In today’s digital world, creating visually appealing and professionally formatted documents is essential. Microsoft Word offers several tools to help users achieve precise alignment and organization of elements within their documents. One such feature is alignment guides. This guide provides a detailed explanation of How To Enable Alignment Guides In Word, enhance your document layout, and improve overall presentation. Discover how alignment assistance contributes to creating polished and professional-looking documents, and visit conduct.edu.vn for further information. The guide also addresses using gridlines, customizing grid settings, document formatting, and visual aids.
1. Understanding the Importance of Alignment in Word Documents
Well-aligned elements in a Word document contribute to a professional and polished appearance. Proper alignment enhances readability, making it easier for readers to follow the content and grasp key information. Clear visual structure, achieved through alignment, reflects attention to detail and elevates the overall quality of your document.
1.1. Enhancing Readability and Visual Appeal
When text, images, and other objects are aligned correctly, the document becomes more visually appealing. Misaligned elements can be distracting and make the document appear cluttered and unprofessional. Alignment guides in Word help ensure that everything is precisely positioned, creating a clean and organized look.
1.2. Creating a Professional Look and Feel
A well-aligned document conveys professionalism and attention to detail. Whether you are creating a business report, an academic paper, or a simple letter, proper alignment can make a significant difference in how your document is perceived. Alignment guides provide the tools necessary to achieve this level of precision.
1.3. Improving Document Structure and Organization
Alignment is not just about aesthetics; it also plays a crucial role in document structure and organization. By aligning elements consistently, you create a clear visual hierarchy that guides the reader through the document. This makes it easier to understand the relationships between different sections and elements.
2. What are Alignment Guides in Microsoft Word?
Alignment guides are visual aids in Microsoft Word that help users align objects, such as images, shapes, and text boxes, with precision. When enabled, these guides appear as temporary lines on the document as you move or resize objects, indicating their alignment with margins, other objects, or specific points on the page.
2.1. Definition and Functionality
Alignment guides are designed to assist users in creating neatly aligned and organized documents. They provide real-time visual feedback as you move objects, ensuring that they are perfectly aligned with other elements on the page. This feature is particularly useful for creating layouts with multiple objects that need to be precisely positioned.
2.2. How Alignment Guides Differ from Gridlines
While both alignment guides and gridlines serve the purpose of aiding alignment in Word, they function differently. Alignment guides appear dynamically as you move objects, helping you align with margins, other objects, or specific points. Gridlines, on the other hand, provide a static grid of lines across the entire document, offering a consistent reference for placing and aligning objects.
2.3. Benefits of Using Alignment Guides
Using alignment guides offers several benefits, including:
- Precision: Achieve accurate alignment of objects, ensuring a professional look.
- Efficiency: Quickly align objects without manual adjustments, saving time and effort.
- Consistency: Maintain uniform alignment throughout the document for a cohesive appearance.
- Ease of Use: Simple to enable and use, making them accessible to users of all skill levels.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Enable Alignment Guides in Word
Enabling alignment guides in Microsoft Word is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to activate and start using alignment guides in your documents:
3.1. Accessing the “Layout” Tab
- Open Microsoft Word: Launch the Microsoft Word application on your computer.
- Open or Create a Document: Open an existing document or create a new one where you want to use alignment guides.
- Navigate to the Ribbon: Look at the top of the Word window to find the ribbon, which contains various tabs such as “File,” “Home,” “Insert,” “Layout,” etc.
- Select the “Layout” Tab: Click on the “Layout” tab. This tab contains options related to page setup, arrangement, and alignment of objects within your document.
3.2. Finding the “Align” Drop-Down Menu
- Locate the “Arrange” Group: Within the “Layout” tab, find the “Arrange” group. This group contains tools for arranging objects in your document.
