Power BI Migration: A Comprehensive Guide for Success
Power BI migration is a crucial step for organizations seeking enhanced data analytics capabilities and strategic decision-making; CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers expert guidance to navigate this complex process effectively. Embracing Power BI unlocks flexible system integration, cutting-edge visualization, and real-time data access. Explore effective data transformation, report conversion, and efficient deployment strategies to maximize the benefits of your migration journey, including data management and business intelligence.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Power of Power BI Migration
- Analyzing the Benefits of Migrating to Power BI
- Power BI Migration Steps: A Comprehensive Guide
- Preparing for Migration: Requirements Gathering
- Stage 1: Requirements Gathering in Detail
- Stage 2: Deployment Plan Essentials
- Stage 3: Creating a Proof of Concept
- Stage 4: Content Creation and Fact Verification
- Stage 5: Deployment and Ongoing Support
- Minimizing Risks During Power BI Migration
- Power BI Migration Best Practices
- Real-World Examples of Successful Power BI Migrations
- Challenges and Solutions in Power BI Migration
- Tools and Technologies for Power BI Migration
- Power BI Migration Checklist
- The Future of Power BI and Data Migration
- Compliance and Security Considerations
- How CONDUCT.EDU.VN Supports Power BI Migrations
- FAQ: Power BI Migration
- Conclusion: Embrace the Power of Data with Power BI
1. Understanding the Power of Power BI Migration
Power BI migration involves moving existing data, reports, dashboards, and configurations from one environment or platform to Power BI. This can include migrating from older versions of Power BI, other business intelligence tools, or even from manual reporting processes. The goal is to leverage Power BI’s advanced features to gain deeper insights and improve decision-making. The migration process is not merely a technical task but a strategic initiative that aligns data analytics with business objectives. By understanding the intricacies of data transformation and reporting capabilities, organizations can unlock the full potential of Power BI and drive significant business value.
2. Analyzing the Benefits of Migrating to Power BI
Migrating to Power BI offers numerous advantages that can transform how businesses operate. These include:
- Flexible System Integration: Power BI seamlessly integrates with various data sources, including Excel, Microsoft Teams, Azure cloud solutions, on-premises databases, and third-party databases. This flexibility ensures a unified view of data across the organization.
- Cutting-Edge Visualization: With low-code/no-code tools, Power BI makes analytics easily accessible to employees. Decision-makers can quickly and effectively make informed decisions, enhancing agility and responsiveness.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Power BI offers a free demo version and affordable monthly plans, providing excellent value for the quality of service. This helps lower the total cost of ownership (TCO) while delivering powerful analytics capabilities.
- Real-Time Data Access: Data is processed and loaded into interactive reports and graphs in real-time, providing a competitive edge in data processing speed and updates. This enables rapid problem-solving and effective modeling of prospects.
- Enhanced Reporting Capabilities: Power BI’s robust reporting features allow for detailed and interactive reports that can be customized to meet specific business needs.
- Improved Collaboration: Power BI facilitates better collaboration among teams by allowing easy sharing of reports and dashboards, fostering a data-driven culture.
- Scalability: Built on the Azure cloud, Power BI offers excellent scalability, accommodating growing data volumes and user demands without compromising performance.
- Mobile Accessibility: Power BI provides mobile apps that allow users to access reports and dashboards on the go, ensuring data is always at their fingertips.
