A Comprehensive Guide To Help Revenue Practitioners enhances revenue management and streamlines operations. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, discover effective revenue strategies to optimize your revenue cycle, ensuring sustainable growth and a seamless customer experience. Explore resources and tools to help you navigate the complexities of revenue operations, compliance guidelines, and ethical business practices.
1. Understanding the Evolving Role of Revenue Practitioners
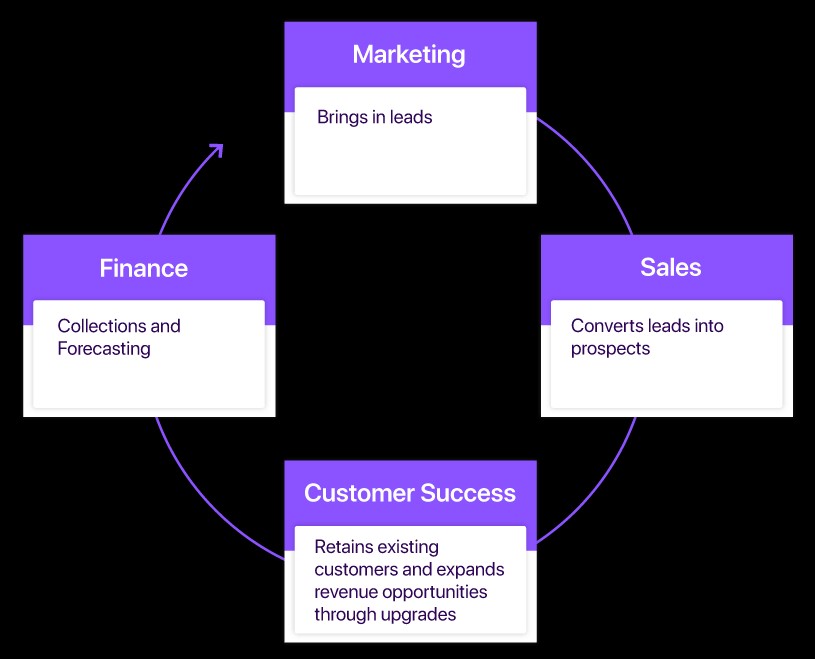
The role of revenue practitioners has significantly evolved, especially with the advent of Software as a Service (SaaS) models. Traditionally, revenue flow was seen as a unidirectional process, moving from marketing and sales to finance. However, the modern recurring revenue model necessitates a more cyclical and integrated approach, emphasizing customer retention and continuous engagement. Revenue practitioners must now possess a broader skill set, encompassing not just financial acumen but also a deep understanding of customer experience, sales strategies, and marketing tactics.
This evolution demands a shift from viewing finance as merely a collections function to recognizing it as a crucial component of the revenue-generating engine. According to an article in Harvard Business Review titled “Ending the War Between Sales and Marketing,” the integration of sales and marketing is essential because both functions share a common goal: generating profitable and increasing revenue. While this holds true for transactional businesses, the recurring revenue model in SaaS requires a more holistic view, involving customer success, support, and finance teams.
The front-loaded costs associated with SaaS businesses make it imperative to focus on maintaining the revenue engine long after a customer is acquired. This requires continuous engagement with customers throughout their lifecycle to drive retention, encourage expansion, and minimize churn. Delivering a seamless customer experience with efficient processes that share insights between all revenue-driving teams becomes a significant competitive advantage. Revenue practitioners play a central role in orchestrating these efforts, ensuring that all teams are aligned and working towards common revenue goals.
The primary responsibilities of a revenue practitioner include:
- Optimizing Revenue Processes: Identifying and eliminating bottlenecks in the revenue cycle to improve efficiency.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Implementing strategies to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Driving Cross-Functional Alignment: Fostering collaboration between sales, marketing, customer success, and finance teams.
- Leveraging Data Analytics: Using data to inform revenue strategies and track performance metrics.
- Ensuring Compliance: Adhering to regulatory requirements and ethical standards in revenue management.
By embracing these responsibilities, revenue practitioners can drive sustainable growth and create lasting value for their organizations. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we provide the resources and guidance necessary to navigate these evolving roles and responsibilities effectively.
2. Key Responsibilities of Revenue Professionals
Revenue professionals play a pivotal role in ensuring an organization’s financial health and sustainable growth. Their responsibilities extend beyond mere revenue collection, encompassing strategic planning, process optimization, and compliance oversight. Understanding these key responsibilities is crucial for anyone aspiring to excel in this dynamic field.