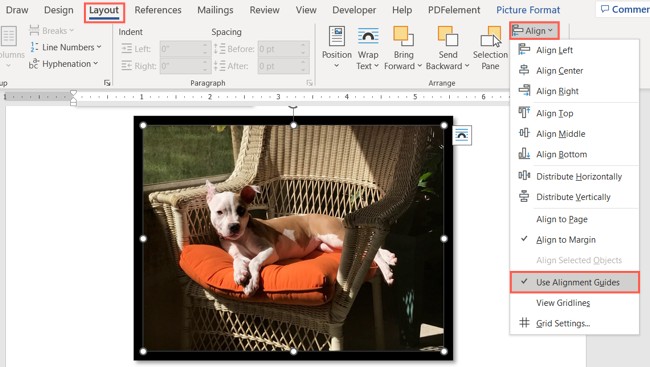
- Identify the “Align” Option: In the “Arrange” group, you will see an “Align” drop-down menu. The icon usually shows several lines indicating alignment options.
- Click on the “Align” Drop-Down Menu: Click on the “Align” drop-down menu to reveal a list of alignment-related options.
3.3. Enabling Alignment Guides
- Open the “Align” Menu: Click the “Align” drop-down menu to see the available options.
- Select “Alignment Guides”: In the drop-down menu, look for the option labeled “Alignment Guides.”
- Enable Alignment Guides: Click on “Alignment Guides” to enable the feature. A checkmark will appear next to the option, indicating that alignment guides are now active.
3.4. Verifying Alignment Guides are Active
- Insert an Object: Insert an object into your document, such as an image, shape, or text box.
- Move the Object: Click and drag the object around the document.
- Observe Alignment Guides: As you move the object, you should see temporary lines (alignment guides) appear, indicating alignment with margins, other objects, or specific points on the page.
- Confirm Activation: If you see these alignment guides, it confirms that the feature is active and working correctly.
By following these steps, you can easily enable alignment guides in Microsoft Word and start using them to improve the alignment and organization of objects in your documents. This feature helps ensure that your documents have a professional and polished appearance.
4. Using Alignment Guides Effectively
Once alignment guides are enabled, it’s essential to know how to use them effectively to achieve the best results in your Word documents. Here are some tips and techniques for using alignment guides to enhance your document layout:
4.1. Aligning Objects with Margins
- Select an Object: Click on the object you want to align with the document margins.
- Drag the Object: Click and drag the object towards the margin (top, bottom, left, or right).
- Observe the Alignment Guide: As you approach the margin, an alignment guide will appear, indicating when the object is perfectly aligned with the margin.
- Release the Object: Once the alignment guide appears, release the object to place it precisely on the margin.
4.2. Aligning Objects with Other Objects
- Select an Object: Choose the object you want to align with another object in the document.
- Drag the Object: Click and drag the selected object towards the other object.
- Observe the Alignment Guide: As the selected object gets closer to the other object, alignment guides will appear, showing when the objects are aligned along their edges or centers.
- Release the Object: Release the object once the alignment guide indicates the desired alignment.
4.3. Aligning Objects to Specific Points on the Page
- Select an Object: Click on the object you want to align to a specific point on the page.
- Determine the Point: Identify the specific point on the page (e.g., a paragraph start, a heading, or a specific coordinate).
- Drag the Object: Click and drag the object towards the determined point.
- Observe the Alignment Guide: As you move the object, alignment guides will appear, helping you align the object with the chosen point.
- Release the Object: Release the object when the alignment guide shows that it is aligned with the desired point.
4.4. Tips for Precise Alignment
- Zoom In: Zoom in on your document to get a closer view and ensure precise alignment.
- Use Keyboard Nudges: Use the arrow keys to nudge objects slightly for fine adjustments after aligning them with the guides.
- Check Alignment in Print Preview: Review the alignment in print preview to see how it will look when printed, ensuring everything is correctly aligned.
- Consistent Spacing: Maintain consistent spacing between objects to create a balanced and professional look.
By following these tips and techniques, you can use alignment guides effectively to create well-aligned and visually appealing documents in Microsoft Word. Accurate alignment enhances the overall quality and professionalism of your documents.
5. Troubleshooting Common Issues with Alignment Guides
While alignment guides in Microsoft Word are generally reliable, users may encounter issues. Here are common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
5.1. Alignment Guides Not Appearing
-
Verify Alignment Guides are Enabled:
- Go to the “Layout” tab.
- Click on the “Align” drop-down menu in the “Arrange” group.
- Ensure “Alignment Guides” is checked. If not, click it to enable.
-
Check View Settings:
- Ensure that you are in a view mode that supports alignment guides (e.g., Print Layout view).
