Artificial intelligence in healthcare PDF documents serve as a comprehensive resource, detailing the utilization of machine learning algorithms and AI techniques to analyze medical data, aid in clinical decisions, and improve healthcare efficiency. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers valuable insights into navigating the complexities of AI in the healthcare industry, providing a practical guide for those seeking to understand its applications and potential. This resource aims to shed light on healthcare innovation, data-driven healthcare, and predictive analytics in medicine.
1. Understanding Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves using computers to automate tasks typically performed by humans. This automation is driving a significant market for AI tools, automation solutions, and big data analytics.
The healthcare AI market is projected to reach $102.7 billion by 2028, driven by the need to automate key processes and generate deeper insights, according to MarketsandMarkets. This growth is underpinned by advancements in machine learning techniques, including deep learning, semantic computing, and neural networks, which are crucial for processing massive volumes of data, as highlighted by Health IT Analytics.
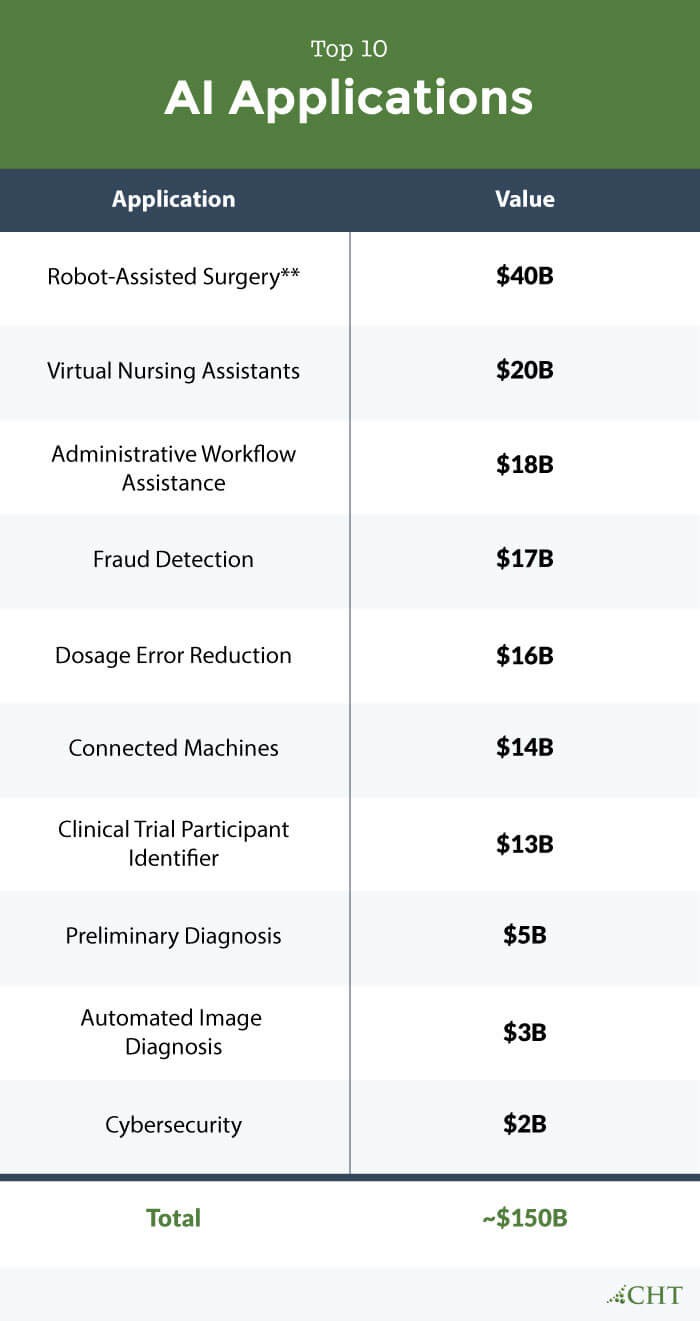
Accenture estimates that clinical health AI applications could save the U.S. healthcare economy $150 billion annually by 2026. Their analysis of ten AI applications with the greatest near-term impact reveals substantial financial and operational benefits.
1.1 Key AI Applications in Healthcare
Several AI applications are transforming the healthcare landscape:
- Robot-Assisted Surgery: Reduces costs and improves patient outcomes with less hospital time.
- Automated Diagnostics: Enhances the accuracy and speed of disease detection.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailors medical interventions based on individual patient data.
- Enhanced Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Improves data management and accessibility.
These applications are pivotal in delivering high-quality and cost-effective care.