2.1. Strategic Revenue Planning
Strategic revenue planning involves developing a comprehensive roadmap for achieving revenue targets. This includes analyzing market trends, identifying growth opportunities, and setting realistic revenue goals. Revenue professionals must collaborate with various departments to align revenue strategies with overall business objectives.
- Market Analysis: Conducting thorough market research to understand customer needs, competitive landscape, and emerging trends.
- Revenue Forecasting: Developing accurate revenue forecasts based on historical data, market insights, and sales projections.
- Goal Setting: Establishing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) revenue goals.
- Resource Allocation: Allocating resources effectively to support revenue-generating activities.
2.2. Optimizing Revenue Cycle
Optimizing the revenue cycle involves streamlining processes from lead generation to revenue collection. This includes identifying and eliminating bottlenecks, improving efficiency, and enhancing the customer experience. Revenue professionals must work closely with sales, marketing, and customer service teams to ensure a seamless revenue process.
- Lead Management: Implementing effective lead generation and nurturing strategies to maximize conversion rates.
- Sales Process Optimization: Streamlining the sales process to reduce cycle times and improve close rates.
- Customer Onboarding: Ensuring a smooth and efficient customer onboarding process to enhance customer satisfaction.
- Billing and Invoicing: Optimizing billing and invoicing processes to minimize errors and improve cash flow.
2.3. Managing Revenue Recognition
Managing revenue recognition involves accurately recording revenue in accordance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. Revenue professionals must understand the principles of revenue recognition and ensure that revenue is recognized appropriately.
- Compliance with Accounting Standards: Adhering to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- Contract Review: Reviewing contracts to ensure proper revenue recognition treatment.
- Audit Preparation: Preparing for audits by maintaining accurate records and documentation.
- Revenue Assurance: Implementing controls to ensure that all revenue is accurately recorded and accounted for.
2.4. Analyzing Revenue Performance
Analyzing revenue performance involves tracking and evaluating key performance indicators (KPIs) to identify areas for improvement. Revenue professionals must use data analytics to gain insights into revenue trends, customer behavior, and market dynamics.
- KPI Tracking: Monitoring KPIs such as revenue growth, customer acquisition cost (CAC), and customer lifetime value (CLTV).
- Variance Analysis: Analyzing variances between actual and budgeted revenue to identify areas of concern.
- Reporting: Preparing regular reports on revenue performance for management and stakeholders.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Using data insights to inform revenue strategies and optimize performance.
2.5. Ensuring Revenue Compliance
Ensuring revenue compliance involves adhering to legal and regulatory requirements related to revenue management. Revenue professionals must stay informed about changes in laws and regulations and implement controls to ensure compliance.
- Tax Compliance: Complying with tax laws and regulations related to revenue.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to industry-specific regulations and standards.
- Internal Controls: Implementing internal controls to prevent fraud and errors.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks related to revenue management.
By effectively managing these key responsibilities, revenue professionals can drive sustainable growth, improve profitability, and ensure the long-term success of their organizations. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we provide the resources and expertise necessary to excel in this critical role.
 strategic revenue planning
strategic revenue planning
3. Essential Skills for Revenue Professionals
To excel as a revenue professional, a combination of technical and soft skills is essential. These skills enable professionals to effectively manage revenue streams, optimize processes, and drive business growth. Here are some of the most critical skills needed in this field:
3.1. Financial Acumen
A strong foundation in finance is paramount for revenue professionals. This includes understanding financial statements, budgeting, forecasting, and revenue recognition principles.
- Financial Statement Analysis: The ability to interpret and analyze financial statements, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, to assess financial performance and identify trends.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Proficiency in creating and managing budgets, as well as developing accurate revenue forecasts based on historical data and market trends.
- Revenue Recognition: A thorough understanding of revenue recognition principles under GAAP and IFRS, ensuring accurate and compliant revenue reporting.
3.2. Data Analysis and Interpretation
Revenue professionals must be adept at collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to identify trends, patterns, and insights that can inform revenue strategies.
- Data Collection: The ability to gather data from various sources, including CRM systems, financial databases, and market research reports.
- Data Analysis Tools: Proficiency in using data analysis tools such as Excel, SQL, and data visualization software like Tableau or Power BI.
- Statistical Analysis: Understanding statistical concepts and methods to analyze data and draw meaningful conclusions.