- Go to the “View” tab and select “Print Layout.”
-
Restart Word:
- Close and reopen Microsoft Word. This can resolve temporary software glitches.
-
Update Microsoft Word:
- Ensure you have the latest updates installed. Go to “File” > “Account” > “Update Options” and click “Update Now.”
5.2. Alignment Guides are Inaccurate
-
Zoom Level:
- Ensure your zoom level is appropriate (100% is ideal for accuracy).
- Zooming in too much or too little can make alignment guides appear inaccurate.
-
Screen Resolution:
- Check your screen resolution settings. Incorrect resolution can affect the display of alignment guides.
- Go to your computer’s display settings and ensure the resolution is set to the recommended level.
-
Graphics Card Drivers:
- Update your graphics card drivers. Outdated drivers can cause display issues.
- Visit the manufacturer’s website (e.g., NVIDIA, AMD, Intel) to download and install the latest drivers.
-
Object Snapping Interference:
- If you have object snapping enabled, it might interfere with precise alignment.
- Go to “Layout” > “Align” > “Grid Settings” and uncheck “Snap objects to grid when the gridlines are not displayed.”
5.3. Alignment Guides are Too Sensitive
-
Grid Settings:
- Adjust the grid settings to reduce sensitivity.
- Go to “Layout” > “Align” > “Grid Settings” and increase the horizontal and vertical spacing.
-
Object Size and Distance:
- Be mindful of the size of the objects you are aligning and the distance between them.
- Smaller objects and closer distances may require more careful adjustments.
-
Practice and Patience:
- Using alignment guides effectively often requires practice. Be patient and take the time to get a feel for how they work.
5.4. Alignment Guides Conflict with Other Features
-
Disable Conflicting Features:
- If you are using other features that affect object placement (e.g., margins, columns), try disabling them temporarily to see if they interfere with alignment guides.
-
Check for Add-ins:
- Some Word add-ins can interfere with alignment guides.
- Go to “File” > “Options” > “Add-ins” and disable any add-ins you suspect might be causing issues.
5.5. Resetting Word Settings
-
Reset to Default:
- If all else fails, reset Word settings to their default values.
- Go to “File” > “Options” > “Customize Ribbon” and click “Reset.”
- Note that this will reset all customizations, so back up your settings if needed.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can resolve common issues with alignment guides and ensure they function correctly in Microsoft Word. Accurate and reliable alignment guides are essential for creating professional and well-organized documents.
6. Alternatives to Alignment Guides
While alignment guides are a useful tool in Microsoft Word, several alternatives can help you achieve precise alignment and organization of objects in your documents. Here are some options to consider:
6.1. Using Gridlines
Gridlines provide a static grid of lines across the entire document, offering a consistent reference for placing and aligning objects. Unlike alignment guides, which appear dynamically, gridlines are always visible, allowing you to align objects with the grid intersections.
-
How to Enable Gridlines:
- Go to the “Layout” tab.
- Click on the “Align” drop-down menu in the “Arrange” group.
- Select “View Gridlines” to enable them.
-
Benefits of Using Gridlines:
- Consistent Reference: Provides a constant visual reference for alignment.
- Uniform Spacing: Helps maintain uniform spacing between objects.
- Accurate Placement: Allows precise placement of objects based on the grid.
6.2. The “Align” Tools
Microsoft Word offers a variety of built-in alignment tools in the “Align” menu. These tools allow you to align selected objects relative to each other or to the page margins.
-
Types of Alignment Tools:
- Align Left: Aligns objects along their left edges.
- Align Center: Centers objects horizontally.
- Align Right: Aligns objects along their right edges.
- Align Top: Aligns objects along their top edges.
- Align Middle: Centers objects vertically.
- Align Bottom: Aligns objects along their bottom edges.
- Distribute Horizontally: Spaces objects evenly between the leftmost and rightmost objects.
- Distribute Vertically: Spaces objects evenly between the topmost and bottommost objects.
-
How to Use Align Tools:
- Select the objects you want to align.
- Go to the “Layout” tab.
- Click on the “Align” drop-down menu in the “Arrange” group.
- Choose the appropriate alignment option from the menu.
6.3. Using Tables for Alignment
Tables can be used to create a structured layout in Word documents, ensuring that elements are aligned correctly within the table cells.
