Sustainable eating is more than just a trend; it’s a commitment to a healthier planet and a healthier you. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we believe that understanding and adopting sustainable eating practices can significantly reduce your environmental footprint while enhancing your well-being. Discover how mindful food choices can transform your life with earth-friendly diets and responsible consumption habits.
1. Understanding Sustainable Eating
Sustainable eating encompasses making informed food choices that minimize environmental harm and maximize nutritional benefits. It’s about considering the entire lifecycle of food, from farm to table, and selecting options that support ecological balance and human health.
1.1. Defining Sustainable Eating
Sustainable eating involves choosing foods based on their impact on the environment, including factors like water usage, pesticide use, land clearing, greenhouse gas emissions, and fossil fuel consumption. People who practice sustainable eating aim to select foods produced through farming practices that are least harmful and most beneficial to the environment. This approach not only benefits the planet but is also widely recognized as more nutritious than conventional diets.
1.2. The Core Principles of a Sustainable Diet
A sustainable diet emphasizes vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and fruits, while minimizing processed foods, sugars, and refined grains. Meat and fish can be included, provided they are sourced from environmentally conscious producers. However, red meat, particularly beef, and dairy products are generally considered unsustainable due to their significant contribution to methane emissions and deforestation.
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines sustainable diets as “those diets with low environmental impacts which contribute to food and nutrition security and to healthy life for present and future generations.” This definition underscores the need to balance nutritional needs with environmental stewardship.
1.3. Benefits Beyond the Environment
Choosing to eat sustainably offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Lowering your carbon footprint and conserving natural resources.
- Improved Health: Consuming nutrient-rich foods that reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Cost Savings: Reducing reliance on expensive meats and processed foods in favor of more affordable plant-based options.
2. The Environmental Impact of Food Production
Modern agriculture has a significant impact on the environment, contributing to climate change, deforestation, and resource depletion. Understanding these impacts is crucial for making informed and sustainable food choices.
2.1. Agriculture’s Role in Climate Change
Agriculture is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for a significant portion of global methane emissions. This largely comes from livestock raising and rice cultivation. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, and its release accelerates global warming.
2.2. Deforestation and Land Use
The expansion of agricultural land, particularly for cattle ranching and soybean cultivation, is a primary driver of deforestation, especially in regions like the Amazon basin. Deforestation not only destroys habitats but also releases stored carbon into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change.
2.3. Water Usage and Pesticide Use
Conventional farming practices often rely heavily on irrigation and synthetic pesticides, which can deplete water resources and harm ecosystems. For example, almond farming in California is a major consumer of water, and the use of pesticides threatens bee populations, which are crucial for pollination.
3. Sustainable Food Practices: A Comprehensive Guide
Adopting sustainable food practices involves making conscious decisions about how food is produced, distributed, and consumed. These practices can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of your diet and support a more sustainable food system.
3.1. Sustainable Agriculture Techniques
Sustainable agriculture aims to minimize environmental harm while maintaining or improving crop yields. Key practices include:
- Reducing Reliance on Chemical Fertilizers: Using organic methods such as manure and compost to enrich the soil.
- Planting Cover Crops: Utilizing cover crops to prevent erosion, suppress weeds, and improve soil health.
- Implementing Agroforestry: Integrating trees into agricultural systems to provide shade, improve biodiversity, and sequester carbon.
- Sustainable Fishing: Employing methods that prevent overfishing and minimize bycatch.
- Grass-Fed Livestock: Raising cattle on grass to reduce the environmental impact of grain-fed systems and improve meat quality.
3.2. Making Sustainable Choices at the Grocery Store
Consumers can support sustainable agriculture by making informed choices when shopping for food. Tips for sustainable grocery shopping include:
- Prioritizing Plant-Based Foods: Choosing vegetables, fruits, and legumes over meat and processed foods.
- Bringing Reusable Bags: Reducing plastic waste by using reusable shopping bags.
- Buying in Bulk: Purchasing grains, legumes, and nuts in bulk to minimize packaging waste and save money.
- Reading Labels: Looking for certifications that indicate sustainable harvesting and production practices.
- Avoiding Overbuying: Planning meals and buying only what you need to prevent food waste.
3.3 Understanding Certifications
Navigating the world of sustainable food certifications can be complex, but understanding the most common labels can help you make informed choices. Here’s a brief overview:
-
USDA Organic: This certification ensures that food is produced without synthetic pesticides, herbicides, or fertilizers. It also prohibits the use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). While organic farming can be more sustainable, it’s essential to remember that organic doesn’t always equal sustainable, especially regarding transportation and packaging.