1.2 The Role of Data in AI Healthcare
The effectiveness of AI in healthcare hinges on the availability of high-quality data. This data includes:
- Medical Records: Patient histories, diagnoses, and treatment plans.
- Imaging Data: X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.
- Genomic Data: Genetic information that can inform personalized medicine.
- Wearable Device Data: Real-time health metrics collected by wearable sensors.
Analyzing this data helps AI systems identify patterns, predict outcomes, and recommend optimal treatments.
2. Overcoming Barriers to Artificial Intelligence Implementation
Despite the potential benefits, several barriers hinder the widespread adoption of AI in healthcare. These challenges span technological, ethical, and regulatory domains.
2.1 Integration of Data
One of the primary challenges is the complexity of integrating data from various sources. Missing and disparate data can compromise the accuracy and reliability of AI algorithms. Standardizing data formats and ensuring interoperability between systems are crucial steps in addressing this issue.
2.2 Trust, Legal, and Liability Issues
Trust is a significant concern, as healthcare professionals and patients need to be confident in the accuracy and reliability of AI-driven recommendations. Legal and liability issues also arise, particularly when AI systems make incorrect diagnoses or treatment decisions. Clear guidelines and regulatory frameworks are necessary to address these concerns.
2.3 Time and Energy Limitations
Implementing AI requires significant time and energy, not only for development but also for training healthcare staff to use new systems effectively. Better hardware designs and streamlined workflows can help mitigate these limitations.
2.4 Talent Shortage
A shortage of skilled professionals with the specific knowledge and expertise to develop and implement AI solutions poses a significant challenge. Investing in education and training programs is essential to building a workforce capable of leveraging AI in healthcare.
2.5 General Fears of AI in Healthcare
- Job Replacement: Concerns that AI will replace physicians and staff.
- Less Human Interaction: Reduced personal care due to increased automation.
- Data Privacy: Concerns about the misuse and protection of patient data.
- Learning New Technology: Difficulties in adapting to new AI-driven systems.
- Development Costs: High initial investment in AI technologies.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Vulnerabilities to cyberattacks and data breaches.
2.6 Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
State and federal regulations can create substantial obstacles to AI adoption. Certificates of Need, risk-based capital requirements, and burdensome reporting requirements can deter new entrants and innovations.
CONDUCT.EDU.VN emphasizes the importance of understanding these challenges and developing strategies to overcome them. By addressing these barriers, healthcare organizations can harness the full potential of AI to improve patient care and outcomes.
3. Advantages of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
Despite the challenges, the advantages of AI in healthcare are compelling. The healthcare AI market is projected to grow rapidly, driven by the potential to improve patient care, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency.
3.1 Better Data-Driven Decisions
AI technology assists doctors in making better data-driven decisions, improving the accuracy and effectiveness of diagnoses and treatment plans. This leads to a positive impact on the reduction in mortality rates.
3.2 Improved Efficiency of Disease Diagnosis and Treatment
AI can significantly improve the efficiency of disease diagnosis, management, and treatment, leading to better patient outcomes. Accessibility of information can be positive and is not always an infringement of privacy, as AI systems can be designed to protect patient data.
3.3 Integrating Information
Integrating information such as medical records with operating metrics can help assist physicians, improving their ability to make informed decisions.
3.4 Reducing Unnecessary Hospital Visits
AI systems can reduce unnecessary hospital visits by alerting staff only when patient care is needed, optimizing resource allocation and reducing costs.
