A Practical Guide To Social Networks is essential for anyone navigating the digital landscape, offering insights into platforms, engagement metrics, and audience understanding. CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive resource that helps you master social media, enhance online presence, and connect effectively with your audience, ultimately improving your social media etiquette. Learn about ethical considerations and build meaningful connections with our social media guide.
1. Understanding Social Networks: A Comprehensive Overview
Social networks have become an integral part of modern life, transforming how we communicate, share information, and conduct business. For students, professionals, and organizations alike, understanding the dynamics of social networks is crucial for effective engagement and ethical conduct. Social media presence can be daunting, but with the right guidance, it can be a powerful tool. This section delves into the fundamental aspects of social networks, providing a clear understanding of their purpose, diverse platforms, and the importance of establishing a strong, ethical online presence.
1.1 What Are Social Networks?
At its core, a social network is a digital platform that allows users to create profiles, connect with others, share content, and engage in conversations. These platforms facilitate the formation of online communities, where individuals can interact based on shared interests, professional affiliations, or personal relationships. The primary purpose of social networks is to enable communication and collaboration among users, regardless of geographical boundaries.
Social networks serve multiple functions, including:
- Communication: Facilitating real-time conversations and asynchronous messaging.
- Information Sharing: Disseminating news, updates, and educational content.
- Networking: Connecting individuals for personal and professional growth.
- Community Building: Creating spaces for like-minded people to interact and support each other.
- Marketing and Branding: Promoting products, services, and organizations to a wide audience.
1.2 Types of Social Networks
The social network landscape is vast and diverse, with platforms catering to different needs and interests. Here are some of the most popular types of social networks:
- Social Networking Sites: These platforms focus on connecting individuals with friends, family, and acquaintances. Examples include Facebook and Instagram, where users share personal updates, photos, and videos.
- Professional Networking Sites: Designed for career-oriented individuals, these platforms facilitate professional connections, job searches, and industry-related discussions. LinkedIn is the most prominent example, offering a space for professionals to showcase their skills, network with peers, and seek career opportunities.
- Microblogging Sites: These platforms allow users to share short, frequent updates with their followers. Twitter is the leading microblogging site, known for its real-time news updates and concise messaging.
- Content Sharing Sites: These platforms focus on sharing specific types of content, such as photos (Instagram, Pinterest), videos (YouTube, TikTok), or music (Spotify).
- Discussion Forums: These platforms provide spaces for users to engage in discussions on various topics. Reddit is a popular example, featuring a wide range of communities (subreddits) where users can share content, ask questions, and participate in debates.
1.3 Why Social Networks Matter
Social networks have become indispensable tools for individuals and organizations for several reasons:
- Global Reach: Social networks enable users to connect with a global audience, transcending geographical limitations.
- Enhanced Communication: They facilitate instant communication, allowing for quick exchange of information and feedback.
- Brand Building: Businesses can use social networks to build brand awareness, engage with customers, and promote their products or services.
- Networking Opportunities: Professionals can expand their networks, connect with industry leaders, and discover new career opportunities.
- Access to Information: Social networks provide access to a wealth of information, news, and educational content.
1.4 Establishing a Strong Online Presence
Creating a positive and professional online presence is essential for anyone using social networks. Here are some tips for building a strong online presence:
- Create a Professional Profile: Use a professional photo and write a compelling bio that highlights your skills, experience, and interests.
- Share Valuable Content: Post content that is informative, engaging, and relevant to your audience.
- Engage with Others: Interact with other users by liking, commenting on, and sharing their posts.
- Maintain Consistency: Regularly update your profile and share new content to stay relevant and visible.
- Be Authentic: Present yourself honestly and transparently, and avoid posting anything that could damage your reputation.
1.5 Ethical Considerations
Navigating social networks requires a strong sense of ethics and responsibility. Here are some key ethical considerations to keep in mind:
- Respect Privacy: Avoid sharing personal information about others without their consent.
- Be Truthful: Do not spread false or misleading information.
- Avoid Cyberbullying: Treat others with respect and avoid engaging in harassment or bullying.
- Disclose Conflicts of Interest: Be transparent about any affiliations or endorsements.
- Protect Intellectual Property: Respect copyright laws and give credit to original sources.
By understanding the basics of social networks and adhering to ethical guidelines, individuals and organizations can leverage these powerful tools for communication, collaboration, and growth. Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN for more detailed guidance on ethical conduct and responsible social media use.
