In today’s data-driven world, a practitioner’s guide to business analytics PDF is an essential resource for professionals looking to harness the power of data. This comprehensive guide will explore the practical applications of business analytics, focusing on key concepts, methodologies, and real-world examples. Discover how business intelligence solutions and statistical analysis can drive smarter decisions and enhance your company’s competitive edge.
1. Understanding Business Analytics
Business analytics involves the use of data, statistical methods, and information technology to derive insights and make informed decisions. It bridges the gap between raw data and actionable strategies, enabling organizations to improve their performance, identify new opportunities, and mitigate risks.
1.1 Defining Business Analytics
Business analytics encompasses a range of techniques and tools used to analyze past, present, and predictive data. It includes data mining, statistical analysis, predictive modeling, and optimization to gain insights that support better decision-making.
1.2 The Evolution of Business Analytics
The field of business analytics has evolved significantly over the decades. Initially, it focused on basic reporting and descriptive statistics. With advancements in technology, particularly in data storage and processing capabilities, more sophisticated techniques such as predictive analytics and prescriptive analytics have emerged.
1.3 Types of Business Analytics
Business analytics can be categorized into several types, each serving a specific purpose:
- Descriptive Analytics: This involves summarizing historical data to understand past performance. It answers the question, “What happened?”
- Diagnostic Analytics: This explores why certain events occurred by examining data patterns and correlations. It answers the question, “Why did it happen?”
- Predictive Analytics: This uses statistical models to forecast future outcomes based on historical data. It answers the question, “What will happen?”
- Prescriptive Analytics: This recommends actions to optimize outcomes, considering various constraints and scenarios. It answers the question, “How can we make it happen?”
2. Key Components of Business Analytics
To effectively implement business analytics, it’s crucial to understand its core components, including data management, analytical techniques, and reporting.
2.1 Data Management
Data management is the foundation of any business analytics initiative. It involves collecting, storing, cleaning, and organizing data from various sources to ensure its quality and accessibility.
- Data Collection: Gathering data from internal and external sources, such as databases, CRM systems, social media, and market research.
- Data Storage: Choosing the right storage solution, whether it’s a traditional data warehouse or a cloud-based data lake, to accommodate the volume and variety of data.
- Data Cleaning: Identifying and correcting errors, inconsistencies, and missing values in the data to ensure its accuracy.
- Data Integration: Combining data from different sources into a unified view for analysis.
2.2 Analytical Techniques
Analytical techniques are the methods used to extract insights from data. These techniques range from basic statistical analysis to advanced machine learning algorithms.
- Statistical Analysis: Using statistical methods such as regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and correlation analysis to identify relationships and trends in the data.
- Data Mining: Discovering patterns and anomalies in large datasets using techniques such as clustering, classification, and association rule mining.
- Predictive Modeling: Building models to forecast future outcomes using techniques such as time series analysis, decision trees, and neural networks.
- Optimization: Identifying the best course of action to achieve a specific goal, considering constraints and trade-offs, using techniques such as linear programming and simulation.
2.3 Reporting and Visualization
Reporting and visualization are essential for communicating insights to stakeholders in a clear and understandable format. Effective reporting can transform complex data into actionable intelligence.
- Data Visualization: Using charts, graphs, and dashboards to represent data in a visually appealing and informative way.
- Reporting: Creating structured reports that summarize key findings and recommendations.
- Interactive Dashboards: Developing interactive dashboards that allow users to explore data and drill down into specific areas of interest.
3. The Business Analytics Process
The business analytics process typically involves several stages, from defining the problem to implementing the solution and monitoring its effectiveness.
3.1 Defining the Problem
The first step is to clearly define the business problem or opportunity that needs to be addressed. This involves understanding the goals, objectives, and constraints of the project.
- Identify the Business Question: What specific question are you trying to answer?
- Set Objectives: What are the desired outcomes of the analysis?
- Define Scope: What data sources and variables are relevant to the analysis?
3.2 Data Collection and Preparation
Once the problem is defined, the next step is to collect and prepare the data for analysis. This involves gathering data from various sources, cleaning it, and transforming it into a usable format.
- Data Sourcing: Identifying and accessing relevant data sources.
- Data Cleaning: Removing errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates from the data.
- Data Transformation: Converting data into a consistent format for analysis.
3.3 Data Analysis and Modeling
In this stage, analytical techniques are applied to the data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. Predictive models may be built to forecast future outcomes.