3.5 Creating Time-Saving Administrative Duties
AI can automate time-saving administrative duties such as voice-to-text transcription, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
3.6 Comparative Analysis of Pros and Cons
The following table summarizes the pros and cons of AI in healthcare:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Better patient care | Fear of job replacement |
| Reduced costs | Data privacy concerns |
| Improved efficiency | Learning new technology |
| Enhanced accuracy | Development costs |
| Data-driven decisions | Cybersecurity threats |
| Personalized treatment plans | Regulatory hurdles |
| Early detection of diseases | Complex data integration |
| Reduction in mortality rates | |
| Automation of administrative tasks |

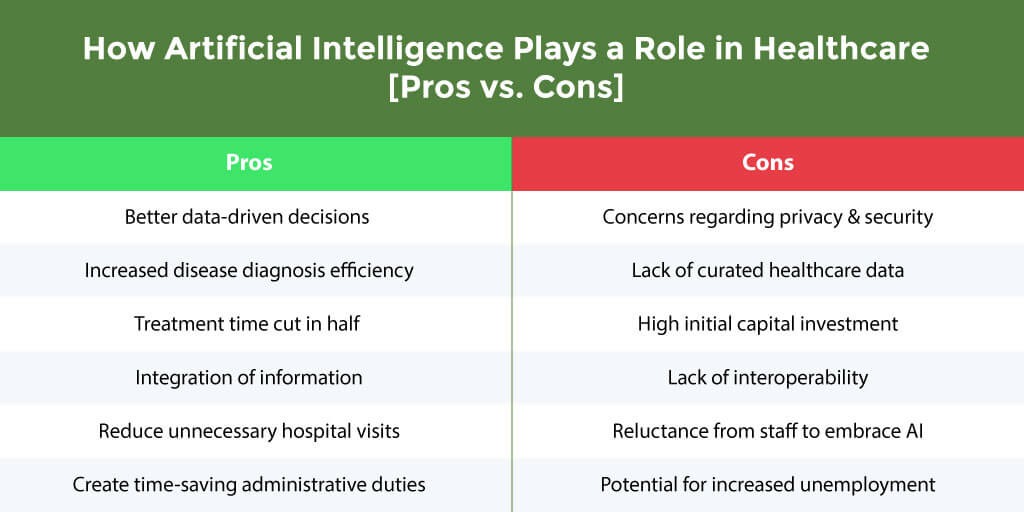
Overall, the benefits, including better patient care, reduced costs, and leveraging the many opportunities offered by the integration of AI, significantly outweigh the fears and challenges. The main goal is to develop AI safely and with purpose for patients, physicians, and developers.
4. Case Study: AI in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
A study at Shanghai Changzheng Hospital in China demonstrates the potential of AI in improving healthcare outcomes.
4.1 Problem
Shanghai Changzheng Hospital faced high lung cancer rates.
4.2 Solution
The hospital used AI and deep learning to diagnose cancer by pairing a computerized tomography (CT) scan with AI. Infervision, a technology company, combined deep learning with medical data to recognize symptoms in medical images.
4.3 AI Technology
The AI technology learns from past imaging reports such as X-Ray, CT, MRI, etc. to assemble automatic diagnostic recommendations. The Infervision intelligent screening system “immediately pushes a warning to the doctor when it detects a medical image with subnormal symptoms.”
4.4 Advantages of AI Technology
- Ability to identify early detection of high-risk diseases.
- Possibility to save on medical expenses.
- Can lower the cost of chronic disease management.
- Provides efficient medical treatment.
This study demonstrates AI’s ability to read medical images, saving time and increasing accuracy for radiologists. Eliot Siegel, chairman of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) Medical Imagine Resource Committee, commented,
“The application of AI will lead to a real digital shift in traditional medical imaging, requiring AI and people to work together to meet the challenges of the medical industry. In the process of lung nodule screening, Infervision is providing preemptive solutions that allow doctors to meet patients’ needs in a short period of time.”
5. The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
As the healthcare industry adopts more of the latest technology, experts predict significant impacts from AI and automation.
5.1 Personalized Healthcare
With the amount of data in the healthcare sphere increasing dramatically every year, AI is able to be trained on more data than ever before. This allows AI systems to personalize treatment recommendations so “specific treatment can be generated based on the patient’s profile, genetics, environment and lifestyle in order to optimize patient outcomes.”
5.2 Improved Legislation and Regulations
Legislative and regulatory bodies often err on the side of caution when regulating the use of AI technology that uses confidential data. As data in the healthcare industry increases at a 48% rate year over year (as reported by the IDC), the ability of AI to overcome unique challenges in the healthcare industry will prompt regulatory groups to create a framework and set of practices that will balance the need to protect confidential patient data with the medical benefits provided by AI.
5.3 Wider Range of Applications
Healthcare systems have been able to see how AI can cut healthcare costs, and expect the same results from expanding the use of AI in more applications. Experts predict that AI will greatly aid drug and treatment discovery and processes, reducing the time traditionally needed for drugs and vaccines to reach the market.
5.4 Increased Automation
AI will be applied for automating tasks such as handling patients’ appointments, care, and records. With AI’s ability to automate a large range of manual tasks, providers will be opened up to focus on providing better care.
5.5 Long-Term Predictions
Tony Hebden, Ph.D. vice president at Health Economics and Outcomes Research (HEOR) and Steve Elmore, Ph.D. vice president at Target Enabling Science and Technology, share their thoughts on how AI will impact healthcare in the future.
5.5.1 Key Insights
- AI will enable physicians, helping in diagnoses and aiding in the most effective treatment for individuals. This will lead to more personalized medicine.