3.3. Sales and Marketing Knowledge
A solid understanding of sales and marketing principles is crucial for revenue professionals to align revenue strategies with sales and marketing efforts.
- Sales Process: Knowledge of the sales process, including lead generation, qualification, and closing techniques.
- Marketing Strategies: Understanding marketing strategies, such as digital marketing, content marketing, and social media marketing, to drive revenue growth.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Proficiency in using CRM systems to manage customer interactions and track sales performance.
3.4. Process Optimization
Revenue professionals must be skilled at identifying and streamlining revenue processes to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Process Mapping: The ability to map out existing revenue processes to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Lean Principles: Knowledge of Lean principles and methodologies to eliminate waste and improve efficiency.
- Six Sigma: Understanding Six Sigma concepts and tools to reduce process variation and improve quality.
3.5. Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration skills are essential for revenue professionals to work with cross-functional teams and stakeholders.
- Verbal Communication: The ability to communicate clearly and concisely, both orally and in writing.
- Presentation Skills: Proficiency in presenting data and insights to stakeholders in a compelling and persuasive manner.
- Teamwork: The ability to work effectively in a team environment, collaborating with colleagues from different departments.
3.6. Problem-Solving and Decision-Making
Revenue professionals must be able to identify problems, analyze root causes, and develop effective solutions to optimize revenue performance.
- Critical Thinking: The ability to analyze information objectively and make sound judgments.
- Decision-Making Frameworks: Knowledge of decision-making frameworks and tools to evaluate alternatives and make informed choices.
- Risk Management: Understanding risk management principles and techniques to identify and mitigate potential risks to revenue performance.
3.7. Technology Proficiency
Revenue professionals must be comfortable using various technology tools and systems to manage revenue processes and analyze data.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Proficiency in using ERP systems to manage financial and operational data.
- Business Intelligence (BI): Knowledge of BI tools to analyze data and generate reports.
- Automation Tools: Understanding automation tools to streamline revenue processes and reduce manual effort.
By developing these essential skills, revenue professionals can effectively manage revenue streams, optimize processes, and drive sustainable business growth. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we offer resources and training to help professionals develop these critical skills and advance their careers.
4. Ethical Considerations for Revenue Practitioners
Ethical considerations are paramount for revenue practitioners, as their decisions and actions directly impact an organization’s financial health and reputation. Maintaining high ethical standards is not only a legal requirement but also a moral imperative. Here are some key ethical considerations for revenue professionals:
4.1. Transparency and Honesty
Transparency and honesty are the cornerstones of ethical revenue management. Revenue practitioners must ensure that all financial information is accurate, complete, and presented in a clear and understandable manner.
- Accurate Reporting: Providing accurate and truthful financial reports to stakeholders, including investors, management, and regulatory agencies.
- Full Disclosure: Disclosing all relevant financial information, including potential risks and uncertainties.
- Honest Communication: Communicating honestly and openly with colleagues, clients, and partners.
4.2. Compliance with Laws and Regulations
Revenue practitioners must adhere to all applicable laws and regulations, including accounting standards, tax laws, and securities regulations.
- Accounting Standards: Complying with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- Tax Laws: Adhering to tax laws and regulations, including accurate reporting and timely payment of taxes.
- Securities Regulations: Complying with securities regulations, such as those enforced by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
4.3. Conflicts of Interest
Revenue practitioners must avoid conflicts of interest that could compromise their objectivity and integrity.
- Disclosure: Disclosing any potential conflicts of interest to management and stakeholders.
- Impartiality: Making decisions based on objective criteria, without regard to personal interests.
- Objectivity: Maintaining objectivity and independence in all professional activities.
4.4. Confidentiality
Revenue practitioners have access to sensitive financial information and must maintain strict confidentiality.
- Data Protection: Protecting confidential data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Privacy: Respecting the privacy of individuals and organizations.
- Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs): Adhering to non-disclosure agreements to protect confidential information.
4.5. Fairness and Integrity
Revenue practitioners must act fairly and with integrity in all their professional dealings.
- Fair Treatment: Treating all individuals and organizations fairly and equitably.
- Integrity: Maintaining high ethical standards and acting with honesty and integrity in all professional activities.
- Ethical Decision-Making: Making ethical decisions based on sound judgment and moral principles.
4.6. Professional Competence
Revenue practitioners must maintain professional competence and continually update their knowledge and skills.
- Continuing Education: Participating in continuing education and professional development activities.