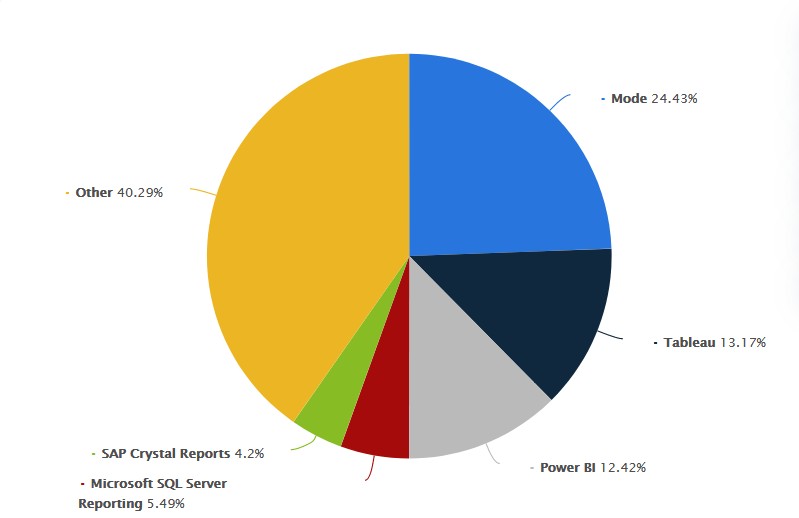 Market Share of Business Intelligence Tools
Market Share of Business Intelligence Tools
3. Power BI Migration Steps: A Comprehensive Guide
A successful Power BI migration involves several key stages, each requiring careful planning and execution. Here’s a detailed guide to help you navigate the process:
3.1. Pre-Migration Steps:
Before diving into the migration stages, it’s crucial to lay the groundwork:
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Evaluate the financial and operational benefits of migrating to Power BI.
- Stakeholder Alignment: Secure buy-in and support from top management and key stakeholders.
- Initial Governance Model: Establish a basic governance framework to manage data and access.
- Initial Deployment Planning: Develop a preliminary plan for deploying Power BI within the organization.
- Initial Architecture Establishment: Define the initial architecture for your Power BI environment.
3.2. Stage 1: Requirements Gathering
This initial stage involves gathering all the necessary information to plan the migration effectively. This includes:
- Identifying Reporting Needs: Determine the purpose, audience, and expected actions for each report.
- Evaluating Existing BI Items: Assess which items require change or refactoring in the new Power BI environment.
- Identifying Key Elements: Determine which elements users engage with to identify those that can be removed or enhanced.
- Defining Responsibilities: Assign owners and subject matter experts (SMEs) for each report to manage changes and approvals.
- Analyzing Security Requirements: Address role-based access control, data sensitivity, privacy issues, regulatory requirements, and compliance considerations.
- Identifying Potential Threats and Issues: Proactively identify and address potential drawbacks.
- Compiling and Prioritizing Data Requirements: Understand data source types, data structure, cleansing needs, data integration requirements, data volume, and latency tolerance.
3.3. Stage 2: Deployment Plan
Once the requirements are gathered, the next step is to create a deployment plan that outlines how Power BI will be implemented. Key considerations include:
- Choosing the Right Platform: Decide between Power BI Service and Power BI Reporting Server based on your organization’s needs.
- Workspace Management Approach: Determine whether to use a single workspace or multiple workspaces for data and reports, and define security settings for each.
- Implementation and Usage: Decide how Power BI will be accessed, whether through a Power BI app, enterprise tools (Teams, SharePoint Online), or mobile devices.
3.4. Stage 3: Creation of Proof of Concept (PoC)
Creating a Proof of Concept (PoC) is crucial for testing the feasibility and functionality of the migration. This involves:
- Outlining PoC Goals and Objectives: Clearly define what you want to achieve with the PoC.
- Understanding Data Flow: Ensure that the necessary data sources can connect and function properly.
- Testing Functionalities and Security Settings: Verify that all functionalities work as expected and that security settings are correctly configured.
- Experimenting with Layout and Design: Tinker with the layout and design to optimize the user experience.
- Identifying Potential Issues: Uncover any basic differences or potential issues that may arise in Power BI.
- Proposing Data Architecture Changes: Determine if changes are needed in the data architecture to accommodate Power BI.
- Planning for Dashboard Conversion: Develop a plan for converting existing Business Intelligence dashboards to Power BI.
3.5. Stage 4: Creating Content and Checking Facts
This stage involves translating the PoC into a production-ready solution. Key steps include:
- Enhancing or Developing Datasets: Collect data from various sources, transform and cleanse data, and create an ideal set of datasets.
- Checking Model Relationships: Ensure that the relationships between data models are correctly established.
- Implementing Row-Level Security: Implement security measures to restrict data access at the row level.
- Creating New Reports and Dashboards: Develop new reports and dashboards using appropriate data visualization tools.
- Defining Terminology: Use clear and consistent terminology to avoid confusion.
- Ensuring Interactivity: Implement interactive elements to enhance the user experience.