-
How to Use Tables for Alignment:
- Insert a table into your document (“Insert” tab > “Table”).
- Place objects, text, and images into the table cells.
- Adjust the table cell sizes and borders as needed.
- Remove table borders for a cleaner look (“Table Design” tab > “Borders” > “No Border”).
-
Benefits of Using Tables:
- Structured Layout: Provides a rigid structure for aligning elements.
- Precise Control: Allows precise control over the placement of objects within cells.
- Consistent Spacing: Helps maintain consistent spacing between elements.
6.4. Drawing Guides (Shapes)
You can create temporary drawing guides using shapes (e.g., lines, rectangles) to help align objects in your document.
-
How to Use Drawing Guides:
- Insert a shape from the “Insert” tab > “Shapes.”
- Position and resize the shape to serve as a guide for aligning objects.
- Align objects to the edges or center of the shape.
- Once alignment is complete, delete the shape.
-
Benefits of Using Drawing Guides:
- Customizable: Allows you to create custom alignment guides tailored to your specific needs.
- Flexible: Can be used to align objects in various ways (e.g., horizontally, vertically, diagonally).
- Temporary: Can be easily removed once alignment is complete.
6.5. Manual Measurement and Positioning
For highly precise alignment, you can manually measure and position objects using the “Position” and “Size” options in Word.
-
How to Manually Measure and Position Objects:
- Select the object you want to position.
- Go to the “Shape Format” or “Picture Format” tab.
- Use the “Position” options to specify the exact horizontal and vertical position of the object.
- Use the “Size” options to specify the exact width and height of the object.
-
Benefits of Manual Measurement:
- High Precision: Provides the highest level of precision in object placement.
- Exact Control: Allows exact control over the position and size of objects.
- Repeatable: Ensures consistent positioning across multiple documents.
By exploring these alternatives to alignment guides, you can find the methods that work best for your specific needs and preferences, ensuring that your Word documents are well-aligned and visually appealing.
7. Customizing Grid Settings for Enhanced Alignment
Customizing grid settings in Microsoft Word can significantly enhance alignment precision and control. Adjusting these settings allows you to tailor the grid to your specific document layout needs, ensuring objects align perfectly.
7.1. Accessing Grid Settings
-
Go to the “Layout” Tab:
- Open Microsoft Word and navigate to the “Layout” tab on the ribbon.
-
Open the “Align” Drop-Down Menu:
- In the “Arrange” group, click on the “Align” drop-down menu.
-
Select “Grid Settings”:
- From the drop-down menu, choose “Grid Settings” to open the Grid and Guides dialog box.
7.2. Adjusting Grid Spacing
The grid spacing determines the frequency of gridlines in your document. Adjusting horizontal and vertical spacing can help you achieve finer or coarser alignment.
-
Horizontal Spacing:
- In the “Grid and Guides” dialog box, locate the “Horizontal spacing” field.
- Enter the desired spacing value (e.g., 0.1 inches, 0.5 cm). Smaller values result in more gridlines, providing finer alignment control.
-
Vertical Spacing:
- Locate the “Vertical spacing” field.
- Enter the desired spacing value. Consistent horizontal and vertical spacing create a uniform grid.
7.3. Changing Grid Origin
The grid origin is the point from which the gridlines are drawn. By default, it is set to the top-left corner of the page margins. You can change the origin to customize the grid’s position.
-
Using Margins as Origin:
- Ensure the “Use margins” checkbox is selected to use the page margins as the grid origin.
-
Custom Origin:
- Uncheck “Use margins” to specify a custom origin.
- Enter the desired horizontal and vertical origin values in the respective fields.
7.4. Object Snapping
Object snapping allows objects to automatically align with the gridlines. Enabling this feature can greatly simplify the alignment process.
-
Enable Object Snapping:
- In the “Grid and Guides” dialog box, check the “Snap objects to grid when the gridlines are not displayed” checkbox.
- This setting ensures objects snap to the grid even when the gridlines are hidden.
7.5. Displaying Gridlines
You can choose to display or hide gridlines based on your preference. Displaying gridlines provides a visual reference for alignment, while hiding them creates a cleaner document appearance.