- Knowledge Updates: Staying informed about changes in accounting standards, tax laws, and regulations.
- Professional Certifications: Obtaining and maintaining professional certifications, such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA).
4.7. Reporting Unethical Behavior
Revenue practitioners have a responsibility to report unethical behavior to the appropriate authorities.
- Whistleblowing: Reporting unethical behavior to management, regulatory agencies, or law enforcement.
- Protection: Providing protection to whistleblowers from retaliation or discrimination.
- Accountability: Holding individuals accountable for unethical behavior.
By adhering to these ethical considerations, revenue practitioners can maintain the trust and confidence of stakeholders and contribute to the long-term success of their organizations. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we provide resources and guidance to help professionals navigate ethical dilemmas and uphold the highest ethical standards. You can reach us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States or contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 555-1234.
5. The Impact of Technology on Revenue Management
Technology has revolutionized revenue management, providing revenue practitioners with powerful tools to streamline processes, improve accuracy, and enhance decision-making. From automated billing systems to advanced data analytics platforms, technology has transformed the way revenue is managed.
5.1. Automation of Revenue Processes
Automation has significantly reduced manual effort and improved the efficiency of revenue processes.
- Automated Billing Systems: Automating billing and invoicing processes to reduce errors and improve cash flow.
- Automated Revenue Recognition: Automating revenue recognition processes to ensure compliance with accounting standards.
- Automated Reporting: Automating the generation of financial reports to provide timely and accurate information to stakeholders.
5.2. Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
Data analytics and business intelligence (BI) tools provide revenue practitioners with valuable insights into revenue performance.
- Revenue Forecasting: Using data analytics to develop accurate revenue forecasts based on historical data and market trends.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) to track revenue performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Data Visualization: Using data visualization tools to present data in a clear and understandable manner.
5.3. Cloud-Based Revenue Management Solutions
Cloud-based revenue management solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Accessibility: Accessing revenue management solutions from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Scalability: Scaling revenue management solutions to meet changing business needs.
- Cost Savings: Reducing IT infrastructure costs by using cloud-based solutions.
5.4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML technologies are transforming revenue management by providing advanced capabilities such as predictive analytics and fraud detection.
- Predictive Analytics: Using AI and ML to predict future revenue trends and customer behavior.
- Fraud Detection: Detecting fraudulent activities and preventing revenue leakage.
- Personalization: Personalizing customer experiences to increase revenue and improve customer satisfaction.
5.5. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers enhanced security and transparency in revenue management.
- Secure Transactions: Ensuring secure and transparent revenue transactions.
- Data Integrity: Maintaining the integrity of revenue data through blockchain technology.
- Auditability: Improving auditability of revenue transactions through blockchain technology.
5.6. Integration with Other Business Systems
Integration with other business systems, such as CRM and ERP, enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of revenue management.
- CRM Integration: Integrating revenue management systems with CRM systems to improve customer relationship management.
- ERP Integration: Integrating revenue management systems with ERP systems to streamline financial processes.
- Data Sharing: Sharing data between revenue management systems and other business systems to improve decision-making.
By embracing technology, revenue practitioners can streamline processes, improve accuracy, and enhance decision-making, ultimately driving sustainable growth and improving profitability. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we provide resources and guidance to help professionals leverage technology to optimize revenue management.
6. Best Practices for Effective Revenue Operations
Effective revenue operations are essential for driving sustainable growth and maximizing profitability. By implementing best practices, revenue practitioners can streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
6.1. Aligning Sales and Marketing
Aligning sales and marketing efforts is crucial for generating leads and closing deals.
- Shared Goals: Establishing shared goals and objectives between sales and marketing teams.
- Communication: Improving communication and collaboration between sales and marketing teams.
- Lead Management: Implementing effective lead management processes to nurture leads and convert them into customers.
6.2. Customer-Centric Approach
Adopting a customer-centric approach is essential for driving customer loyalty and increasing revenue.
- Customer Feedback: Gathering and analyzing customer feedback to improve products and services.
- Personalization: Personalizing customer experiences to meet individual needs and preferences.
- Customer Service: Providing excellent customer service to resolve issues and build customer loyalty.
6.3. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Continuously monitoring and improving revenue processes is essential for identifying and addressing issues.
- KPI Tracking: Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor revenue performance.
- Process Analysis: Analyzing revenue processes to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Performance Reviews: Conducting regular performance reviews to assess progress and identify areas for improvement.