3.6. Stage 5: Deployment and Support
The final stage involves deploying the solution and providing ongoing support. This includes:
- Installing in a Test Environment: Deploy the solution in a test environment for user acceptance testing.
- Implementing in the Production Environment: Deploy the solution in the production environment after successful testing.
- Conducting a Retrospective: Review the migration process to identify areas for improvement.
- Parallel Testing: Run the new solution parallel to the old one for a period to minimize risk.
- Monitoring and Control: Continuously monitor activity logs, content updates, and subscriptions.
- Post-Migration Support: Provide ongoing support to address any issues and ensure the solution continues to meet the organization’s needs.
4. Preparing for Migration: Requirements Gathering
The requirements gathering phase is a critical first step in any Power BI migration project. This phase involves identifying and documenting the specific needs and expectations of the organization. A thorough understanding of these requirements is essential for a successful migration. Key activities in this phase include:
- Stakeholder Interviews: Conducting interviews with key stakeholders to understand their reporting needs, data requirements, and expectations for Power BI.
- Current State Assessment: Evaluating the existing BI environment to identify current reports, dashboards, data sources, and data models.
- Future State Definition: Defining the desired future state of the BI environment in Power BI, including new reports, dashboards, and data models.
- Data Source Analysis: Analyzing the data sources that will be used in Power BI, including their structure, quality, and accessibility.
- Security Requirements: Defining the security requirements for Power BI, including user access, data security, and compliance regulations.
- Performance Requirements: Identifying the performance requirements for Power BI, including report load times, data refresh frequency, and user concurrency.
- Training Requirements: Determining the training needs for users who will be using Power BI, including report authors, data analysts, and business users.
- Documentation: Documenting all requirements in a clear and concise manner, including report specifications, data models, and security policies.
By thoroughly gathering and documenting these requirements, organizations can ensure that the Power BI migration project is aligned with their business objectives and that the resulting solution meets their specific needs.
5. Stage 1: Requirements Gathering in Detail
The first stage of Power BI migration, requirements gathering, is crucial for a successful transition. It involves a comprehensive analysis of current and future needs, ensuring the new environment aligns with business objectives. This stage includes several key steps:
- 5.1. Identify Reporting Needs:
- Purpose: Define the objective of each report. What questions should it answer?
- Audience: Identify who will use the report. What is their level of technical expertise?
- Expected Actions: Determine what actions users will take based on the report’s insights.
- 5.2. Evaluate Existing BI Items:
- Assess: Review current reports, dashboards, and data models.
- Change or Refactor: Determine which items need modification in Power BI.
- 5.3. Identify Key Elements:
- User Engagement: Analyze how users interact with reports. Which elements are most used?
- Remove or Enhance: Decide which elements to remove or improve in the new architecture.
- 5.4. Define Responsibilities:
- Report Owners: Assign individuals responsible for each report.
- Subject Matter Experts (SMEs): Identify SMEs to manage changes and approvals.
- 5.5. Analyze Security Requirements:
- Role-Based Access Control: Define user access levels.
- Data Sensitivity: Identify sensitive data and implement protection measures.
- Privacy Issues: Address data privacy concerns.
- Regulatory Requirements: Ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
- 5.6. Identify Potential Threats and Issues:
- Drawbacks: Proactively identify potential issues and challenges.
- 5.7. Compile and Prioritize Data Requirements:
- Data Source Types: Identify all data sources.
- Data Structure: Understand the structure of the data.
- Data Cleansing: Determine data cleansing needs.
- Data Integration: Define data integration requirements.
- Data Volume: Assess the amount of data involved.
- Latency Tolerance: Determine acceptable latency levels.
By addressing these steps in detail, organizations can ensure a thorough understanding of their requirements, setting the stage for a successful Power BI migration.
6. Stage 2: Deployment Plan Essentials
After gathering requirements, the next crucial step is developing a comprehensive deployment plan. This plan serves as a roadmap, outlining how Power BI will be implemented within the organization. Key elements of the deployment plan include:
- 6.1. Choosing the Right Platform:
- Power BI Service: A cloud-based platform ideal for organizations seeking scalability and ease of use.
- Power BI Report Server: An on-premises solution for organizations with strict data governance requirements.
- 6.2. Workspace Management Approach:
- Single Workspace: Suitable for smaller organizations with simple data structures.