- Exploratory Data Analysis: Examining the data to identify key variables and relationships.
- Model Building: Developing statistical or machine learning models to predict future outcomes.
- Model Validation: Testing the accuracy and reliability of the models.
3.4 Interpretation and Insights
The results of the analysis are interpreted to generate insights that can inform decision-making. This involves translating the findings into actionable recommendations.
- Identify Key Findings: What are the most important insights from the analysis?
- Develop Recommendations: What actions should be taken based on the findings?
- Communicate Results: How can the results be presented in a clear and understandable way?
3.5 Implementation and Monitoring
The final stage involves implementing the recommendations and monitoring their effectiveness. This includes tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and making adjustments as needed.
- Implement Solutions: Putting the recommendations into practice.
- Monitor Performance: Tracking KPIs to measure the impact of the solutions.
- Refine and Adjust: Making adjustments to the solutions based on the results of monitoring.
4. Business Analytics Tools and Technologies
Numerous tools and technologies are available to support business analytics, ranging from traditional statistical software to modern cloud-based platforms.
4.1 Statistical Software
Statistical software packages such as SAS, SPSS, and R provide a wide range of statistical functions and analytical tools.
- SAS: A comprehensive statistical software suite used for data management, advanced analytics, and business intelligence.
- SPSS: A user-friendly statistical software package used for data analysis and reporting.
- R: An open-source programming language and environment for statistical computing and graphics.
4.2 Business Intelligence (BI) Platforms
BI platforms such as Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik provide tools for data visualization, reporting, and dashboarding.
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive dashboards and reports.
- Power BI: A cloud-based BI platform that offers data visualization, reporting, and analytics capabilities.
- Qlik: A data analytics platform that provides self-service data discovery and visualization tools.
4.3 Data Warehousing and Data Lakes
Data warehousing and data lakes are used to store and manage large volumes of data for analysis.
- Data Warehouses: Centralized repositories of structured data optimized for reporting and analysis.
- Data Lakes: Storage repositories that hold vast amounts of raw data in its native format, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
4.4 Cloud-Based Analytics Platforms
Cloud-based analytics platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provide scalable and cost-effective solutions for business analytics.
- AWS: Offers a wide range of analytics services, including data warehousing, machine learning, and data visualization.
- Azure: Provides a comprehensive set of analytics tools and services, including data storage, data processing, and machine learning.
- GCP: Offers a variety of analytics solutions, including data warehousing, data analytics, and machine learning.
5. Applications of Business Analytics
Business analytics can be applied in various industries and functional areas to improve decision-making and performance.
5.1 Marketing Analytics
Marketing analytics involves using data and analytics to understand customer behavior, optimize marketing campaigns, and improve return on investment (ROI).
- Customer Segmentation: Dividing customers into groups based on their characteristics and behaviors.
- Campaign Optimization: Improving the effectiveness of marketing campaigns by analyzing data and making adjustments.
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting customer behavior and identifying potential leads.
5.2 Sales Analytics
Sales analytics focuses on using data to improve sales performance, optimize sales processes, and increase revenue.
- Sales Forecasting: Predicting future sales based on historical data and market trends.
- Sales Performance Analysis: Evaluating the performance of sales teams and identifying areas for improvement.
- Lead Scoring: Ranking leads based on their likelihood of conversion.
5.3 Financial Analytics
Financial analytics involves using data to improve financial decision-making, manage risk, and optimize financial performance.
- Financial Forecasting: Predicting future financial performance based on historical data and market conditions.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating financial risks.
- Fraud Detection: Detecting fraudulent transactions and activities.
5.4 Supply Chain Analytics
Supply chain analytics focuses on using data to optimize supply chain operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
- Demand Forecasting: Predicting future demand for products and services.
- Inventory Optimization: Determining the optimal level of inventory to meet demand while minimizing costs.
- Logistics Optimization: Improving the efficiency of transportation and distribution.
5.5 Human Resources (HR) Analytics
HR analytics involves using data to improve HR processes, optimize workforce management, and enhance employee engagement.
- Talent Acquisition: Identifying and recruiting the best candidates for open positions.
- Employee Retention: Identifying factors that contribute to employee turnover and implementing strategies to improve retention.
- Performance Management: Evaluating employee performance and identifying areas for development.
6. Case Studies in Business Analytics
Real-world case studies illustrate the power of business analytics in solving complex problems and driving business value.
