Product metrics are vital for understanding user behavior and product success; CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers comprehensive guidance. This article serves as A Guide To Product Metrics, exploring their definitions, applications, and benefits. Learn how to measure product value and drive growth with key metrics.
1. Understanding Product Value
The core of every successful product lies in the value it offers. If customers perceive value, they engage with the product. Conversely, if they don’t, they cease using it. This fundamental principle underscores the importance of defining your product’s value proposition upfront. While product analytics tools can provide insights, they cannot define the value for you.
To understand your product’s value, step back and consider, “What are my users hoping to achieve with my product? And what is my product truly about?” Successful digital products simplify, reduce costs, or enhance the convenience of people’s lives. Identifying behaviors that signal value is crucial for building a sustainable product.
Knowing when users experience value helps optimize the path to that critical value moment, leading to increased user engagement and potential monetization. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we emphasize the importance of aligning product features with user needs to maximize value delivery.
2. Monetizing Your Product Effectively
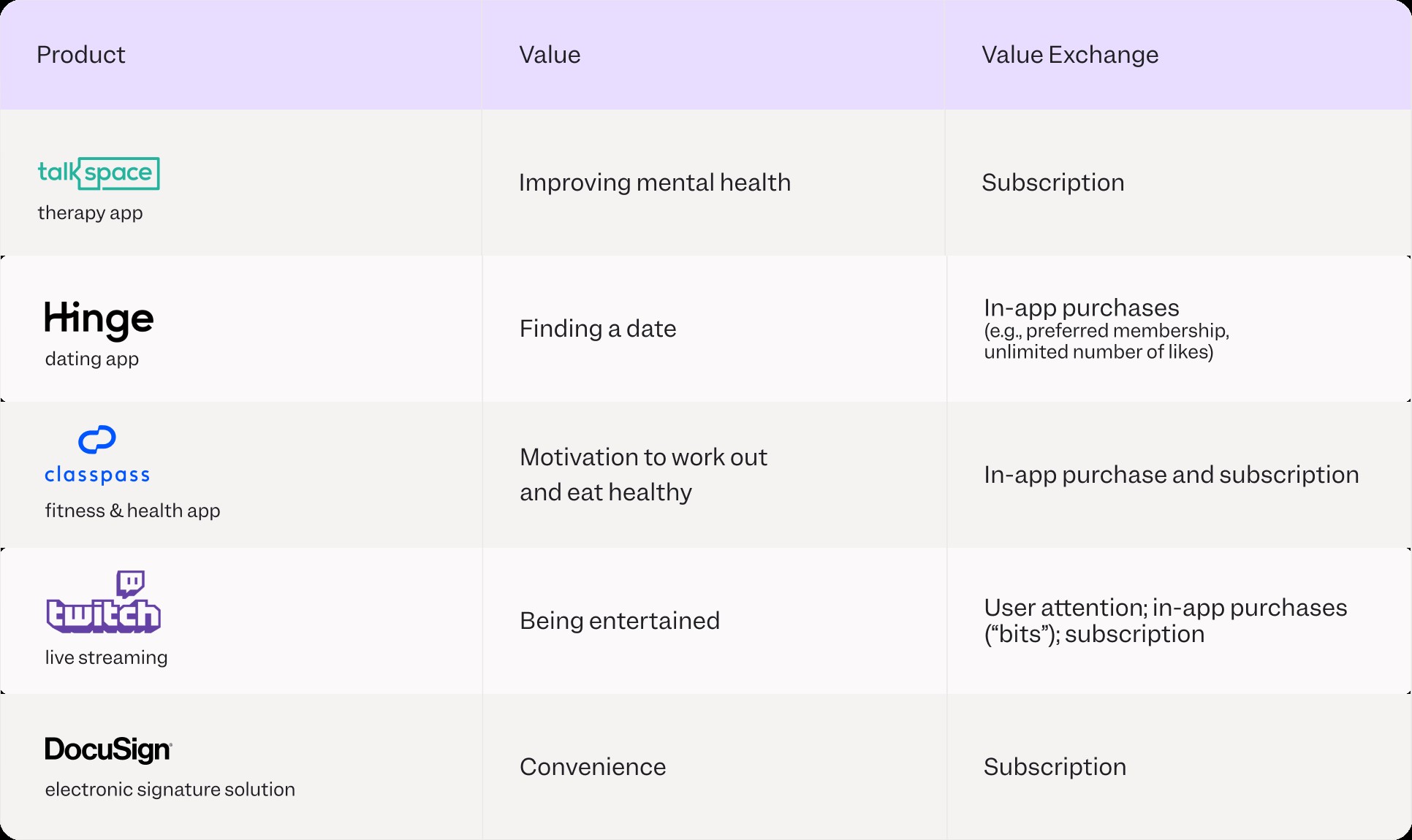
A fundamental value exchange involves users paying for a product or service. Depending on your profit model, common types of value exchange include transactional, subscription, licensing, and freemium models.