- Integration of additional types of data, such as tracked steps, blood sugar, and lipid levels, will provide real-time feedback.
- AI will identify patients before they get sick, allowing for treatment before they become patients.
- Synergies between human intelligence and artificial intelligence will provide doctors with far more powerful tools to do their job.
6. Specific Applications of AI in Healthcare
AI is making significant strides across various aspects of healthcare. Here are some key areas where AI is currently being applied and is expected to expand in the future:
6.1 Diagnostics and Imaging
AI algorithms are being used to analyze medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to detect anomalies and assist radiologists in making more accurate diagnoses. This is particularly useful in identifying early signs of diseases such as cancer and neurological disorders. Companies like Infervision are at the forefront of this technology.
6.2 Drug Discovery and Development
AI is accelerating the drug discovery process by analyzing vast amounts of data to identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy and safety. This can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with bringing new drugs to market.
6.3 Personalized Medicine
AI can analyze a patient’s genetic information, lifestyle, and medical history to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to their specific needs. This approach promises to improve treatment outcomes and reduce side effects.
6.4 Remote Patient Monitoring
AI-powered wearable devices and remote monitoring systems are enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health in real-time, detect potential problems early, and intervene before they escalate. This is particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions and reducing hospital readmissions.
6.5 Virtual Assistants and Chatbots
AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots are being used to provide patients with information, schedule appointments, answer questions, and offer support. These tools can improve patient engagement and reduce the workload on healthcare staff.
6.6 Healthcare Administration
AI is streamlining administrative tasks such as billing, claims processing, and appointment scheduling, reducing costs and improving efficiency in healthcare organizations.
7. Ethical Considerations in AI Healthcare
The increasing use of AI in healthcare raises several ethical considerations that must be addressed to ensure that AI is used responsibly and for the benefit of all.
7.1 Data Privacy and Security
Protecting patient data is paramount. AI systems must be designed to comply with privacy regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR, and robust security measures must be implemented to prevent data breaches.
7.2 Bias and Fairness
AI algorithms can perpetuate and amplify biases present in the data they are trained on, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. It is crucial to ensure that AI systems are trained on diverse and representative datasets and that their performance is regularly evaluated for bias.
7.3 Transparency and Explainability
AI systems can sometimes be “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their decisions. Transparency and explainability are essential for building trust in AI and ensuring that healthcare professionals can understand and validate AI-driven recommendations.
7.4 Accountability and Liability
Determining who is accountable when an AI system makes an incorrect diagnosis or treatment decision is a complex issue. Clear guidelines and regulatory frameworks are needed to address liability concerns and ensure that patients are protected.
7.5 Human Oversight
AI should augment, not replace, human expertise in healthcare. Healthcare professionals should always have the final say in treatment decisions, and AI systems should be used to support their judgment, not to dictate it.
8. The Role of CONDUCT.EDU.VN in AI Healthcare Education
CONDUCT.EDU.VN plays a vital role in educating healthcare professionals and the public about the potential and limitations of AI in healthcare.
8.1 Providing Accessible Information
CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers accessible and easy-to-understand information about AI in healthcare, helping to demystify the technology and promote its responsible use.
8.2 Addressing Ethical Considerations
CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides resources and guidance on the ethical considerations surrounding AI in healthcare, helping to ensure that AI is used in a way that is consistent with ethical principles and values.
8.3 Promoting Best Practices
CONDUCT.EDU.VN promotes best practices for implementing and using AI in healthcare, helping healthcare organizations to maximize the benefits of AI while minimizing the risks.
8.4 Fostering Collaboration
CONDUCT.EDU.VN fosters collaboration between healthcare professionals, AI developers, and policymakers, helping to create a shared understanding of the challenges and opportunities presented by AI in healthcare.
By providing education and resources, CONDUCT.EDU.VN helps to ensure that AI is used in a way that improves patient care, reduces costs, and enhances the efficiency of the healthcare system.
9. Examples of AI-Driven Healthcare Solutions
To further illustrate the transformative potential of AI in healthcare, let’s explore some specific examples of AI-driven solutions that are already making a difference:
9.1 IBM Watson Health
IBM Watson Health is an AI platform that helps healthcare organizations analyze data, identify insights, and make more informed decisions. Watson Health is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment: Watson for Oncology helps oncologists develop personalized treatment plans for cancer patients based on their individual characteristics and medical history.
- Drug Discovery: Watson Discovery helps researchers identify potential drug candidates and accelerate the drug discovery process.
- Clinical Trial Matching: Watson Clinical Trial Matching helps patients find clinical trials that they may be eligible for.