-
Fair Trade Certified: This label indicates that the product was produced following fair labor practices and that farmers and workers received fair prices and wages. Fair Trade certification is particularly relevant for products like coffee, chocolate, and bananas, often grown in developing countries.
-
Marine Stewardship Council (MSC): The MSC certification ensures that seafood comes from fisheries that meet strict sustainability standards. These standards include maintaining healthy fish populations, minimizing environmental impact, and effective fisheries management.
-
Rainforest Alliance Certified: This certification covers a range of agricultural products, including coffee, cocoa, and tea. It ensures that the products are grown using sustainable farming practices that protect forests, conserve biodiversity, and promote the rights and well-being of workers and communities.
-
Certified Humane: This label guarantees that animals are raised with humane treatment standards, including access to adequate space, shelter, and veterinary care. It’s particularly relevant for meat, poultry, and dairy products.
3.4 Avoiding Greenwashing
“Greenwashing” is when companies falsely promote their products or practices as environmentally friendly. Here are some tips to avoid falling for greenwashing tactics:
- Be Skeptical of Vague Claims: Look for specific and verifiable information rather than broad, unsubstantiated claims like “eco-friendly” or “natural.”
- Check for Third-Party Certifications: Look for certifications from reputable organizations that independently verify sustainability claims.
- Research the Company: Investigate the company’s overall environmental and social performance, not just the specific product you’re considering.
- Read the Fine Print: Pay attention to the details of the product’s packaging and ingredients to ensure that the claims are accurate and meaningful.
4. Adopting Sustainable Eating Habits
Sustainable eating habits extend beyond grocery shopping to encompass how food is stored, prepared, and consumed. These habits can reduce food waste, promote healthier eating, and support a more sustainable lifestyle.
4.1. Embracing a Plant-Based Diet
A plant-based diet, rich in vegetables, fruits, legumes, and nuts, is generally more sustainable than a diet heavy in animal protein or processed sugars. While not everyone needs to become vegan or vegetarian, reducing meat consumption and increasing plant-based foods can significantly lower your environmental impact.
4.2. Buying Local and Seasonal Foods
Purchasing local and seasonal foods can reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation and support local farmers. While the impact of food transportation on overall emissions is relatively small, buying locally can have other benefits, such as supporting local economies and promoting food security.
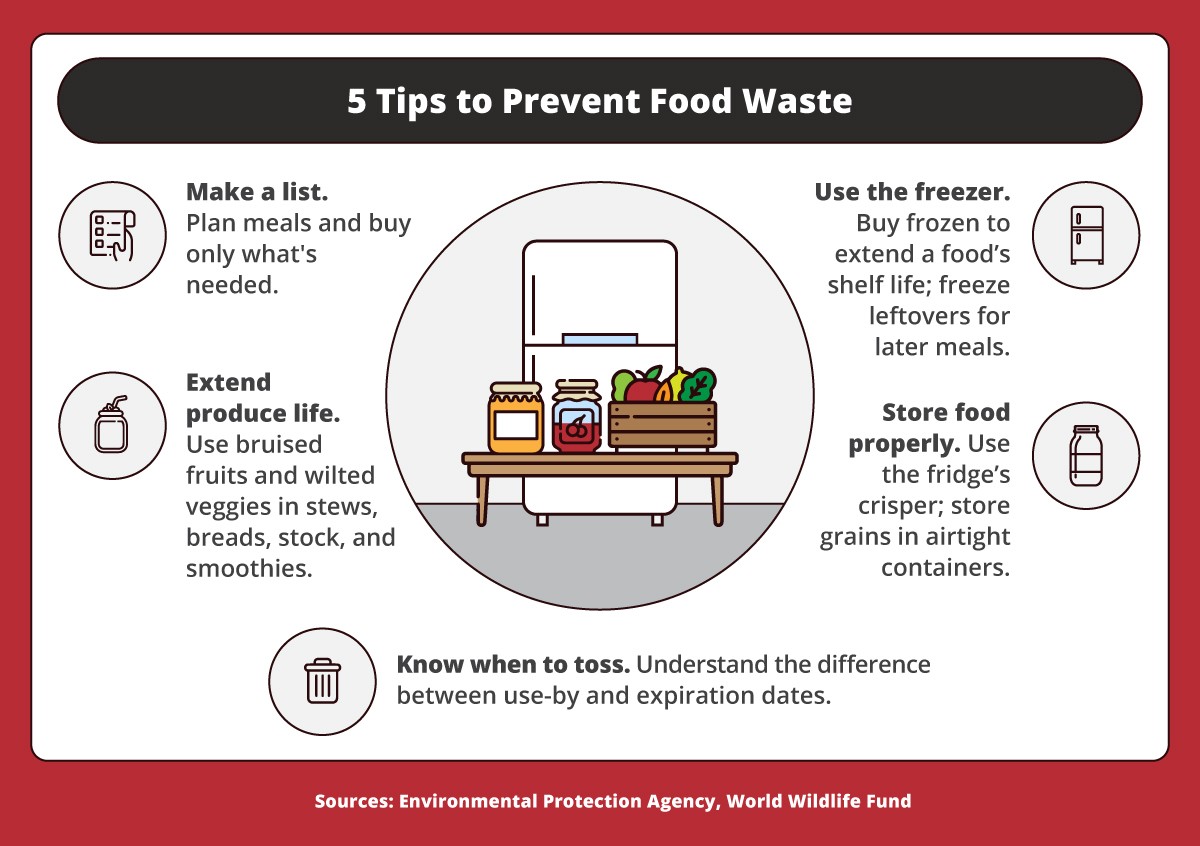
4.3. Minimizing Food Waste
Reducing food waste is a crucial aspect of sustainable eating. The FDA estimates that 30-40% of all food produced in the U.S. is wasted. Strategies for reducing food waste include:
- Planning Meals: Creating a meal plan before grocery shopping to avoid impulse purchases.
- Using Leftovers: Incorporating leftovers into future meals.