-
Transactional: Users pay a fixed price per unit, such as $3.99 for a mobile app.
-
Subscription: Users pay a fixed price per time unit, receiving a fixed number of units or unlimited use.
-
Licensing: Users pay a license fee to use, sell, or copy a product.
-
Freemium: Some users receive a free version, while others pay for a premium version with enhanced features.
However, value exchange isn’t always directly tied to money. User attention, monetized through advertising, and data used for training machine learning models are valuable. Product managers must consider user experience and transparent data-sharing practices to build trust.
2.1. Monetization Strategies Post-COVID-19
COVID-19 has significantly impacted monetization strategies. As Dan Hockenmaier, Founder of Basis One, notes, understanding customer willingness to pay is crucial. The pandemic has altered customer behavior, necessitating a reassessment of monetization strategies. Companies should leverage the changes brought about by COVID-19 to implement significant monetization changes they have been considering.
3. Measuring and Analyzing Product Value
Product value, regardless of its intangible nature, can be quantitatively measured. While gauging fun and entertainment from a video streaming service might seem difficult, you can measure weekly video views or time spent per video.
For meditation apps, measuring anxiety reduction may appear challenging. However, you can measure completion rates for meditation sessions and the percentage of returning users. Observing behavioral differences between returning and non-returning users provides additional insights.
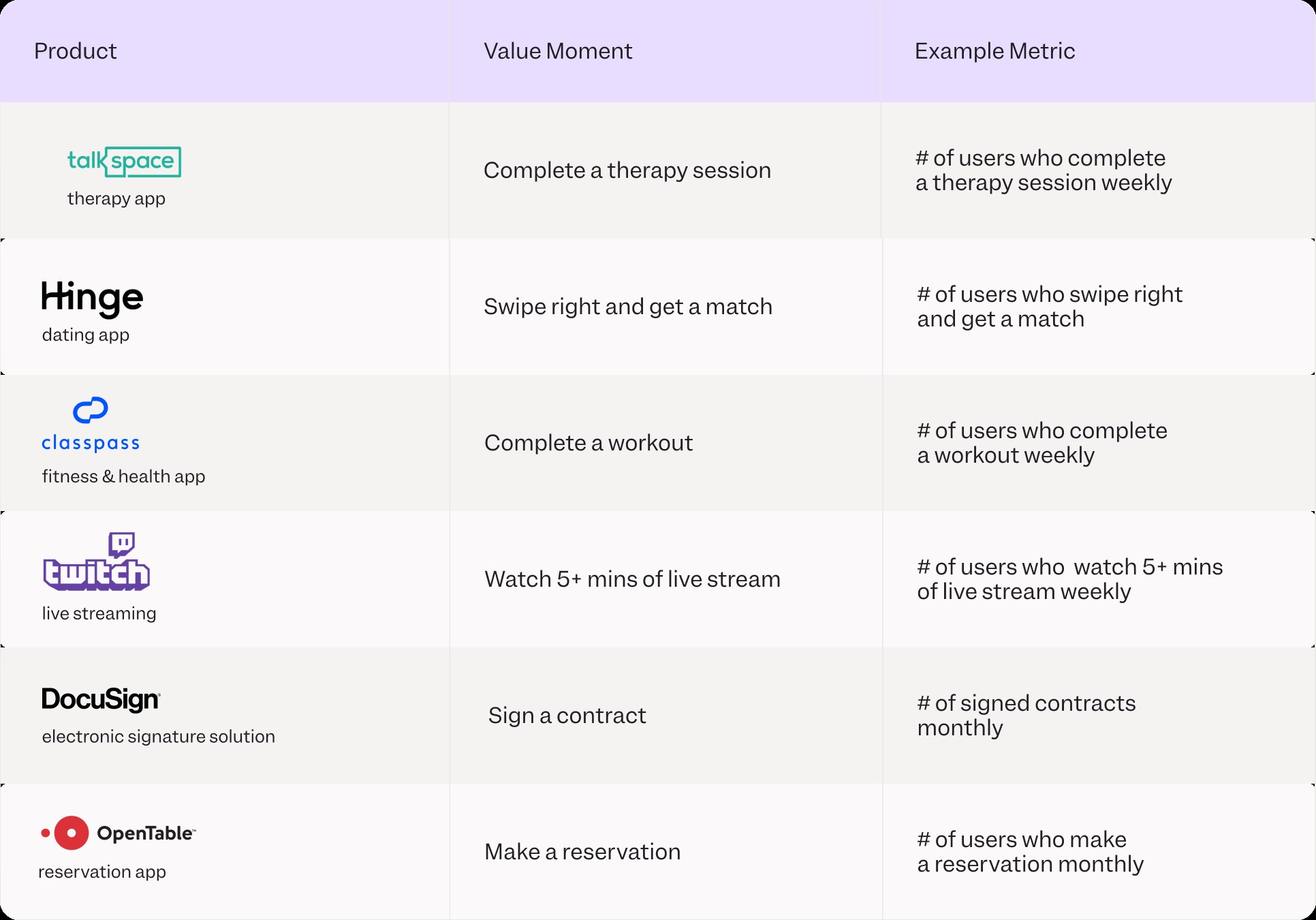
Fuzzy measurement is valuable if it provides new information. A helpful tool for measuring product value is defining “value moments”—user events indicating that a person is benefiting from your product. CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides detailed guidance on setting up effective measurement frameworks.