-
Show Gridlines:
- Check the “Display gridlines on screen” checkbox to show the gridlines.
-
Hide Gridlines:
- Uncheck the “Display gridlines on screen” checkbox to hide the gridlines.
- Objects will still snap to the grid if “Snap objects to grid” is enabled.
7.6. Alignment Guides Settings
You can customize alignment guides to snap to different parts of the document such as page, margin, and paragraph.
-
Page Guides:
- Check the “Page guides” box to enable alignment guides that snap to the edges of the page.
-
Margin Guides:
- Check the “Margin guides” box to enable alignment guides that snap to the margins of the page.
-
Paragraph Guides:
- Check the “Paragraph guides” box to enable alignment guides that snap to the edges of paragraphs.
7.7. Saving Grid Settings
Once you have customized the grid settings to your liking, you can save them as the default for all new documents.
-
Set as Default:
- Click the “Set As Default” button in the “Grid and Guides” dialog box.
- This saves the current grid settings as the default for all new Word documents.
By customizing these grid settings, you can optimize the alignment capabilities in Microsoft Word, creating well-organized and visually appealing documents with ease.
8. Real-World Examples of Using Alignment Guides
To illustrate the practical benefits of using alignment guides in Microsoft Word, here are several real-world examples where these guides can be invaluable:
8.1. Creating Business Reports
In business reports, precise alignment is crucial for conveying professionalism and clarity. Alignment guides can help ensure that:
-
Headings and Subheadings:
- Headings and subheadings are aligned consistently with the left margin, creating a clear visual hierarchy.
-
Images and Charts:
- Images and charts are aligned with the surrounding text and margins, preventing a cluttered appearance.
-
Tables and Figures:
- Tables and figures are aligned with the text and captions, ensuring they are easy to read and understand.
-
Margins and Indents:
- Margins and indents are consistent throughout the document, providing a uniform look and feel.
8.2. Designing Academic Papers
Academic papers require a high degree of precision and attention to detail. Alignment guides can assist in:
-
Title and Abstract:
- The title and abstract are centered and aligned correctly at the top of the page.
-
Paragraphs and Citations:
- Paragraphs are aligned with consistent indentation, and citations are correctly formatted.
-
Figures and Captions:
- Figures and their captions are aligned, ensuring they are correctly positioned and labeled.
-
Equations and Formulas:
- Equations and formulas are centered or aligned with the text, maintaining a professional look.
8.3. Formatting Resumes and Cover Letters
Resumes and cover letters need to be visually appealing and easy to read. Alignment guides can help:
-
Contact Information:
- Contact information is aligned neatly at the top of the page, making it easy for recruiters to find.
-
Section Headings:
- Section headings (e.g., “Experience,” “Education,” “Skills”) are aligned consistently.
-
Bullet Points:
- Bullet points are aligned with consistent indentation, creating a well-organized list.
-
Dates and Locations:
- Dates and locations for work experience and education are aligned, enhancing readability.
8.4. Preparing Newsletters and Marketing Materials
Newsletters and marketing materials benefit from a visually engaging layout. Alignment guides can ensure:
-
Headlines and Body Text:
- Headlines are aligned with the body text, creating a cohesive look.
-
Images and Graphics:
- Images and graphics are aligned with the text and margins, enhancing visual appeal.
-
Call-to-Action Buttons:
- Call-to-action buttons are aligned and positioned effectively, drawing attention to key actions.
-
Columns and Sections:
- Columns and sections are aligned, providing a structured and easy-to-follow layout.
8.5. Creating Training Manuals and Guides
Training manuals and guides need to be clear and well-organized. Alignment guides can assist in:
-
Step-by-Step Instructions:
- Step-by-step instructions are aligned with consistent indentation and spacing.
-
Screenshots and Diagrams:
- Screenshots and diagrams are aligned with the text, providing clear visual references.
-
Notes and Tips:
- Notes and tips are aligned in boxes or callouts, making them easy to spot.
-
Table of Contents:
- The table of contents is aligned correctly, allowing users to navigate the manual easily.
8.6. Designing Presentations and Slides
When creating presentations using Microsoft Word, alignment guides can help ensure that:
-
Titles and Subtitles:
- Titles and subtitles are consistently aligned on each slide, creating a professional appearance.