6.4. Data-Driven Decision Making
Making data-driven decisions is essential for optimizing revenue strategies and improving performance.
- Data Collection: Collecting data from various sources, including CRM systems, financial databases, and market research reports.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing data to identify trends, patterns, and insights.
- Reporting: Preparing regular reports on revenue performance for management and stakeholders.
6.5. Investing in Training and Development
Investing in training and development for revenue professionals is essential for keeping them up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies.
- Continuing Education: Providing opportunities for continuing education and professional development.
- Skills Development: Developing the skills and competencies of revenue professionals.
- Mentoring: Providing mentoring opportunities for revenue professionals.
6.6. Compliance and Risk Management
Ensuring compliance and managing risks is essential for protecting the organization from legal and financial liabilities.
- Compliance Training: Providing compliance training to revenue professionals.
- Risk Assessments: Conducting regular risk assessments to identify and mitigate potential risks.
- Internal Controls: Implementing internal controls to prevent fraud and errors.
By implementing these best practices, revenue practitioners can optimize revenue operations, drive sustainable growth, and maximize profitability. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we provide resources and guidance to help professionals implement these best practices effectively.
7. Common Challenges Faced by Revenue Teams
Revenue teams often encounter various challenges that can hinder their ability to drive growth and achieve financial targets. Understanding these common challenges is crucial for developing effective strategies to overcome them.
7.1. Siloed Data and Systems
Siloed data and systems can create inefficiencies and hinder decision-making.
- Lack of Integration: Lack of integration between different systems, such as CRM, ERP, and marketing automation platforms.
- Data Inconsistency: Inconsistent data across different systems, leading to inaccurate reporting and analysis.
- Manual Processes: Reliance on manual processes to reconcile data and generate reports.
7.2. Inaccurate Revenue Forecasting
Inaccurate revenue forecasting can lead to poor resource allocation and missed opportunities.
- Lack of Data: Lack of historical data and market insights.
- Bias: Biased assumptions and subjective judgments.
- Complexity: Complexity of forecasting models and methodologies.
7.3. Inefficient Revenue Processes
Inefficient revenue processes can lead to delays, errors, and increased costs.
- Bottlenecks: Identifying and addressing bottlenecks in revenue processes.
- Redundancies: Eliminating redundancies and streamlining workflows.
- Automation: Automating manual tasks to improve efficiency.
7.4. Lack of Alignment Between Teams
Lack of alignment between sales, marketing, and finance teams can lead to missed opportunities and inefficiencies.
- Conflicting Goals: Conflicting goals and objectives between different teams.
- Poor Communication: Poor communication and collaboration between teams.
- Lack of Trust: Lack of trust and transparency between teams.
7.5. Compliance and Regulatory Issues
Compliance and regulatory issues can create significant challenges for revenue teams.
- Changing Regulations: Keeping up with changing regulations and compliance requirements.
- Complexity: Complexity of compliance requirements and reporting obligations.
- Enforcement: Enforcement of compliance requirements and penalties for non-compliance.
7.6. Technology Adoption and Integration
Technology adoption and integration can be challenging for revenue teams.
- Resistance to Change: Resistance to change and adoption of new technologies.
- Integration Issues: Integration issues between different systems and platforms.
- Training: Lack of training and support for new technologies.
7.7. Customer Retention and Churn
Customer retention and churn are critical challenges for revenue teams.
- Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Churn Reduction: Reducing customer churn and improving retention rates.
- Customer Engagement: Enhancing customer engagement and building relationships.
By understanding these common challenges, revenue teams can develop effective strategies to overcome them and drive sustainable growth. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we provide resources and guidance to help professionals address these challenges and improve revenue performance.
8. Strategies for Overcoming Revenue Challenges
Overcoming revenue challenges requires a proactive and strategic approach. By implementing effective strategies, revenue teams can improve performance, drive growth, and achieve financial targets.
8.1. Centralizing Data and Systems
Centralizing data and systems can improve efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making.
- Data Integration: Integrating data from different systems into a centralized data warehouse or data lake.
- Data Governance: Implementing data governance policies and procedures to ensure data quality and consistency.
- Automation: Automating data collection, processing, and reporting.
8.2. Improving Revenue Forecasting
Improving revenue forecasting can help revenue teams make better decisions and allocate resources more effectively.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing historical data, market trends, and sales forecasts.
- Collaboration: Collaborating with sales, marketing, and finance teams to gather insights and refine forecasts.