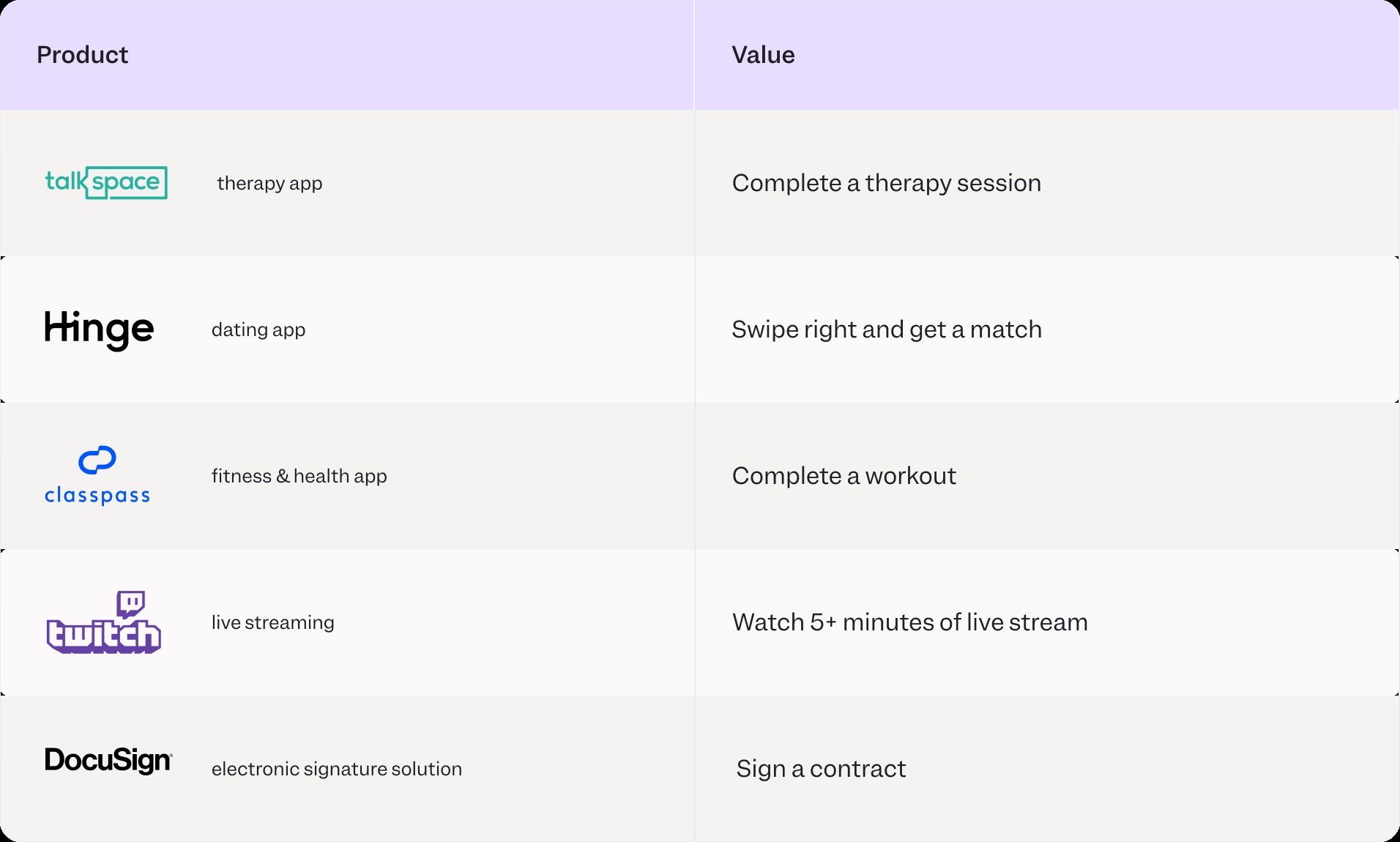
4. Identifying the Value Moment
A product’s value moment is an event or series of actions where a user finds value in your product. Examples include:
User journeys to the value moment vary. Some require registration, verification, adding friends, or entering credit card information before activation. The initial journey to value is critical; the faster users reach value and the clearer the value proposition, the more likely they will remain engaged.