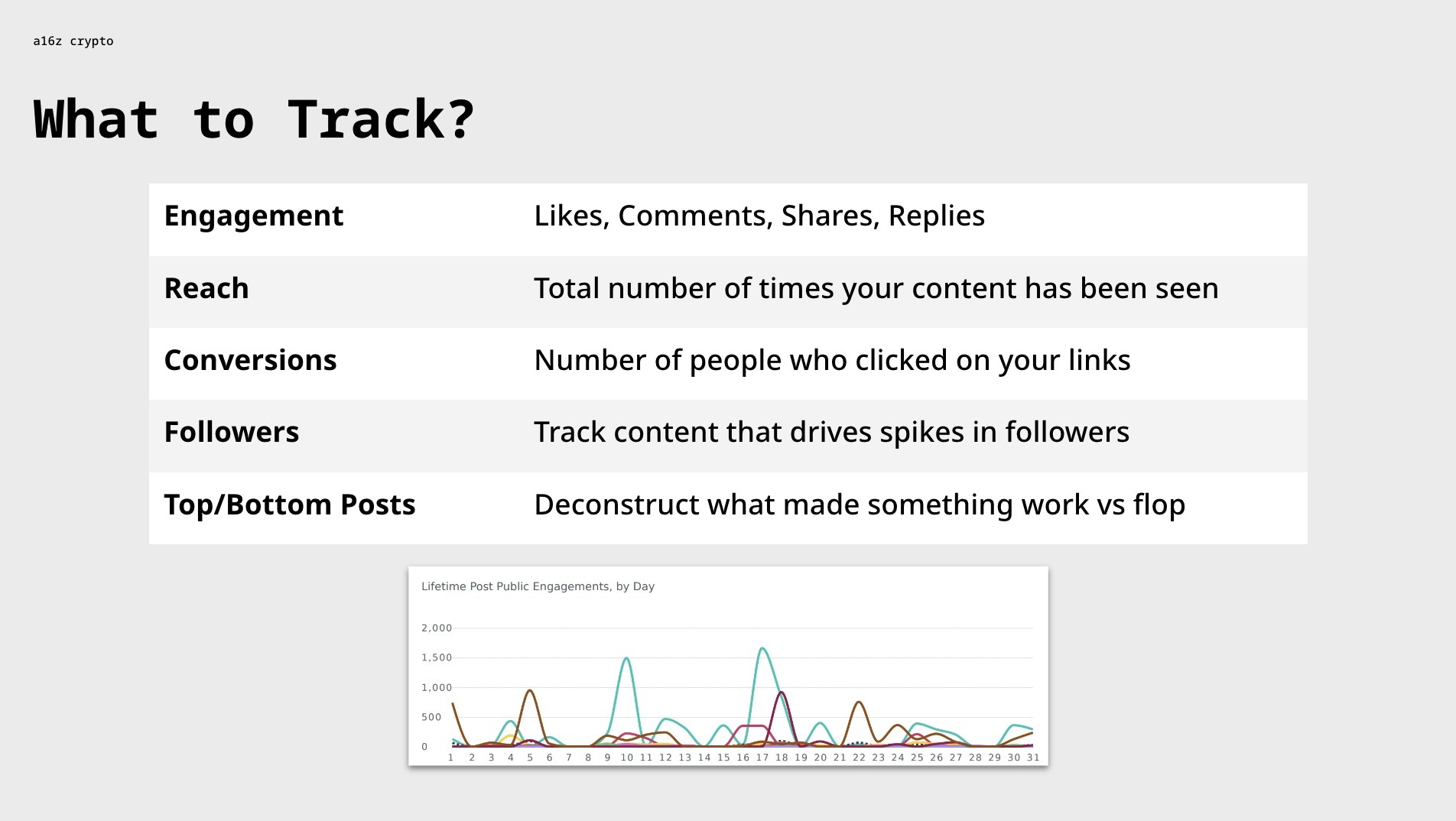
2. Quantitative Metrics: Measuring Social Network Success
Quantitative metrics are essential for evaluating the effectiveness of your social network strategies. These metrics provide measurable data that can help you understand audience growth, engagement levels, and conversion rates. By tracking these key indicators, you can refine your approach and optimize your performance. This section explores the most important quantitative metrics and how to use them to gauge your success on social networks.
2.1 Engagement Rate
Engagement rate is a crucial metric that measures the level of interaction your content receives from your audience. It reflects how actively your followers are engaging with your posts, indicating the quality and relevance of your content.