9.2 Google DeepMind Health
Google DeepMind Health is an AI company that develops AI solutions for healthcare. DeepMind Health’s products include:
- Streams: A mobile app that helps clinicians monitor patients at risk of deterioration and respond more quickly.
- Verily: A research organization focused on developing new technologies to prevent, detect, and manage diseases.
9.3 PathAI
PathAI is an AI company that develops AI-powered pathology solutions. PathAI’s products help pathologists make more accurate diagnoses and improve patient outcomes.
9.4 Zebra Medical Vision
Zebra Medical Vision is an AI company that develops AI solutions for medical imaging. Zebra Medical Vision’s products help radiologists detect anomalies in medical images and improve the efficiency of the imaging workflow.
These are just a few examples of the many AI-driven healthcare solutions that are being developed and deployed today. As AI technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of AI in healthcare in the years to come.
10. Essential Considerations Before Implementing AI in Healthcare
Implementing AI in healthcare requires careful planning and consideration. Here are several essential considerations to keep in mind:
10.1 Define Clear Objectives
Before implementing AI, it’s crucial to define clear objectives and identify the specific problems that AI can help solve. This will help to ensure that AI is used effectively and that its benefits are realized.
10.2 Ensure Data Quality and Availability
AI algorithms require high-quality data to perform effectively. Ensure that the data used to train AI systems is accurate, complete, and representative of the population being served.
10.3 Prioritize Data Privacy and Security
Protecting patient data is paramount. Implement robust security measures to prevent data breaches and comply with privacy regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
10.4 Address Ethical Considerations
Consider the ethical implications of AI in healthcare, including bias, transparency, and accountability. Develop policies and procedures to ensure that AI is used in a way that is consistent with ethical principles and values.
10.5 Provide Training and Support
Provide healthcare professionals with the training and support they need to use AI systems effectively. This will help to ensure that AI is integrated seamlessly into the clinical workflow and that its benefits are realized.
10.6 Monitor and Evaluate Performance
Regularly monitor and evaluate the performance of AI systems to ensure that they are meeting their objectives and that their benefits outweigh their risks.
By considering these essential factors, healthcare organizations can increase the likelihood of successfully implementing AI and realizing its full potential.
FAQ: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
Q1: What is artificial intelligence in healthcare?
AI in healthcare involves using machine learning and other AI techniques to analyze medical data, assist in clinical decisions, and improve healthcare delivery.
Q2: How is AI used in healthcare today?
AI is used in various applications, including diagnostics, drug discovery, personalized medicine, and remote patient monitoring.
Q3: What are the benefits of AI in healthcare?
The benefits include better patient care, reduced costs, improved efficiency, and enhanced accuracy in diagnoses and treatment plans.
Q4: What are the challenges of implementing AI in healthcare?
Challenges include data integration, trust issues, talent shortages, regulatory hurdles, and ethical considerations.
Q5: How can data privacy be ensured when using AI in healthcare?
Data privacy can be ensured by implementing robust security measures, complying with privacy regulations, and ensuring transparency in data usage.
Q6: What role does CONDUCT.EDU.VN play in AI healthcare education?
CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides accessible information, addresses ethical considerations, promotes best practices, and fosters collaboration in AI healthcare.
Q7: How does AI improve drug discovery?
AI analyzes vast amounts of data to identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy and safety, accelerating the drug discovery process.
Q8: What are the ethical considerations when using AI in healthcare?
Ethical considerations include data privacy, bias and fairness, transparency and explainability, and accountability.
Q9: How can AI help with personalized medicine?
AI analyzes a patient’s genetic information, lifestyle, and medical history to develop personalized treatment plans.
Q10: What are some examples of AI-driven healthcare solutions?
Examples include IBM Watson Health, Google DeepMind Health, PathAI, and Zebra Medical Vision.
Conclusion
The potential of artificial intelligence to transform healthcare is immense. By addressing the challenges and leveraging the advantages, AI can enhance patient care, reduce costs, and improve the efficiency of healthcare systems. Artificial intelligence promises to make sense of complex medical data, gain insights, and better recognize patterns in behavior. AI is a “decision engine” that can exponentially increase the effectiveness and efficiencies of healthcare organizations.
To navigate the complexities of AI in healthcare and ensure responsible implementation, turn to CONDUCT.EDU.VN for comprehensive guidance and resources. Discover best practices, address ethical considerations, and foster collaboration to maximize the benefits of AI while minimizing the risks.
Visit conduct.edu.vn at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (707) 555-1234. Let us help you unlock the full potential of AI for a healthier future.