- Freezing Food: Preserving food by freezing it before it spoils.
- Composting: Composting food scraps to reduce landfill waste and create nutrient-rich soil.
- Understanding “Use By” and “Sell By” Dates: Knowing the difference between these dates to avoid throwing out perfectly good food.
4.4 Composting at Home
Composting is a great way to reduce food waste and create nutrient-rich soil for your garden. Here’s a simple guide to composting at home:
-
Choose a Compost Bin: You can buy a compost bin or build your own. Ensure it has good ventilation and drainage.
-
Layer Green and Brown Materials: Alternate layers of “green” materials (e.g., food scraps, coffee grounds, grass clippings) and “brown” materials (e.g., dried leaves, shredded paper, cardboard).
-
Maintain Moisture: Keep the compost pile moist but not waterlogged. Aim for the consistency of a wrung-out sponge.
-
Turn the Compost Regularly: Turn the compost pile every few weeks to aerate it and speed up decomposition.
-
Be Patient: Composting can take several months to a year, depending on the climate and materials.
4.5 Sustainable Packaging Choices
Packaging plays a significant role in the sustainability of food products. Choosing sustainable packaging options can help reduce waste and minimize environmental impact.
-
Opt for Minimal Packaging: Choose products with minimal packaging to reduce waste.
-
Select Recyclable Materials: Look for packaging made from recyclable materials like paper, cardboard, and certain plastics.
-
Choose Compostable Packaging: Some packaging is made from compostable materials, such as plant-based plastics, which can be composted at home or in commercial facilities.
-
Avoid Single-Use Plastics: Minimize your use of single-use plastics, such as plastic bags, straws, and utensils.
5. Practical Steps to Eating Sustainably
Transitioning to a sustainable diet can be a gradual process. Starting with small changes and gradually incorporating more sustainable practices can make the transition manageable and enjoyable.
5.1. Start Small and Be Patient
Begin by making one or two small changes at a time. For example, commit to one meatless dinner a week or start buying local produce at a farmers market. As you become more comfortable with these changes, you can gradually incorporate more sustainable practices into your diet.
5.2. Replace Red Meat with Alternatives
Reducing red meat consumption is one of the most impactful changes you can make. Replace hamburgers with veggie burgers or try incorporating more beans, lentils, and tofu into your meals.
5.3. Choose Sustainable Seafood
Opt for seafood that is sustainably harvested. Look for certifications like the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) label. Consider alternatives like mussels, scallops, and clams, which are more environmentally sustainable than many farmed fish.
5.4. Explore New Foods and Recipes
Sustainable eating can be an opportunity to try new foods and recipes. Explore different cuisines and experiment with plant-based dishes. Spices and sauces can add flavor and variety to your meals.
6. Meal Planning and Preparation
Effective meal planning and preparation are essential for sustainable eating. These practices can save you money, reduce food waste, and ensure you have healthy, sustainable meals readily available.