- Multiple Workspaces: Recommended for larger organizations with complex data structures and diverse user groups.
- 6.3. Security Settings:
- Role-Based Access Control: Implement granular access controls to ensure data security.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data to protect it from unauthorized access.
- 6.4. Implementation and Usage:
- Power BI App: A dedicated application for accessing Power BI reports and dashboards.
- Enterprise Tools (Teams, SharePoint Online): Integrate Power BI with existing enterprise tools for seamless access.
- Mobile Devices: Enable access to Power BI reports and dashboards on mobile devices for on-the-go insights.
- 6.5. Data Governance:
- Data Quality: Establish processes to ensure data quality and accuracy.
- Data Lineage: Track the origin and flow of data to ensure transparency and accountability.
- 6.6. Training and Support:
- User Training: Provide training to users on how to use Power BI effectively.
- Technical Support: Offer technical support to address any issues or questions that may arise.
- 6.7. Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor Power BI performance to ensure optimal performance.
- Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance to keep the Power BI environment up-to-date.
By carefully considering these elements, organizations can develop a robust deployment plan that sets the stage for a successful Power BI migration.
7. Stage 3: Creating a Proof of Concept
Creating a Proof of Concept (PoC) is a crucial step in the Power BI migration process. It allows organizations to test the feasibility and functionality of Power BI before committing to a full-scale migration. The PoC should focus on key aspects of the migration, including data connectivity, data transformation, report development, and security. Key steps in creating a PoC include:
- 7.1. Define Objectives: Clearly define the goals of the PoC. What specific questions should it answer?
- 7.2. Select Data Sources: Choose representative data sources that will be used in the PoC.
- 7.3. Develop Reports: Create sample reports and dashboards that demonstrate the capabilities of Power BI.
- 7.4. Test Data Connectivity: Ensure that Power BI can connect to the selected data sources.
- 7.5. Validate Data Transformation: Verify that data can be transformed and cleansed as needed.
- 7.6. Test Security Settings: Validate that security settings are correctly configured.
- 7.7. Evaluate Performance: Assess the performance of Power BI with the selected data sources and reports.
- 7.8. Document Findings: Document all findings and recommendations from the PoC.
By creating a PoC, organizations can identify potential issues and challenges early in the migration process, allowing them to make informed decisions about how to proceed.
8. Stage 4: Content Creation and Fact Verification
Stage 4, content creation and fact verification, is where the actual migration and development of reports and dashboards take place. This stage involves translating the PoC into a production-ready solution and ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data and insights presented. Key steps include:
- 8.1. Data Integration: Connect Power BI to the required data sources.
- 8.2. Data Modeling: Create data models that accurately reflect the relationships between data entities.
- 8.3. Data Transformation: Transform and cleanse data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- 8.4. Report Development: Develop interactive reports and dashboards that meet the needs of the business.
- 8.5. Fact Verification: Verify the accuracy of the data and insights presented in the reports and dashboards.
- 8.6. User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Conduct UAT to ensure that the reports and dashboards meet the needs of the users.
- 8.7. Documentation: Document the data models, reports, and dashboards for future reference.
By following these steps, organizations can ensure that the content created in Power BI is accurate, reliable, and meets the needs of the business.
9. Stage 5: Deployment and Ongoing Support
The final stage of the Power BI migration process involves deploying the solution to the production environment and providing ongoing support to ensure its continued success. Key steps in this stage include:
- 9.1. Deployment: Deploy the Power BI solution to the production environment.
- 9.2. User Training: Provide training to users on how to use the new Power BI solution.
- 9.3. Monitoring: Monitor the performance and usage of the Power BI solution.
- 9.4. Support: Provide ongoing support to address any issues or questions that may arise.
- 9.5. Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance to keep the Power BI environment up-to-date.
- 9.6. Updates: Apply updates and patches to the Power BI environment as needed.
- 9.7. Optimization: Optimize the Power BI solution to improve performance and efficiency.
- 9.8. Documentation: Maintain up-to-date documentation for the Power BI solution.
By following these steps, organizations can ensure that the Power BI solution is successfully deployed and continues to provide value to the business.