4.1. Examples of Value Moments
-
Vrbo: Booking is the primary objective.
-
Avira: Completing a Smart Scan flow activates and engages users.
-
Viber: Starting a conversation is critical for growth in new markets.
When designing a user journey toward the value moment, steps should reflect brand values. For example, Primephonic prioritizes user experience over immediate conversion by keeping credit cards out of the signup process.
Henrique Boregio, CTO of Primephonic, explains that while adding a credit card requirement could increase conversion numbers, it would create a negative user experience.
5. Selecting Product Metrics for Success
Think of your value moment as a building block for successful product adoption. More value moments increase the likelihood of users building a habit around your product and remaining long-term customers. Turning value into a single key metric, the “north star metric,” helps teams set tangible goals.
To learn more about defining your focus metric, check out Mixpanel’s Guide to Product Metrics, available at Mixpanel’s Guide to Product Metrics.
5.1. Examples of Focus Metrics
-
Mad Paws: The number of bookings per customer.
-
ZipRecruiter: The conversion rate of job seekers completing the Apply flow.
-
The Weather Company: Active user sessions, conversation rate, and engagement.
-
Primephonic: Media minutes consumed.
-
DocuSign: Speed, with 82% of agreements completed in less than 24 hours.
A common mistake is tracking every user event and considering them all equally. Prioritizing a single value moment is a more straightforward way to gauge your product’s value. Focusing on value leads to long-term retention.
6. Common Mistakes in Defining Value Metrics
Product leaders often err by relying too much on intuition or data. Shreyas Doshi, Lead PM at Stripe, emphasizes that a product’s specific context is more important than industry best practices. A north star metric should be responsive to product changes, an aggregate measure of user value, tied to business goals, and relevant for 2-3 years. It should also be complemented by balancing metrics to measure negative impacts.
Brian Balfour, CEO of Reforge, notes that a single metric cannot capture the entire business picture. However, one metric can be most important at any given time. Most products should have acquisition, retention, engagement, and monetization metrics, forming a system where one influences the others.
Lenny Rachitsky, Advisor & Former Lead PM at Airbnb, advises being data-informed rather than data-driven. Data tells you what is happening, while intuition tells you why.
7. Differentiating Good and Great Product Managers
Great PMs understand that metrics are not the mission. Metrics are useful markers for whether the product is achieving its mission and creating value for the company. It’s crucial to recognize that certain products lend themselves well to metrics-based decisions, while others do not.
Shreyas Doshi highlights that early-stage products with infinitesimal usage should rely more on qualitative user feedback and competitive analysis than current usage metrics. Great PMs diligently track metrics but use them as one of many inputs for product decisions.
Vinati Malik, Senior Vice President of New Product Development at TataSky, emphasizes that a great PM prioritizes each new product feature based on how it can move the key value metric.
8. Actionable Strategies for Implementing Product Metrics
Implementing product metrics effectively requires a strategic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you leverage product metrics to drive growth and improve user experience:
8.1. Define Clear Objectives
Before diving into data, clarify your objectives. What are you trying to achieve with your product? Are you aiming to increase user engagement, boost retention rates, or improve conversion rates? Clearly defined objectives will guide your metric selection process.
Example: If your objective is to increase user engagement, you might focus on metrics like daily active users (DAU), session duration, and feature usage.
8.2. Identify Key Value Moments
Identify the critical moments where users experience the core value of your product. These are the moments that lead to long-term engagement and retention.
Example: For a social media platform, a value moment might be when a user connects with friends, shares a post, or joins a group.
8.3. Select Relevant Metrics
Choose metrics that directly reflect the value moments and align with your objectives. Avoid vanity metrics that look good but don’t provide actionable insights.