- Technology: Using forecasting tools and technologies to improve accuracy and efficiency.
8.3. Streamlining Revenue Processes
Streamlining revenue processes can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Process Mapping: Mapping out existing revenue processes to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Automation: Automating manual tasks and streamlining workflows.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously monitoring and improving revenue processes.
8.4. Enhancing Team Alignment
Enhancing team alignment can improve communication, collaboration, and performance.
- Shared Goals: Establishing shared goals and objectives between teams.
- Communication: Improving communication and collaboration between teams.
- Transparency: Promoting transparency and trust between teams.
8.5. Ensuring Compliance and Managing Risk
Ensuring compliance and managing risk can protect the organization from legal and financial liabilities.
- Compliance Training: Providing compliance training to revenue professionals.
- Risk Assessments: Conducting regular risk assessments to identify and mitigate potential risks.
- Internal Controls: Implementing internal controls to prevent fraud and errors.
8.6. Investing in Technology
Investing in technology can improve efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making.
- Research: Researching and evaluating different technology solutions.
- Implementation: Implementing and integrating new technologies.
- Training: Providing training and support for new technologies.
8.7. Improving Customer Retention
Improving customer retention can increase revenue and reduce churn.
- Customer Feedback: Gathering and analyzing customer feedback to improve products and services.
- Personalization: Personalizing customer experiences to meet individual needs and preferences.
- Customer Service: Providing excellent customer service to resolve issues and build customer loyalty.
By implementing these strategies, revenue teams can overcome common challenges and drive sustainable growth. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we provide resources and guidance to help professionals implement these strategies effectively.
9. Building a High-Performing Revenue Team
Building a high-performing revenue team is essential for driving sustainable growth and achieving financial targets. A high-performing team is characterized by strong leadership, clear goals, effective communication, and a culture of continuous improvement.
9.1. Establishing Clear Goals and Objectives
Establishing clear goals and objectives is essential for aligning team efforts and measuring performance.
- SMART Goals: Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
- Alignment: Aligning team goals with overall business objectives.
- Communication: Communicating goals and objectives clearly to all team members.
9.2. Recruiting and Hiring Top Talent
Recruiting and hiring top talent is essential for building a high-performing team.
- Job Descriptions: Creating clear and concise job descriptions.
- Interview Process: Implementing a structured interview process.
- Assessment: Assessing candidates’ skills, knowledge, and experience.
9.3. Providing Training and Development
Providing training and development opportunities is essential for enhancing team skills and knowledge.
- Technical Skills: Providing training on technical skills, such as data analysis, financial modeling, and revenue management.
- Soft Skills: Providing training on soft skills, such as communication, collaboration, and leadership.
- Mentoring: Providing mentoring opportunities for team members.
9.4. Fostering a Culture of Collaboration
Fostering a culture of collaboration is essential for improving team performance and innovation.
- Communication: Encouraging open and honest communication.
- Teamwork: Promoting teamwork and collaboration.
- Respect: Fostering a culture of respect and trust.
9.5. Empowering Team Members
Empowering team members can increase engagement and improve performance.
- Autonomy: Providing team members with autonomy and decision-making authority.
- Recognition: Recognizing and rewarding team members for their contributions.
- Feedback: Providing regular feedback and coaching.
9.6. Using Technology Effectively
Using technology effectively can improve efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making.
- Automation: Automating manual tasks and streamlining workflows.
- Data Analysis: Using data analysis tools to gain insights and make informed decisions.
- Collaboration Tools: Using collaboration tools to improve communication and teamwork.
9.7. Monitoring and Evaluating Performance
Monitoring and evaluating performance is essential for identifying areas for improvement and recognizing achievements.
- KPI Tracking: Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Performance Reviews: Conducting regular performance reviews.
- Feedback: Providing regular feedback and coaching.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can build a high-performing revenue team that drives sustainable growth and achieves financial targets. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we offer resources and guidance to help leaders build and manage effective revenue teams.
10. Future Trends in Revenue Management
Revenue management is a dynamic field that is constantly evolving. Understanding future trends is essential for revenue practitioners to stay ahead of the curve and drive sustainable growth.
10.1. Increased Automation
Increased automation will continue to transform revenue management.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA will automate repetitive tasks and improve efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI will provide advanced capabilities such as predictive analytics and fraud detection.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML will enable revenue teams to make data-driven decisions and optimize revenue strategies.