10. Minimizing Risks During Power BI Migration
Power BI migration, while beneficial, can present several risks that need careful management. Minimizing these risks is crucial for a smooth and successful transition. Here are some key strategies:
- 10.1. Thorough Planning: Develop a detailed migration plan that outlines all steps, timelines, and responsibilities.
- 10.2. Data Backup: Back up all data before starting the migration process to prevent data loss.
- 10.3. Pilot Testing: Conduct pilot testing with a small group of users to identify and resolve any issues before full deployment.
- 10.4. Data Validation: Validate data accuracy and completeness after migration to ensure data integrity.
- 10.5. Security Measures: Implement robust security measures to protect data during and after migration.
- 10.6. User Training: Provide comprehensive training to users on the new Power BI environment.
- 10.7. Performance Monitoring: Monitor performance after migration to identify and address any performance issues.
- 10.8. Contingency Plan: Develop a contingency plan to address any unexpected issues that may arise during migration.
- 10.9. Communication: Maintain clear and consistent communication with stakeholders throughout the migration process.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can minimize the risks associated with Power BI migration and ensure a successful transition.
11. Power BI Migration Best Practices
To ensure a smooth and successful Power BI migration, it’s essential to follow best practices. These practices help minimize risks, optimize performance, and maximize the value of your Power BI investment. Key best practices include:
- 11.1. Start with a Clear Strategy: Define your goals, objectives, and success metrics before starting the migration.
- 11.2. Assess Your Current Environment: Evaluate your existing BI environment to understand its strengths, weaknesses, and dependencies.
- 11.3. Plan Your Data Model: Design a robust and scalable data model that meets your reporting needs.
- 11.4. Optimize Data Transformation: Use Power Query to efficiently transform and cleanse your data.
- 11.5. Choose the Right Visualizations: Select visualizations that effectively communicate your data insights.
- 11.6. Implement Row-Level Security: Secure your data by implementing row-level security to restrict access to sensitive information.
- 11.7. Test Thoroughly: Conduct thorough testing to ensure data accuracy, report functionality, and performance.
- 11.8. Provide User Training: Train your users on how to use the new Power BI environment effectively.
- 11.9. Monitor Performance: Monitor the performance of your Power BI environment to identify and address any issues.
- 11.10. Continuously Improve: Continuously improve your Power BI environment based on user feedback and changing business needs.
By following these best practices, organizations can ensure a successful Power BI migration that delivers significant business value.
12. Real-World Examples of Successful Power BI Migrations
Examining real-world examples of successful Power BI migrations can provide valuable insights and inspiration for your own migration project. Here are a few examples:
- 12.1. Manufacturing Company: A manufacturing company migrated from Excel-based reporting to Power BI, resulting in improved data accuracy, faster reporting times, and better decision-making.
- 12.2. Retail Chain: A retail chain migrated from a legacy BI tool to Power BI, resulting in improved data visualization, enhanced collaboration, and increased sales.
- 12.3. Healthcare Provider: A healthcare provider migrated from a manual reporting process to Power BI, resulting in improved data analysis, better patient outcomes, and reduced costs.
- 12.4. Financial Services Firm: A financial services firm migrated from a complex data warehouse to Power BI, resulting in improved data accessibility, faster report generation, and better risk management.
- 12.5. Government Agency: A government agency migrated from a decentralized reporting system to Power BI, resulting in improved data consistency, better transparency, and increased efficiency.
These examples demonstrate the diverse benefits that organizations can achieve by migrating to Power BI.
13. Challenges and Solutions in Power BI Migration
Power BI migration, while offering numerous benefits, also presents several challenges. Understanding these challenges and implementing effective solutions is crucial for a successful migration. Some common challenges include:
- 13.1. Data Compatibility: Ensuring that data from different sources is compatible with Power BI.
- Solution: Use Power Query to transform and cleanse data before loading it into Power BI.
- 13.2. Data Security: Protecting sensitive data during and after migration.
- Solution: Implement row-level security and other security measures to restrict access to sensitive information.
- 13.3. Performance Issues: Addressing performance issues that may arise after migration.
- Solution: Optimize data models, reports, and queries to improve performance.
- 13.4. User Adoption: Encouraging users to adopt the new Power BI environment.
- Solution: Provide comprehensive training and support to users.
- 13.5. Legacy Systems: Integrating Power BI with legacy systems.