6.1 Netflix: Personalized Recommendations
Netflix uses business analytics to personalize recommendations for its users, improving engagement and retention. By analyzing viewing habits, ratings, and demographics, Netflix can suggest movies and TV shows that users are likely to enjoy.
6.2 Amazon: Supply Chain Optimization
Amazon uses business analytics to optimize its supply chain, reducing costs and improving delivery times. By analyzing demand patterns, inventory levels, and logistics data, Amazon can efficiently manage its vast network of warehouses and transportation systems.
6.3 Procter & Gamble: Marketing Campaign Optimization
Procter & Gamble (P&G) uses business analytics to optimize its marketing campaigns, increasing ROI and brand awareness. By analyzing sales data, customer feedback, and market trends, P&G can target its marketing efforts more effectively.
7. Challenges in Business Analytics
Despite its potential benefits, business analytics also presents several challenges that organizations need to address.
7.1 Data Quality Issues
Poor data quality can undermine the accuracy and reliability of business analytics results. Organizations need to invest in data cleaning and validation processes to ensure the integrity of their data.
7.2 Skill Gaps
Business analytics requires specialized skills in data management, statistical analysis, and programming. Many organizations struggle to find and retain qualified professionals with these skills.
7.3 Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security are critical concerns in business analytics, particularly with the increasing use of personal data. Organizations need to implement robust security measures and comply with privacy regulations.
7.4 Resistance to Change
Implementing business analytics often requires significant changes in organizational processes and culture. Resistance to change can hinder the adoption and effectiveness of business analytics initiatives.
8. Best Practices for Business Analytics
To maximize the benefits of business analytics, organizations should follow these best practices:
8.1 Define Clear Objectives
Clearly define the business objectives and goals of the analytics initiative before starting any analysis. This will help focus efforts and ensure that the results are relevant and actionable.
8.2 Ensure Data Quality
Invest in data quality initiatives to ensure that the data used for analysis is accurate, complete, and consistent.
8.3 Use the Right Tools and Techniques
Select the appropriate tools and techniques for the specific problem or opportunity being addressed. Consider the complexity of the analysis, the volume of data, and the skills of the team.
8.4 Communicate Results Effectively
Present the results of the analysis in a clear and understandable format, using visualizations and reports that highlight key findings and recommendations.
8.5 Foster a Data-Driven Culture
Promote a data-driven culture throughout the organization, encouraging employees to use data and analytics to inform their decisions.
9. The Future of Business Analytics
The field of business analytics is constantly evolving, driven by advances in technology and changes in the business environment.
9.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are playing an increasingly important role in business analytics, enabling organizations to automate complex tasks, make more accurate predictions, and gain deeper insights from their data.
9.2 Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics involves analyzing large volumes of data from various sources to identify patterns and trends. With the growth of big data, organizations need to leverage advanced analytics techniques to extract value from their data.
9.3 Cloud Analytics
Cloud analytics is becoming increasingly popular, offering organizations scalable and cost-effective solutions for data storage, processing, and analysis.
9.4 Augmented Analytics
Augmented analytics uses AI and ML to automate data preparation, analysis, and insight generation, making analytics more accessible to a wider range of users.
10. Conclusion: Embracing Business Analytics
Business analytics is a powerful tool that can help organizations make better decisions, improve performance, and gain a competitive advantage. By understanding the key concepts, techniques, and best practices of business analytics, organizations can effectively leverage data to drive business value. For more insights and guidance, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, where you can explore a wealth of resources to help you excel in the world of business analytics.
Navigating the complexities of business analytics requires a blend of technical expertise and strategic thinking. Whether you’re a student, a seasoned professional, or a business leader, embracing business analytics can unlock new opportunities and drive significant improvements in your organization. Remember to focus on data quality, choose the right tools, and foster a data-driven culture to maximize the benefits of business analytics.
Ready to take your business analytics skills to the next level? Explore CONDUCT.EDU.VN for in-depth articles, practical guides, and expert advice. Let us help you transform data into actionable insights and achieve your business goals.
For additional support and resources, contact us at:
Address: 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (707) 555-1234
Website: CONDUCT.EDU.VN
Unlock the full potential of your data with conduct.edu.vn and lead your organization to success.
FAQ: A Practitioner’s Guide to Business Analytics
1. What is business analytics?
Business analytics is the process of using data, statistical methods, and technology to analyze past performance, predict future outcomes, and improve decision-making.
2. What are the main types of business analytics?
The main types are descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, each answering different questions about the data.