-
Text Boxes:
- Text boxes are aligned with other elements, ensuring a clean and organized layout.
-
Images and Charts:
- Images and charts are aligned with the text and slide margins, making the presentation visually appealing.
-
Bullet Points and Lists:
- Bullet points and lists are aligned with consistent indentation, improving readability.
By using alignment guides in these real-world scenarios, you can create documents that are not only visually appealing but also professional and easy to understand.
9. Integrating Alignment Guides into Your Workflow
Integrating alignment guides into your regular Microsoft Word workflow can significantly improve the quality and efficiency of your document creation process. Here’s how to seamlessly incorporate alignment guides into your daily tasks:
9.1. Setting Up Default Grid Settings
To ensure consistency across all your documents, set up default grid settings that suit your most common needs.
-
Customize Grid Settings:
- Go to “Layout” > “Align” > “Grid Settings.”
- Adjust horizontal and vertical spacing, grid origin, and object snapping options to your preferred settings.
-
Set as Default:
- Click the “Set As Default” button. This saves your settings for all new documents.
-
Consistency:
- With default settings, every new document automatically uses your preferred grid, saving you time and effort.
9.2. Using Alignment Guides as a First Step
Make enabling alignment guides the first step in your document creation process to ensure everything is aligned from the start.
-
Enable Alignment Guides:
- Open a new or existing document.
- Go to “Layout” > “Align” and select “Alignment Guides.”
-
Initial Layout:
- As you add and position elements, use the guides to align them with margins, other objects, or specific points.
-
Early Alignment:
- By aligning elements early, you avoid having to make adjustments later, saving time and ensuring consistency.
9.3. Combining Alignment Guides with Other Tools
Use alignment guides in conjunction with other Word tools for enhanced precision and control.
-
Gridlines:
- Enable gridlines for a constant visual reference.
- Use alignment guides for dynamic alignment and gridlines for overall structure.
-
Align Tools:
- Use the “Align” menu options (e.g., Align Left, Align Center) for quick and precise alignment of multiple objects.
- Combine with alignment guides for fine-tuning.
-
Tables:
- Use tables for structured layouts and alignment guides to ensure elements within tables are correctly positioned.
9.4. Creating Templates with Pre-Set Alignment
Develop custom templates with pre-set alignment to streamline document creation for specific purposes.
-
Design a Template:
- Create a new Word document and set up the layout with your desired fonts, margins, and alignment settings.
- Use alignment guides to position placeholders for text, images, and other elements.
-
Save as Template:
- Go to “File” > “Save As” and choose “Word Template (.dotx)” as the file type.
- Save the template in a location where you can easily access it.
-
Consistent Documents:
- When you need to create a new document, use your custom template to ensure consistent alignment and formatting.
9.5. Regular Practice and Experimentation
Like any skill, using alignment guides effectively requires practice. Experiment with different techniques and settings to find what works best for you.
-
Practice Alignment:
- Regularly create documents that require precise alignment, such as newsletters, reports, or presentations.
- Focus on using alignment guides to position elements accurately.
-
Explore Settings:
- Experiment with different grid and alignment settings to see how they affect the layout of your documents.
-
Learn New Techniques:
- Continuously learn new techniques and tips for using alignment guides to improve your workflow.
9.6. Reviewing and Refining Alignment
Make it a habit to review and refine the alignment of elements in your documents before finalizing them.
-
Print Preview:
- Use Print Preview to check the layout and alignment of elements as they will appear when printed.
-
Zoom In:
- Zoom in on different sections of your document to check for any misalignments or inconsistencies.
-
Final Adjustments:
- Make any necessary adjustments to ensure that all elements are perfectly aligned and the document looks professional.
By integrating these strategies into your workflow, you can ensure that alignment guides become a natural and essential part of your document creation process, leading to more professional and visually appealing results.
10. Advanced Techniques for Perfect Alignment
To take your alignment skills in Microsoft Word to the next level, explore these advanced techniques for achieving perfect alignment in your documents:
10.1. Using the “Snap to Shape” Feature
The “Snap to Shape” feature allows objects to automatically align with the edges, corners, or center of other shapes, providing precise alignment for complex layouts.