Table 1: Examples of Relevant Metrics
| Objective | Value Moment | Relevant Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Increase User Engagement | User connects with friends | Daily Active Users (DAU), Session Duration |
| Boost Retention Rates | User shares a post | Monthly Active Users (MAU), Churn Rate |
| Improve Conversion Rates | User joins a group | Conversion Rate, Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) |
| Enhance Feature Adoption | User completes onboarding process | Feature Usage Rate, Time to First Key Action |
8.4. Implement Tracking and Analytics
Use robust analytics tools to track user behavior and measure your selected metrics. Ensure that your tracking is accurate and comprehensive.
Tools to Consider:
- Mixpanel: Offers detailed user analytics and event tracking.
- Amplitude: Provides insights into user behavior across platforms.
- Google Analytics: A widely used tool for web and app analytics.
8.5. Analyze Data and Identify Trends
Regularly analyze your data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Look for correlations between user behavior and your key metrics.
Example: If you notice a drop in DAU, investigate potential causes, such as a recent product update or a change in user experience.
8.6. Experiment and Iterate
Use your insights to experiment with different product features, marketing strategies, and user experiences. Iterate based on the results of your experiments.
A/B Testing: Conduct A/B tests to compare different versions of a feature and determine which performs best.
8.7. Communicate and Align Teams
Share your insights and findings with your team to ensure everyone is aligned on the product’s goals and progress. Use metrics to drive decision-making and prioritize tasks.
Regular Reporting: Create regular reports that track your key metrics and highlight progress towards your objectives.
8.8. Continuously Monitor and Refine
Product metrics are not static. Continuously monitor your metrics and refine your strategy as your product evolves and your user base grows.
Stay Updated: Keep up with industry trends and best practices in product analytics.
9. The Importance of Qualitative Insights
While quantitative metrics provide valuable data, it’s essential to complement them with qualitative insights. Understanding the “why” behind user behavior can provide a deeper understanding of your product’s strengths and weaknesses.
9.1. User Feedback
Collect user feedback through surveys, interviews, and usability testing. Ask users about their experiences, pain points, and suggestions for improvement.
Example Questions:
- What do you like most about our product?
- What could we do to improve your experience?
- What problems are you trying to solve with our product?
9.2. Customer Support Interactions
Analyze customer support interactions to identify common issues and areas where users are struggling. This can provide valuable insights into usability problems and unmet needs.
Sentiment Analysis: Use sentiment analysis tools to gauge the overall sentiment of customer support interactions and identify potential pain points.
9.3. Usability Testing
Conduct usability testing to observe how users interact with your product in a controlled environment. This can help you identify usability issues and areas where users are getting confused or frustrated.
Think-Aloud Protocol: Ask users to verbalize their thoughts and actions as they use your product.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Product Metrics
Q1: What are product metrics?
Product metrics are quantifiable measurements used to track and assess the success of a product, its features, and its impact on user behavior.
Q2: Why are product metrics important?
Product metrics provide insights into user engagement, retention, and overall product performance, enabling data-driven decisions and continuous improvement.
Q3: What is a north star metric?
A north star metric is a single, key metric that aligns the entire team and reflects the core value that the product delivers to its users.
Q4: How do I choose the right product metrics?
Choose metrics that directly reflect your product’s value moments, align with your objectives, and provide actionable insights.
Q5: What are some common mistakes in defining value metrics?
Common mistakes include relying too much on intuition or data, not aligning metrics with business goals, and focusing on vanity metrics.
Q6: How can I measure intangible product value?
Even intangible values can be measured by quantifying related behaviors, such as completion rates for meditation sessions or time spent watching videos.
Q7: What is a value moment?
A value moment is an event or action where a user experiences the core value of your product.
Q8: How often should I analyze product metrics?
Regular analysis is essential. The frequency depends on your product and business, but aim for at least monthly reviews.
Q9: What tools can I use to track product metrics?
Tools like Mixpanel, Amplitude, and Google Analytics are popular choices for tracking user behavior and measuring product metrics.
Q10: How can I use product metrics to improve user experience?
Use product metrics to identify areas where users are struggling, experiment with different solutions, and iterate based on the results.
Conclusion: Driving Product Success with Metrics
Understanding and implementing product metrics is essential for driving product success. By focusing on value moments, selecting relevant metrics, and continuously analyzing data, you can create a product that meets user needs and achieves your business goals. CONDUCT.EDU.VN is committed to providing you with the knowledge and tools you need to succeed.
For more detailed information and guidance on product metrics and ethical conduct, visit conduct.edu.vn or contact us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States. You can also reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 555-1234. Let us help you build products that deliver value and make a positive impact.