3. Why is data management important in business analytics?
Data management ensures data quality, accuracy, and accessibility, which are crucial for generating reliable insights.
4. What are some popular business analytics tools?
Popular tools include SAS, SPSS, R, Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik.
5. How is business analytics used in marketing?
In marketing, business analytics is used for customer segmentation, campaign optimization, and predictive analytics to enhance ROI.
6. What are some challenges in implementing business analytics?
Challenges include data quality issues, skill gaps, data privacy concerns, and resistance to change.
7. What is the role of AI and ML in business analytics?
AI and ML automate complex tasks, improve prediction accuracy, and enable deeper insights from data.
8. How can organizations ensure data quality in business analytics?
Organizations can invest in data cleaning and validation processes, implement data governance policies, and use data quality tools.
9. What are the key steps in the business analytics process?
The key steps include defining the problem, data collection and preparation, data analysis and modeling, interpretation and insights, and implementation and monitoring.
10. How can a company foster a data-driven culture?
A company can foster a data-driven culture by promoting data literacy, encouraging data-informed decision-making, and providing training and resources for employees to use data effectively.
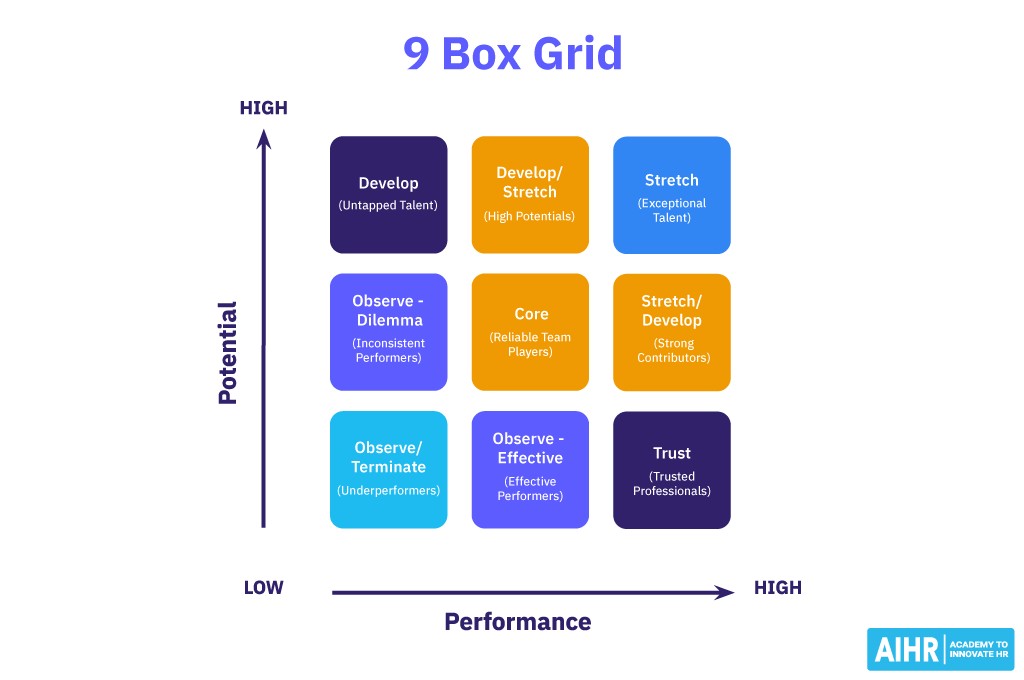
10. 9 Box Grid and Talent Analytics
The 9 box grid is a popular tool used in talent management to assess and categorize employees based on their performance and potential. It’s particularly useful in identifying high-potential employees and those who may need additional support to improve their performance.
Action plan
- Identify personal roadblocks that may cause low performance and lack of growth. However, be careful not to over-invest and know when to move them out or sever ties. Sit with the individual to see if there is a more appropriate assignment where they (and you) can utilize their skills better.
- If the first two options don’t bring quick wins, you should create an exit plan together where you help the person find a role that better suits their skills outside of your organization.
If these underperformers are a common phenomenon in your organization, review your talent acquisition and your selection process.
11. Excel Template and Guide
Beside a dedicated HR performance management software, Excel is a great tool to segment your employees based on their performance and potential. You can get a quick overview of the talent segments within your organization, enabling you to make informed talent decisions.
This 9 box grid Excel template helps you visualize which employees belong to which of the nine talent segments. You simply fill in employee names and their performance and potential levels, and they will automatically be sorted into the right talent segment.