6.1. The Benefits of Meal Planning
Meal planning involves creating a detailed plan of your meals for the week. This can help you:
- Save Money: By reducing impulse purchases and preventing food waste.
- Eat Healthier: By ensuring you have a balanced and varied diet.
- Reduce Stress: By eliminating the last-minute scramble to figure out what to eat.
6.2. Tips for Effective Meal Planning
- Start with a List: Create a list of meals you want to eat during the week.
- Check Your Pantry: Take inventory of what you already have to avoid buying duplicates.
- Plan for Leftovers: Incorporate leftovers into future meals to reduce waste.
- Shop with a List: Stick to your shopping list to avoid impulse purchases.
6.3. Advance Meal Preparation
Advance meal preparation involves preparing meals or meal components ahead of time. This can be a great way to save time during the week and ensure you have healthy, sustainable options available.
6.4. Time-Saving Cooking Techniques
- Slow Cookers and Multi-Cookers: These appliances can cook meals while you’re at work or asleep.
- Batch Cooking: Cook large batches of meals and freeze them for later use.
- Pre-Cut Vegetables: Save time by buying pre-cut vegetables or prepping them in advance.
6.5 Utilizing Technology
Several apps and online tools can help you plan sustainable meals and reduce food waste. Here are a few popular options:
-
Meal Planning Apps: Apps like Mealime and Plan to Eat can help you create meal plans based on your dietary preferences and reduce food waste by suggesting recipes that use ingredients you already have.
-
Food Waste Tracking Apps: Apps like Olio and Too Good To Go connect you with local businesses and neighbors who have surplus food to share, helping you rescue edible food that would otherwise go to waste.
-
Recipe Apps: Apps like Epicurious and Allrecipes offer a vast library of recipes, including many plant-based and sustainable options.
7. Navigating the Organic vs. Non-Organic Debate
The choice between organic and non-organic foods can be confusing. While organic foods are often considered more sustainable, it’s essential to understand the nuances and consider other factors, such as the environmental impact of transportation and packaging.
7.1. Understanding Organic Farming
Organic farming practices aim to minimize environmental impact by avoiding synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. Organic farming can also promote biodiversity and improve soil health.
7.2. The Limitations of Organic
While organic farming has many benefits, it’s not always the most sustainable option. For example, organic beef and dairy can still produce significant methane emissions. Additionally, the transportation of organic foods can offset some of the environmental benefits.
7.3. Making Informed Choices
When choosing between organic and non-organic foods, consider the following:
-
Prioritize Local: Buying local produce can reduce the environmental impact of transportation, regardless of whether it’s organic or not.
-
Focus on Key Foods: Prioritize buying organic for foods that are heavily sprayed with pesticides, such as apples, strawberries, and spinach.
-
Consider the Environmental Impact: Research the environmental impact of different farming practices to make informed choices.
7.4 The Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
Technology plays an increasingly important role in promoting sustainable agriculture practices. Precision farming, for example, uses sensors, GPS, and data analytics to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, reducing resource waste and environmental impact. Vertical farming, another emerging technology, allows for growing crops indoors in stacked layers, minimizing land and water use.
8. Sustainable Food Examples and Best Practices
Certain foods and practices are particularly sustainable, offering significant environmental and nutritional benefits.
8.1. Grass-Fed Beef and Lamb
When consumed in moderation, grass-fed beef and lamb can be part of a sustainable diet. Grass-fed livestock can help maintain healthy pastureland and reduce the environmental impact of grain-fed systems.
8.2. Mussels and Other Bivalves
Mussels, clams, oysters, and scallops are highly sustainable seafood options. These filter feeders can improve water quality and create habitats for other marine life.
8.3. Local Fruits and Vegetables
Local fruits and vegetables support local farmers and reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation. Eating seasonally can also lead to a more varied and nutritious diet.
8.4. Seaweed
Seaweed is a highly nutritious and sustainable food source. It can be used as a fertilizer, animal feed, and a replacement for plastics. Seaweed cultivation can also help prevent ocean acidification and reduce agricultural runoff.
8.5 Edible Insects
Insects are a nutritious and sustainable food source that is commonly consumed in many parts of the world. They are high in protein, vitamins, and minerals, and they require significantly less land, water, and feed than traditional livestock. While eating insects may not be common in Western cultures, they offer a promising solution for sustainable food production.
9. The Importance of Thoughtful Eating
Sustainable eating is about more than just choosing the right foods; it’s about adopting a mindful approach to food consumption.
9.1. Considering the Entire Food System
Think about the entire journey of your food, from where it was grown to how it arrived at your table. Support local farmers, reduce food waste, and choose sustainable packaging options.