- Solution: Use Power BI connectors or APIs to connect to legacy systems.
- 13.6. Data Governance: Establishing data governance policies and procedures.
- Solution: Define data ownership, data quality standards, and data security policies.
- 13.7. Complex Data Models: Managing complex data models.
- Solution: Simplify data models by breaking them down into smaller, more manageable components.
- 13.8. Limited Resources: Addressing limited resources, such as time, budget, and staff.
- Solution: Prioritize migration tasks and leverage external resources, such as consultants or partners.
By addressing these challenges and implementing effective solutions, organizations can ensure a successful Power BI migration.
14. Tools and Technologies for Power BI Migration
Power BI migration involves using various tools and technologies to facilitate the process. These tools help in data extraction, transformation, loading, and validation. Some commonly used tools and technologies include:
- 14.1. Power BI Desktop: Used for developing reports and dashboards.
- 14.2. Power BI Service: Used for publishing and sharing reports and dashboards.
- 14.3. Power Query: Used for transforming and cleansing data.
- 14.4. DAX (Data Analysis Expressions): Used for creating calculations and measures.
- 14.5. Azure Data Factory: Used for orchestrating data pipelines.
- 14.6. SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS): Used for data extraction, transformation, and loading.
- 14.7. Azure Synapse Analytics: Used for data warehousing and analytics.
- 14.8. Data Gateway: Used for connecting to on-premises data sources.
- 14.9. PowerShell: Used for automating migration tasks.
- 14.10. Third-Party Migration Tools: Used for simplifying and automating the migration process.
By leveraging these tools and technologies, organizations can streamline the Power BI migration process and ensure a successful transition.
15. Power BI Migration Checklist
A Power BI migration checklist can help ensure that all necessary steps are completed during the migration process. Here’s a comprehensive checklist:
- 15.1. Planning Phase:
- [ ] Define migration goals and objectives.
- [ ] Assess current BI environment.
- [ ] Identify data sources and dependencies.
- [ ] Develop a migration plan.
- [ ] Allocate resources and budget.
- 15.2. Requirements Gathering Phase:
- [ ] Gather requirements from stakeholders.
- [ ] Document reporting needs.
- [ ] Analyze data sources.
- [ ] Define security requirements.
- [ ] Identify performance requirements.
- 15.3. Design Phase:
- [ ] Design data models.
- [ ] Design reports and dashboards.
- [ ] Plan data transformation.
- [ ] Implement security measures.
- 15.4. Development Phase:
- [ ] Develop data models.
- [ ] Develop reports and dashboards.
- [ ] Implement data transformation.
- [ ] Implement security measures.
- 15.5. Testing Phase:
- [ ] Conduct unit testing.
- [ ] Conduct integration testing.
- [ ] Conduct user acceptance testing (UAT).
- [ ] Validate data accuracy.
- [ ] Test performance.
- 15.6. Deployment Phase:
- [ ] Deploy Power BI solution to production environment.
- [ ] Provide user training.
- [ ] Monitor performance.
- [ ] Provide ongoing support.
- 15.7. Post-Migration Phase:
- [ ] Monitor performance and usage.
- [ ] Provide ongoing support.
- [ ] Optimize Power BI environment.
- [ ] Continuously improve based on user feedback.
By following this checklist, organizations can ensure that all necessary steps are completed during the Power BI migration process.
16. The Future of Power BI and Data Migration
The future of Power BI and data migration is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and changing business needs. Key trends shaping the future include:
- 16.1. AI and Machine Learning: Increased use of AI and machine learning to automate migration tasks and improve data quality.
- 16.2. Cloud Migration: Growing adoption of cloud-based Power BI and data migration solutions.
- 16.3. Self-Service Migration: Tools and technologies that empower users to perform migrations themselves.
- 16.4. Data Governance: Increased focus on data governance and security during migration.
- 16.5. Real-Time Data Migration: Solutions that enable real-time data migration for up-to-date insights.
- 16.6. Low-Code/No-Code Migration: Tools that simplify migration processes with low-code/no-code interfaces.
- 16.7. Hybrid Migration: Solutions that support hybrid environments, combining on-premises and cloud-based data sources.
- 16.8. Enhanced Data Visualization: Advanced data visualization techniques for better insights and decision-making.