10.2. Shift to Subscription-Based Models
The shift to subscription-based models will continue to drive changes in revenue management.
- Recurring Revenue Recognition: Revenue teams will need to adapt to recurring revenue recognition requirements.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): CLTV will become an increasingly important metric for measuring customer value.
- Churn Management: Churn management will be critical for retaining customers and maximizing revenue.
10.3. Data-Driven Decision Making
Data-driven decision making will become even more important in revenue management.
- Big Data: Big data will provide revenue teams with more insights into customer behavior and market trends.
- Data Visualization: Data visualization tools will enable revenue teams to present data in a clear and understandable manner.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics will help revenue teams forecast future revenue trends and optimize revenue strategies.
10.4. Enhanced Customer Experience
Enhanced customer experience will be a key differentiator for revenue teams.
- Personalization: Personalizing customer experiences to meet individual needs and preferences.
- Customer Service: Providing excellent customer service to resolve issues and build customer loyalty.
- Customer Engagement: Enhancing customer engagement and building relationships.
10.5. Increased Focus on Compliance
Increased focus on compliance will be essential for protecting organizations from legal and financial liabilities.
- Regulatory Changes: Revenue teams will need to stay up-to-date with regulatory changes.
- Data Privacy: Data privacy will become an increasingly important concern.
- Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity will be critical for protecting sensitive data.
10.6. Remote Work and Distributed Teams
Remote work and distributed teams will become more common in revenue management.
- Collaboration Tools: Collaboration tools will be essential for enabling remote teams to work effectively.
- Communication: Clear and consistent communication will be critical for managing remote teams.
- Training: Training will need to be adapted to remote work environments.
10.7. Integration of Finance and Operations
Integration of finance and operations will become more important for driving efficiency and improving decision-making.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Cross-functional collaboration will be essential for aligning finance and operations.
- Data Sharing: Data sharing between finance and operations will improve decision-making.
- Process Automation: Process automation will streamline workflows and reduce costs.
By understanding these future trends, revenue practitioners can prepare for the future and drive sustainable growth. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we provide resources and guidance to help professionals stay ahead of the curve and excel in the field of revenue management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Revenue Practices
Here are some frequently asked questions related to revenue practices to help you better understand this field:
- What is a revenue practitioner?
A revenue practitioner is a professional responsible for managing and optimizing an organization’s revenue streams, ensuring compliance, and driving sustainable growth. - What are the key responsibilities of a revenue practitioner?
Key responsibilities include strategic revenue planning, optimizing the revenue cycle, managing revenue recognition, analyzing revenue performance, and ensuring revenue compliance. - What skills are essential for a revenue practitioner?
Essential skills include financial acumen, data analysis and interpretation, sales and marketing knowledge, process optimization, communication, problem-solving, and technology proficiency. - What ethical considerations should revenue practitioners keep in mind?
Ethical considerations include transparency, compliance with laws and regulations, avoiding conflicts of interest, maintaining confidentiality, fairness, and professional competence. - How has technology impacted revenue management?
Technology has automated revenue processes, enabled data analytics, and provided cloud-based solutions, enhancing efficiency and decision-making. - What are some best practices for effective revenue operations?
Best practices include aligning sales and marketing, adopting a customer-centric approach, continuous monitoring, data-driven decision making, and investing in training. - What are common challenges faced by revenue teams?
Common challenges include siloed data, inaccurate revenue forecasting, inefficient processes, lack of alignment, compliance issues, and technology adoption. - How can revenue teams overcome these challenges?
Strategies include centralizing data, improving forecasting, streamlining processes, enhancing team alignment, ensuring compliance, and investing in technology. - What future trends are expected in revenue management?
Future trends include increased automation, a shift to subscription models, data-driven decision-making, enhanced customer experience, and a focus on compliance. - Where can I find more information and guidance on revenue practices?
You can find more information and guidance at CONDUCT.EDU.VN, which offers resources, articles, and training for revenue professionals. Our address is 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, and you can reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 555-1234.
For those eager to deepen their understanding and enhance their effectiveness in revenue management, conduct.edu.vn offers a wealth of resources. Whether you’re seeking to refine your strategies, stay abreast of industry trends, or ensure ethical practices, our platform is designed to equip you with the knowledge and tools you need. We understand the challenges revenue practitioners face and provide clear, actionable guidance to help you succeed. Visit us today to explore how we can support your professional growth and contribute to your organization’s success.