-
Enable “Snap to Shape”:
- Go to “Layout” > “Align” > “Grid Settings.”
- Check the “Snap objects to other objects” checkbox.
-
Align Objects:
- Drag an object near another shape, and it will automatically snap to the nearest edge, corner, or center.
-
Precise Positioning:
- Use this feature to align objects precisely with other shapes, creating visually appealing and structured designs.
10.2. Creating Custom Guides with Shapes
For unique alignment needs, create custom guides using shapes to help align objects in specific ways.
-
Insert a Shape:
- Insert a shape (e.g., line, rectangle) from the “Insert” tab > “Shapes.”
-
Position and Resize:
- Position and resize the shape to serve as a guide for aligning objects.
-
Align Objects:
- Align objects to the edges or center of the custom shape.
-
Remove the Shape:
- Once alignment is complete, delete the custom shape.
-
Tailored Alignment:
- This technique allows you to create custom alignment guides tailored to your specific document layout requirements.
10.3. Using the “Distribute” Options
The “Distribute” options in the “Align” menu evenly space objects horizontally or vertically, ensuring uniform spacing in your documents.
-
Select Objects:
- Select the objects you want to distribute evenly.
-
Distribute Horizontally or Vertically:
- Go to “Layout” > “Align” and choose “Distribute Horizontally” or “Distribute Vertically.”
-
Even Spacing:
- The selected objects will be spaced evenly between the leftmost and rightmost objects (horizontally) or between the topmost and bottommost objects (vertically).
-
Professional Look:
- Use this technique to create a balanced and professional look in your documents.
10.4. Combining Alignment Guides with the Ruler
Use alignment guides in conjunction with the ruler to achieve precise alignment based on specific measurements.
-
Show the Ruler:
- Go to the “View” tab and check the “Ruler” checkbox to display the ruler at the top and left of the document.
-
Position Objects:
- Use the ruler to measure and position objects accurately, using alignment guides for additional precision.
-
Consistent Measurements:
- This technique allows you to align objects based on specific measurements, ensuring uniformity and accuracy.
10.5. Leveraging the “Format Painter” for Alignment
The “Format Painter” tool can be used to copy and apply the alignment and formatting of one object to other objects in your document.
-
Select the Source Object:
- Select the object with the desired alignment and formatting.
-
Click “Format Painter”:
- Click the “Format Painter” button in the “Home” tab.
-
Apply to Other Objects:
- Click on other objects to apply the same alignment and formatting.
-
Consistent Formatting:
- This technique ensures consistent alignment and formatting across multiple objects, saving time and effort.
10.6. Using Layout Options for Precise Positioning
Explore the layout options available for images and shapes to achieve precise positioning relative to the text.
-
Select an Object:
- Select the image or shape you want to position.
-
Open Layout Options:
- Click the “Layout Options” button next to the object or go to “Shape Format” or “Picture Format” and choose “Wrap Text.”
-
Choose a Layout:
- Select a layout option (e.g., “In Line with Text,” “Square,” “Tight,” “Behind Text,” “In Front of Text”) to control how the object interacts with the surrounding text.
-
Adjust Positioning:
- Adjust the horizontal and vertical position of the object using the layout options or by dragging it with alignment guides.
-
Text Integration:
- This technique allows you to seamlessly integrate images and shapes with the text, creating visually appealing and well-aligned documents.
By mastering these advanced techniques, you can achieve perfect alignment in your Microsoft Word documents, creating professional and visually stunning results.
11. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Alignment Guides
While alignment guides are a valuable tool, it’s easy to make mistakes that can undermine their effectiveness. Here are common pitfalls to avoid when using alignment guides in Microsoft Word:
11.1. Ignoring Zoom Level
Working at an incorrect zoom level can lead to inaccurate alignment.
-
Problem:
- Zooming in too much or too little can distort your perception of alignment.
-
Solution:
- Work at a zoom level of 100% for the most accurate view.
- Use the zoom slider in the bottom-right corner of the Word window to adjust the zoom level.
11.2. Relying Solely on Visual Alignment
Relying only on what looks aligned without checking precise measurements can lead to inconsistencies.
-
Problem:
- Visual perception can be deceiving, and what appears aligned may not be perfectly so.
-
Solution:
- Combine visual alignment