Definition: Engagement rate is typically calculated as the total number of interactions (likes, comments, shares, clicks) divided by the total number of followers or impressions, multiplied by 100 to express it as a percentage.
Formula:
Engagement Rate = (Total Interactions / Total Followers or Impressions) x 100
Importance: A high engagement rate indicates that your content resonates with your audience, fostering a strong sense of community and loyalty. It can also lead to increased visibility and reach, as engaged users are more likely to share your content with their networks.
Tips for Improving Engagement:
- Post High-Quality Content: Create content that is informative, entertaining, and visually appealing.
- Ask Questions: Encourage interaction by posing questions and inviting your audience to share their thoughts.
- Run Polls and Quizzes: Use interactive content formats to engage your audience and gather valuable feedback.
- Respond to Comments: Acknowledge and respond to comments from your followers to build relationships and show that you value their input.
- Use Relevant Hashtags: Increase the discoverability of your content by using relevant and trending hashtags.
2.2 Impressions
Impressions refer to the number of times your content is displayed to users, regardless of whether they click on it or not. This metric provides a broad measure of your content’s visibility and potential reach.
Definition: An impression is counted each time your post is displayed in a user’s feed or search results.
Importance: While impressions don’t directly indicate engagement, they are a valuable indicator of your content’s visibility. A high number of impressions suggests that your content is being seen by a large audience, increasing the chances of engagement and brand awareness.
Strategies for Increasing Impressions:
- Post Regularly: Maintain a consistent posting schedule to keep your content visible in users’ feeds.
- Optimize Posting Times: Identify the times when your audience is most active and schedule your posts accordingly.
- Use Visual Content: Incorporate eye-catching images and videos to capture users’ attention and increase the likelihood of impressions.
- Cross-Promote Your Content: Share your posts on multiple platforms to maximize their reach and visibility.
- Engage with Influencers: Collaborate with influencers to promote your content to their followers and expand your reach.
2.3 Reach
Reach refers to the number of unique users who have seen your content. Unlike impressions, which count each display of your content, reach measures the actual number of individuals who have viewed it.
Definition: Reach is the total number of unique users who have been exposed to your content.
Importance: Reach provides a more accurate measure of your content’s actual audience size compared to impressions. It helps you understand how effectively your content is reaching new users and expanding your network.
Methods for Expanding Your Reach:
- Create Shareable Content: Develop content that is valuable, interesting, and easy to share with others.
- Run Contests and Giveaways: Incentivize users to share your content by offering prizes and rewards.
- Use Paid Advertising: Invest in social media advertising to target specific demographics and expand your reach.
- Participate in Industry Discussions: Engage in relevant conversations and share your expertise to attract new followers.
- Collaborate with Other Brands: Partner with complementary brands to cross-promote your content and reach new audiences.
2.4 Conversions
Conversions measure the number of users who take a desired action as a result of interacting with your social media content. This could include clicking on a link to your website, signing up for a newsletter, making a purchase, or downloading a resource.
Definition: A conversion occurs when a user completes a specific action that aligns with your business goals.
Importance: Conversions are a critical metric for assessing the ROI (Return on Investment) of your social media efforts. They demonstrate how effectively your content is driving tangible results, such as lead generation, sales, and customer acquisition.
Techniques for Driving Conversions:
- Include Clear Calls to Action: Use compelling calls to action (CTAs) in your posts to guide users towards the desired action.
- Create Landing Pages: Direct users to dedicated landing pages that are optimized for conversions.
- Offer Incentives: Provide exclusive discounts, free trials, or bonus content to encourage conversions.
- Use Targeted Advertising: Focus your advertising efforts on users who are most likely to convert.
- Track Your Results: Monitor your conversion rates and analyze the data to identify what’s working and what’s not.
2.5 Follower Growth
Follower growth measures the rate at which your social media audience is expanding. This metric provides a direct indication of your ability to attract new followers and build a larger network.
Definition: Follower growth is the increase in the number of followers over a specific period.
Importance: A growing follower count suggests that your content is resonating with users and that your network is expanding. It can also lead to increased visibility, engagement, and opportunities for collaboration.
Strategies for Accelerating Follower Growth:
- Provide Valuable Content: Consistently share content that is informative, entertaining, and relevant to your target audience.
- Engage with Your Followers: Respond to comments, answer questions, and participate in discussions to build relationships.