- 16.9. Collaboration: Improved collaboration tools for migration teams.
- 16.10. Automation: Increased automation of migration tasks to reduce manual effort and errors.
By staying informed about these trends, organizations can prepare for the future of Power BI and data migration and leverage new technologies to improve their migration processes.
17. Compliance and Security Considerations
Compliance and security are critical considerations during Power BI migration. Organizations must ensure that their migration process complies with relevant regulations and protects sensitive data. Key compliance and security considerations include:
- 17.1. Data Privacy: Comply with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
- 17.2. Data Security: Protect data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- 17.3. Access Control: Implement role-based access control to restrict access to sensitive data.
- 17.4. Data Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit.
- 17.5. Audit Logging: Enable audit logging to track data access and changes.
- 17.6. Compliance Standards: Comply with industry-specific compliance standards, such as HIPAA and PCI DSS.
- 17.7. Data Residency: Ensure that data is stored in compliance with data residency requirements.
- 17.8. Data Masking: Use data masking to protect sensitive data in reports and dashboards.
- 17.9. Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- 17.10. Incident Response Plan: Develop an incident response plan to address security incidents.
By addressing these compliance and security considerations, organizations can ensure that their Power BI migration is secure and compliant.
18. How CONDUCT.EDU.VN Supports Power BI Migrations
CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides comprehensive support for organizations undertaking Power BI migrations. Our services include:
- 18.1. Consulting: Expert consulting services to help you plan and execute your migration.
- 18.2. Training: Comprehensive training programs to train your users on Power BI.
- 18.3. Implementation: Implementation services to help you deploy Power BI.
- 18.4. Support: Ongoing support to address any issues or questions that may arise.
- 18.5. Data Governance: Data governance services to help you establish data governance policies and procedures.
- 18.6. Security: Security services to help you secure your Power BI environment.
- 18.7. Optimization: Optimization services to help you improve the performance of your Power BI environment.
- 18.8. Custom Solutions: Custom solutions tailored to your specific needs.
- 18.9. Project Management: Project management services to ensure your migration is completed on time and within budget.
- 18.10. Best Practices: Guidance on Power BI migration best practices.
Contact us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or WhatsApp at +1 (707) 555-1234, or visit our website at CONDUCT.EDU.VN to learn more about how we can support your Power BI migration.
19. FAQ: Power BI Migration
Here are some frequently asked questions about Power BI migration:
- 19.1. What is Power BI migration?
- Power BI migration involves moving existing data, reports, dashboards, and configurations from one environment or platform to Power BI.
- 19.2. Why should I migrate to Power BI?
- Power BI offers numerous benefits, including improved data visualization, enhanced collaboration, and better decision-making.
- 19.3. What are the steps involved in Power BI migration?
- The steps include planning, requirements gathering, design, development, testing, deployment, and post-migration support.
- 19.4. What are the challenges of Power BI migration?
- Challenges include data compatibility, data security, performance issues, and user adoption.
- 19.5. How can I minimize the risks of Power BI migration?
- You can minimize risks by thorough planning, data backup, pilot testing, data validation, and security measures.
- 19.6. What tools and technologies are used for Power BI migration?
- Tools include Power BI Desktop, Power Query, DAX, Azure Data Factory, and SQL Server Integration Services.
- 19.7. How long does Power BI migration take?
- The duration depends on the complexity of the migration and the size of the organization.
- 19.8. How much does Power BI migration cost?
- The cost depends on the scope of the migration and the resources required.
- 19.9. What are the best practices for Power BI migration?
- Best practices include starting with a clear strategy, assessing your current environment, and planning your data model.
- 19.10. How can CONDUCT.EDU.VN help with Power BI migration?
- CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides consulting, training, implementation, and support services for Power BI migration.
20. Conclusion: Embrace the Power of Data with Power BI
Power BI migration is a strategic investment that can transform how your organization uses data to drive business success. By following a well-planned migration process, leveraging the right tools and technologies, and partnering with experienced professionals like CONDUCT.EDU.VN, you can unlock the full potential of Power BI and gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven world. Don’t let outdated systems hold you back; embrace the power of data with Power BI and take your organization to the next level. For more information and expert guidance, visit conduct.edu.vn today.