9.2. Making Tradeoffs
Recognize that not every food choice will be perfectly sustainable. A “flexitarian” diet, which emphasizes plant-based foods but includes some meat, can be a sustainable and practical option for many people.
9.3. Embracing Continuous Improvement
Sustainable eating is an ongoing journey, not a destination. Continue to learn and adapt your practices as new information and technologies emerge.
10. Case Studies: Sustainable Eating in Action
Examining real-world examples of sustainable eating practices can provide valuable insights and inspiration.
10.1 The Rise of Urban Farming
Urban farming is the practice of growing crops in urban areas, such as rooftops, balconies, and vacant lots. It can reduce the carbon footprint of food transportation, provide access to fresh produce in underserved communities, and promote community engagement. Cities like Detroit and New York are leading the way in urban farming initiatives.
10.2 Sustainable Restaurants
Some restaurants are adopting sustainable practices, such as sourcing ingredients from local farms, reducing food waste, and using energy-efficient equipment. These restaurants serve as models for sustainable food businesses and inspire consumers to make more sustainable choices.
10.3 Community Gardens
Community gardens provide opportunities for people to grow their own food, connect with nature, and build community. They can also improve access to fresh produce in low-income neighborhoods and promote sustainable food practices.
11. Resources for Further Learning
There are numerous resources available to help you learn more about sustainable eating.
11.1. Websites and Organizations
- CONDUCT.EDU.VN: Provides information and resources on sustainable eating and responsible conduct.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO): Offers data and publications on sustainable diets and food systems.
- The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Provides information on reducing food waste and promoting sustainable agriculture.
11.2. Books and Articles
- “Diet for a Hot Planet: The Climate Crisis at the End of Your Fork and What You Can Do About It” by Anna Lappé: Explores the connection between food and climate change.
- “The Third Plate: Field Notes on the Future of Food” by Dan Barber: Discusses the importance of sustainable agriculture and regional cuisine.
11.3. Courses and Workshops
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and edX offer courses on sustainable food systems and nutrition.
- Local Workshops: Check with local farms, community gardens, and environmental organizations for workshops on sustainable eating and gardening.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
12.1. What is sustainable eating?
Sustainable eating involves making food choices that minimize environmental harm and promote human health.
12.2. Why is sustainable eating important?
Sustainable eating can reduce your carbon footprint, conserve natural resources, and improve your health.
12.3. How can I start eating sustainably?
Start with small changes, such as reducing meat consumption, buying local produce, and minimizing food waste.
12.4. Is organic food always more sustainable?
Not necessarily. Consider factors like transportation and the environmental impact of different farming practices.
12.5. What are some sustainable food choices?
Sustainable food choices include grass-fed beef, mussels, local fruits and vegetables, and seaweed.
12.6. How can I reduce food waste?
Plan meals, use leftovers, freeze food, and compost food scraps to reduce waste.
12.7. What is a plant-based diet?
A plant-based diet emphasizes vegetables, fruits, legumes, and nuts while minimizing meat and processed foods.
12.8. How can I find local and seasonal foods?
Visit farmers markets, join a CSA, or check with local farms and grocery stores.
12.9. What are the benefits of meal planning?
Meal planning can save you money, reduce food waste, and help you eat healthier.
12.10. Where can I learn more about sustainable eating?
Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN and other reputable websites and organizations for more information.
13. Conclusion: Embrace Sustainable Eating for a Better World
Sustainable eating is a powerful way to protect the environment and improve your health. By making informed food choices, reducing waste, and supporting sustainable agriculture, you can contribute to a more resilient and equitable food system. Join us at CONDUCT.EDU.VN in embracing sustainable eating and creating a better world for future generations.
Navigating the complexities of ethical conduct can be challenging, but with the right resources and guidance, you can confidently uphold the highest standards. If you’re facing a difficult ethical dilemma or need clarification on specific guidelines, don’t hesitate to reach out for support. Contact us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or connect with us via WhatsApp at +1 (707) 555-1234. For more comprehensive information and additional resources, visit our website at conduct.edu.vn. Together, we can foster a culture of integrity and accountability in all aspects of life.
By embracing sustainable eating habits, we not only contribute to a healthier planet but also nourish our bodies with nutrient-rich foods. The journey towards sustainability may seem daunting at first, but with each conscious choice, we move closer to a more balanced and harmonious relationship with our environment. Let us cultivate a future where sustainable eating is not just a trend, but a way of life, ensuring the well-being of both present and future generations.