- Promote Your Social Media Accounts: Include links to your social media profiles on your website, email signature, and other marketing materials.
- Run Follower Campaigns: Host contests or giveaways that require users to follow your account to enter.
- Collaborate with Influencers: Partner with influencers to promote your account to their followers.
By tracking these key quantitative metrics and implementing strategies to improve your performance, you can effectively measure your success on social networks and achieve your business goals. For more detailed guidance and resources, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
3. Qualitative Data: Understanding Sentiment and Context
While quantitative metrics provide measurable data, qualitative data offers valuable insights into the sentiment and context behind social media interactions. Qualitative data helps you understand how people feel about your brand, the reasons behind their engagement, and the nuances of their opinions. This section explores the importance of qualitative data and how to use it to gain a deeper understanding of your audience.
3.1 What is Qualitative Data?
Qualitative data refers to non-numerical information that describes the characteristics, qualities, or opinions of a subject. In the context of social networks, qualitative data includes:
- Comments: Feedback, opinions, and discussions shared by users in response to your content.
- Messages: Private messages and inquiries sent to your account.
- Mentions: Instances where your brand or account is mentioned by other users.
- Reviews: Ratings and reviews of your products or services.
- Sentiment: The overall emotion or attitude expressed in social media interactions.
3.2 Why Qualitative Data Matters
Qualitative data provides a deeper understanding of your audience and their perceptions of your brand. It helps you:
- Gauge Sentiment: Determine whether users have positive, negative, or neutral feelings towards your brand.
- Identify Trends: Uncover recurring themes and patterns in user feedback.
- Understand Customer Needs: Gain insights into the needs, preferences, and pain points of your customers.
- Improve Customer Service: Address customer concerns and provide personalized support.
- Refine Your Content Strategy: Tailor your content to better resonate with your audience.
3.3 Methods for Collecting Qualitative Data
There are several methods for collecting qualitative data from social networks:
- Manual Monitoring: Manually review comments, messages, and mentions to identify key themes and sentiment.
- Social Listening Tools: Use specialized tools to track mentions of your brand and analyze the sentiment behind them.
- Surveys and Polls: Conduct surveys and polls to gather direct feedback from your audience.
- Focus Groups: Organize virtual or in-person focus groups to discuss specific topics and gather in-depth insights.
- Interviews: Conduct one-on-one interviews with customers to understand their experiences and perspectives.
3.4 Analyzing Qualitative Data
Analyzing qualitative data involves identifying patterns, themes, and sentiment within the collected information. Here are some techniques for analyzing qualitative data:
- Sentiment Analysis: Use sentiment analysis tools to automatically classify the sentiment expressed in social media interactions.
- Content Analysis: Systematically analyze the content of comments, messages, and mentions to identify key themes and topics.
- Thematic Analysis: Identify recurring themes and patterns within the data and group them into meaningful categories.
- Text Mining: Use text mining techniques to extract valuable insights from large volumes of text data.
3.5 Turning Qualitative Data into Actionable Insights
Once you have analyzed your qualitative data, you can use the insights to improve your social media strategy and overall business performance. Here are some ways to turn qualitative data into actionable insights:
- Address Customer Concerns: Respond to negative feedback and address customer concerns promptly and effectively.
- Improve Your Products and Services: Use customer feedback to identify areas for improvement in your products and services.
- Tailor Your Content: Create content that addresses the needs and interests of your audience.
- Enhance Customer Service: Provide personalized support and build stronger relationships with your customers.
- Monitor Your Brand Reputation: Track mentions of your brand and respond to negative comments to protect your reputation.
By understanding and leveraging qualitative data, you can gain a deeper understanding of your audience, improve your social media strategy, and build stronger relationships with your customers. For more guidance and resources, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
4. Integrating Qualitative and Quantitative Data for a Holistic View
To gain a comprehensive understanding of your social network performance, it’s essential to integrate both qualitative and quantitative data. While quantitative metrics provide numerical insights into audience growth and engagement, qualitative data offers context and sentiment, revealing the “why” behind the numbers. This section explores how to combine these two types of data to create a holistic view of your social media presence.
4.1 The Synergistic Relationship
Qualitative and quantitative data are complementary, each providing unique insights that enhance the other. By integrating these data types, you can:
- Validate Quantitative Findings: Use qualitative data to confirm or challenge the trends and patterns identified through quantitative analysis.
