unlock your potential and prepare for a brighter future with conduct.edu.vn.