- Provide Context to Numbers: Add depth and meaning to quantitative metrics by understanding the sentiment and opinions behind them.
- Identify Hidden Opportunities: Uncover insights that might be missed by relying solely on one type of data.
- Improve Decision-Making: Make more informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of your audience and their perceptions.
4.2 Practical Examples of Integration
Here are some practical examples of how to integrate qualitative and quantitative data:
- Analyzing Engagement Spikes: If you notice a sudden spike in engagement (quantitative), analyze the comments and messages (qualitative) to understand the reason behind it. Was it due to a viral post, a successful campaign, or a controversial issue?
- Investigating Low Conversion Rates: If you have low conversion rates (quantitative), analyze customer feedback (qualitative) to identify potential roadblocks. Are customers confused by the checkout process, dissatisfied with the product, or hesitant due to pricing concerns?
- Understanding Follower Growth: If you experience a surge in followers (quantitative), analyze the comments and mentions (qualitative) to determine what content or campaigns are attracting new followers.
- Assessing Brand Sentiment: Track brand mentions and sentiment (qualitative) alongside metrics like reach and impressions (quantitative) to understand how your brand is perceived by the public.
4.3 Tools for Integrating Data
Several tools can help you integrate qualitative and quantitative data:
- Social Media Analytics Platforms: Platforms like Sprout Social and HubSpot offer integrated analytics dashboards that combine quantitative metrics with qualitative sentiment analysis.
- Data Visualization Tools: Tools like Tableau and Power BI can help you visualize both types of data in a single dashboard, making it easier to identify trends and patterns.
- Spreadsheet Software: Use spreadsheet software like Excel or Google Sheets to combine data from different sources and perform custom analyses.
4.4 Steps for Effective Integration
Follow these steps to effectively integrate qualitative and quantitative data:
- Define Your Goals: Clearly define your objectives and the questions you want to answer through data analysis.
- Collect Relevant Data: Gather both qualitative and quantitative data from various sources, such as social media platforms, surveys, and customer feedback forms.
- Clean and Organize Data: Ensure that your data is accurate, consistent, and properly organized.
- Analyze Data: Use appropriate analytical techniques to identify trends, patterns, and insights within the data.
- Visualize Data: Create visual representations of your data, such as charts and graphs, to make it easier to understand and communicate.
- Interpret Findings: Interpret the findings in the context of your business goals and identify actionable insights.
- Implement Changes: Implement changes based on your findings and monitor the results to ensure that your efforts are effective.
By integrating qualitative and quantitative data, you can gain a more complete and nuanced understanding of your social network performance, leading to more effective strategies and better business outcomes. Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN for more information on data-driven decision-making and ethical social media practices.
5. Addressing the Challenge of Silent Supporters
One of the significant challenges in accurately gauging social media sentiment is the presence of “silent supporters” – individuals who consume your content without actively engaging through likes, comments, or shares. This section explores the reasons behind silent support and strategies for encouraging greater interaction.
5.1 Understanding Silent Supporters
Silent supporters are users who appreciate your content but do not publicly express their support. This behavior can be attributed to several factors:
- Privacy Concerns: Some users may prefer to avoid public reactions on platforms like LinkedIn to maintain a professional image or avoid potential scrutiny.
- Time Constraints: Busy individuals may consume content passively without taking the time to engage.
- Platform Preferences: Some users may prefer to engage with content in other ways, such as sharing it privately or discussing it offline.
- Fear of Judgment: Some users may be hesitant to express their opinions publicly due to fear of criticism or disagreement.
5.2 Strategies to Encourage Interaction
Despite the challenges posed by silent supporters, there are several strategies you can employ to encourage greater interaction:
- Start Conversations: Engage with your audience by asking questions, soliciting feedback, and encouraging discussions. This can make users feel more comfortable sharing their thoughts and opinions.
- Host Events: Organize virtual or in-person events to deepen relationships with your audience. Attending an event can make followers more publicly supportive.
- Focus on Community Management: Engage in proactive community management by interacting with individual followers, responding to their comments, and addressing their concerns.
- Test Different Content Formats: Experiment with different content formats, such as videos, photos, short-form posts, and long-form articles, to see what resonates best with your audience.
- Incorporate Interactive Elements: Use interactive elements like polls, quizzes, and Q&A sessions to encourage participation and gather feedback.
5.3 Measuring Impact Beyond Engagement
It’s essential to recognize that social media success extends beyond traditional engagement metrics like likes and comments. Other indicators of impact include:
- Leads Generated: The number of potential customers who have expressed interest in your products or services through social media.
- Email Subscribers: The number of users who have signed up for your email list as a result of your social media efforts.
- Brand Sentiment: The overall perception of your brand on social media, even among silent supporters.
- 1-on-1 Relationship Building: The quality of individual relationships you have built with followers through personalized interactions.
- Product Feedback Loops: The extent to which you are receiving valuable feedback from users to improve your products or services.
5.4 Adapting to Evolving Social Media Trends
As social media continues to evolve, it’s crucial to adapt your strategies to stay relevant and engage your audience effectively. This includes:
- Staying Informed: Keep up with the latest trends and best practices in social media marketing.
- Experimenting with New Platforms: Explore emerging social media platforms and channels to reach new audiences.
- Personalizing Your Approach: Tailor your content and messaging to resonate with individual users.
- Prioritizing Authenticity: Focus on building genuine relationships with your audience based on trust and transparency.
By understanding the challenges posed by silent supporters and implementing strategies to encourage greater interaction, you can more accurately measure the impact of your social media efforts and achieve your business goals. For more insights and guidance, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
6. Best Practices for Ethical Social Networking
Ethical social networking is crucial for maintaining trust, protecting privacy, and fostering positive online interactions. This section outlines best practices for individuals and organizations to ensure responsible and ethical conduct on social networks.
6.1 Respecting Privacy
- Obtain Consent: Always obtain consent before sharing personal information or photos of others.
- Protect Sensitive Data: Avoid sharing sensitive personal or financial information on social media.
- Adjust Privacy Settings: Review and adjust your privacy settings to control who can see your posts and personal information.
- Respect Boundaries: Be mindful of others’ boundaries and avoid oversharing or invading their privacy.
6.2 Being Truthful and Accurate
- Verify Information: Before sharing news or information, verify its accuracy from reliable sources.
- Avoid Spreading Misinformation: Do not spread false or misleading information, even if it aligns with your beliefs.
- Correct Errors: If you make a mistake or share inaccurate information, correct it promptly and transparently.
- Be Transparent: Disclose any affiliations or conflicts of interest when sharing information.
6.3 Avoiding Cyberbullying and Harassment
- Treat Others with Respect: Treat all users with respect and avoid engaging in personal attacks, insults, or threats.
- Report Abuse: Report any instances of cyberbullying or harassment to the platform administrators.
- Do Not Participate: Refrain from participating in or encouraging online harassment or bullying.
- Promote Positivity: Foster a positive and inclusive online environment by promoting kindness and respect.
6.4 Protecting Intellectual Property
- Respect Copyright Laws: Obtain permission before using copyrighted material, such as images, videos, or music.
- Give Credit: Properly attribute sources and give credit to original creators when sharing content.
- Avoid Plagiarism: Do not plagiarize content from other sources and present it as your own.
- Use Fair Use Guidelines: Understand and adhere to fair use guidelines when using copyrighted material for educational or informational purposes.
6.5 Disclosing Conflicts of Interest
- Be Transparent: Disclose any affiliations or sponsorships when promoting products, services, or brands.
- Avoid Deception: Do not deceive or mislead your audience about your relationship with a brand or product.
- Maintain Objectivity: Strive to maintain objectivity and provide unbiased opinions, even when you have a financial interest.
- Follow FTC Guidelines: Adhere to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) guidelines for endorsements and testimonials.
6.6 Maintaining Professionalism
- Be Mindful of Your Online Presence: Remember that your social media posts can reflect on your professional reputation.
- Avoid Controversial Topics: Exercise caution when discussing controversial or sensitive topics that could alienate or offend others.
- Use Appropriate Language: Use professional and respectful language in your posts and interactions.
- Represent Your Organization Well: If you are representing an organization, ensure that your social media conduct aligns with its values and policies.
By adhering to these best practices, individuals and organizations can ensure ethical and responsible conduct on social networks, fostering trust, protecting privacy, and promoting positive online interactions. Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN for more comprehensive guidance on ethical conduct and responsible social media use. Our address is 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States. You can reach us on Whatsapp at +1 (707) 555-1234.
7. Building a Social Media Policy for Your Organization
A well-defined social media policy is essential for organizations to guide employee behavior, protect the brand reputation, and ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards. This section provides a step-by-step guide to creating an effective social media policy for your organization.
7.1 Key Components of a Social Media Policy
An effective social media policy should include the following key components:
- Purpose and Scope: Clearly define the purpose of the policy and its scope, including who it applies to (e.g., employees, contractors, volunteers) and what platforms it covers.
- Code of Conduct: Establish a code of conduct that outlines the expected behavior of employees on social media, including guidelines for respecting privacy, being truthful, and avoiding harassment.
- Brand Guidelines: Provide guidelines for representing the brand on social media, including the use of logos, trademarks, and messaging.
- Confidentiality and Disclosure: Address issues related to confidentiality and disclosure of sensitive information, including trade secrets, customer data, and financial information.
- Legal Compliance: Ensure that the policy complies with all relevant laws and regulations, including copyright laws, privacy laws, and advertising regulations.
- Monitoring and Enforcement: Outline the procedures for monitoring employee social media activity and enforcing the policy, including disciplinary actions for violations.
- Training and Education: Provide training and education to employees on the social media policy and best practices for responsible online behavior.
7.2 Steps to Create a Social Media Policy
Follow these steps to create an effective social media policy for your organization:
- Form a Team: Assemble a team of representatives from different departments, such as legal, HR, marketing, and IT, to collaborate on the policy.
- Research and Benchmarking: Research industry best practices and benchmark your policy against those of other organizations.
- Draft the Policy: Draft the policy based on your research and the key components outlined above.
- Review and Revise: Review the draft policy with stakeholders and revise it based on their feedback.
- Legal Review: Have the policy reviewed by legal counsel to ensure compliance with all relevant laws and regulations.
- Communicate the Policy: Communicate the policy to all employees and provide training on its content and enforcement.
- Enforce the Policy: Enforce the policy consistently and fairly, and take disciplinary action for violations.
- Review and Update Regularly: Review and update the policy regularly to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
7.3 Example Guidelines
Here are some example guidelines that you can include in your social media policy:
- “Employees must respect the privacy of customers, colleagues, and partners.”
- “Employees must be truthful and accurate when sharing information on social media.”
- “Employees must avoid engaging in cyberbullying or harassment.”
- “Employees must protect the organization’s intellectual property and confidential information.”
- “Employees must disclose any affiliations or conflicts of interest when promoting products or services.”
7.4 Implementing and Enforcing the Policy
Implementing and enforcing the social media policy requires a proactive approach:
- Training: Provide comprehensive training to all employees on the policy and its implications.
- Monitoring: Monitor social media activity to ensure compliance with the policy.
- Enforcement: Enforce the policy consistently and fairly, taking disciplinary action when necessary.
- Feedback: Solicit feedback from employees on the policy and make adjustments as needed.
By creating and implementing a comprehensive social media policy, your organization can protect its reputation, ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards, and foster responsible online behavior among employees. For more detailed guidance and resources, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
8. Case Studies: Social Networking Success Stories
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into how organizations have successfully leveraged social networks to achieve their goals. This section presents several case studies highlighting different strategies and outcomes.
8.1 Case Study 1: Dove’s Real Beauty Campaign
Overview: Dove’s “Real Beauty” campaign is a classic example of using social media to promote a positive and inclusive message. The campaign aimed to challenge conventional beauty standards and celebrate the diversity of women’s appearances.
Strategy: Dove used social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube to share videos, images, and stories featuring real women of all shapes, sizes, and ethnicities. They also encouraged users to share their own stories and participate in discussions about beauty and self-esteem.
Results: The “Real Beauty” campaign was a huge success, generating millions of views, shares, and comments on social media. It helped Dove build a strong brand reputation as a champion of diversity and body positivity, leading to increased brand loyalty and sales.
Key Takeaways:
- Authenticity: The campaign’s authenticity resonated with audiences, making it highly shareable and impactful.
- Engagement: Encouraging user participation and dialogue fostered a strong sense of community.
- Social Impact: The campaign contributed to a broader conversation about beauty standards and self-esteem.
8.2 Case Study 2: Wendy’s Twitter Roasts
Overview: Wendy’s is known for its bold and humorous presence on Twitter, particularly its “roasting” of competitors and customers. This strategy has helped Wendy’s stand out from the crowd and generate significant buzz.
Strategy: Wendy’s Twitter account engages in playful banter with other brands and customers, often using witty and sarcastic humor. This approach has garnered attention and made Wendy’s one of the most entertaining brands on social media.
Results: Wendy’s Twitter roasts have gone viral on numerous occasions, generating millions of impressions and engagements. This strategy has helped Wendy’s increase brand awareness, attract new followers, and drive traffic to its restaurants.
Key Takeaways:
- Boldness: Wendy’s willingness to take risks and use humor has helped it stand out in a crowded market.
- Engagement: Engaging with followers in a playful and entertaining way has fostered a loyal and active community.
- Virality: The humorous nature of Wendy’s tweets has made them highly shareable, leading to widespread virality.
8.3 Case Study 3: Airbnb’s Community Building
Overview: Airbnb has successfully leveraged social media to build a strong community of hosts and guests. The company uses social media platforms to connect with its users, share stories, and provide support.
Strategy: Airbnb uses social media to showcase unique properties, highlight local experiences, and celebrate its community of hosts and guests. They also provide customer support and respond to inquiries through social media channels.
Results: Airbnb has built a loyal and engaged community of users on social media. This community has helped Airbnb grow its brand, attract new customers, and improve customer satisfaction.
Key Takeaways:
- Community Focus: Airbnb’s emphasis on building a strong community has fostered brand loyalty and advocacy.
- Storytelling: Sharing stories of hosts and guests has helped Airbnb connect with its audience on an emotional level.
- Customer Support: Providing timely and helpful customer support through social media has improved customer satisfaction.
8.4 Case Study 4: Patagonia’s Environmental Activism
Overview: Patagonia is known for its commitment to environmental activism and sustainability. The company uses social media platforms to raise awareness about environmental issues and advocate for change.
Strategy: Patagonia uses social media to share information about environmental issues, promote sustainable practices, and advocate for policy changes. They also encourage their followers to take action and get involved in environmental causes.
Results: Patagonia has built a strong brand reputation as a leader in environmental activism. This has helped Patagonia attract environmentally conscious customers and build a loyal following.
Key Takeaways:
- Values-Driven: Patagonia’s commitment to its values has resonated with its target audience.
- Advocacy: Using social media to advocate for change has helped Patagonia make a positive impact on the world.
- Brand Alignment: Aligning its brand with environmental causes has helped Patagonia attract and retain customers who share its values.
These case studies demonstrate the diverse ways in which organizations can successfully leverage social networks to achieve their goals. By studying these examples, you can gain valuable insights and inspiration for your own social media strategy. For more case studies and best practices, visit conduct.edu.vn.
9. Social Media Ethics and Legal Considerations
Navigating social media requires a strong understanding of ethical principles and legal considerations. This section outlines the key ethical and legal aspects of social networking to ensure responsible and compliant online behavior.
9.1 Privacy Laws and Regulations
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): The GDPR is a European Union law that regulates the processing of personal data of EU citizens. It requires organizations to obtain consent before collecting and using personal data, and to provide users with the right to access, rectify, and erase their data.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): The CCPA is a California law that gives consumers greater control over their personal information. It requires businesses to disclose what personal information they collect, how they use it, and with whom they share it. It also gives consumers the right to opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
- Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA): COPPA is a US law that protects the privacy of children under the age of 13 online. It requires websites and online services to obtain parental consent before collecting personal information from children.
9.2 Intellectual Property Rights
- Copyright Law: Copyright law protects original works of authorship, including text, images, videos, and music. It gives the copyright holder the exclusive right to reproduce, distribute, and display the work.
- Trademark Law: Trademark law protects brand names, logos, and other symbols used to identify and distinguish goods or services. It gives the trademark holder the exclusive right to use the mark in connection with their goods or services.
- Patent Law: Patent law protects inventions and discoveries. It gives the patent holder the exclusive right to make, use, and sell the invention.
9.3 Defamation and Libel
- Defamation: Defamation is the act of making false statements that harm someone’s reputation.
- Libel: Libel is written defamation.
- Slander: Slander is spoken defamation.
To prove defamation, the plaintiff must show that the statement was false, published to a third party, and caused harm to their reputation.
9.4 Advertising Regulations
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Guidelines: The FTC has issued guidelines for online advertising to ensure that ads are truthful, not misleading, and substantiated by evidence.
- Endorsement Guidelines: The FTC also has specific guidelines for endorsements and testimonials, requiring endorsers to disclose any material connections with the brand or product being promoted.
9.5 Ethical Considerations
- Transparency: Be transparent about your identity, affiliations, and intentions on social media.
- Honesty: Be honest and truthful in your