Inserting a tampon can seem daunting, but with the right guidance, it can become a simple part of your period routine. This How To Put In A Tampon Visual Guide from CONDUCT.EDU.VN will walk you through each step, ensuring comfort and confidence. Learn the proper tampon insertion techniques and discover tips for a hassle-free experience, promoting better menstrual hygiene and understanding.
1. Understanding the Basics of Tampons
Tampons are small, absorbent plugs designed to be inserted into the vaginal canal to absorb menstrual flow. They come in various sizes and types, each catering to different flow levels and preferences. Understanding the different types of tampons available is crucial for a comfortable and effective experience. Let’s explore the basics of tampons to help you make an informed choice.
1.1 What are Tampons and How Do They Work?
Tampons are made of materials like cotton or rayon and are designed to absorb menstrual blood internally. A tampon works by expanding once inside the vaginal canal to prevent leakage. They are a popular choice for many due to their discreetness and ease of use during activities like swimming or sports.
1.2 Types of Tampons: Applicator vs. Non-Applicator
Tampons come in two main types: applicator and non-applicator. Applicator tampons include a plastic or cardboard applicator to aid in insertion. Non-applicator tampons require you to use your finger to insert them. Both types are effective, and the choice depends on personal preference.
- Applicator Tampons: These tampons come with a plastic or cardboard applicator that helps guide the tampon into the correct position. They are often preferred by beginners for their ease of use.
- Non-Applicator Tampons: These tampons do not have an applicator. You insert them directly with your finger. They are more compact and generate less waste.
1.3 Absorbency Levels: Choosing the Right Size
Tampons come in various absorbency levels, indicated by terms like “light,” “regular,” “super,” and “super plus.” Choosing the right absorbency level is essential to prevent leaks and reduce the risk of Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS). Start with the lowest absorbency needed and adjust as necessary.
| Absorbency Level | Grams of Fluid Absorbed | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Light | Up to 6 grams | Light flow days |
| Regular | 6-9 grams | Moderate flow days |
| Super | 9-12 grams | Heavy flow days |
| Super Plus | 12-15 grams | Very heavy flow days |

1.4 Organic vs. Synthetic Tampons
Tampons can be made from organic cotton or synthetic materials like rayon. Organic tampons are made from cotton grown without pesticides or synthetic fertilizers, which may be preferable for those with sensitive skin or environmental concerns. Synthetic tampons are typically more absorbent but may contain chemicals that some people prefer to avoid.
1.5 Features to Look for in a Tampon
When choosing a tampon, consider the following features:
- Applicator Type: Plastic or cardboard
- Material: Organic cotton or synthetic
- Absorbency Level: Light, regular, super, or super plus
- Comfort: Rounded tip for easy insertion
- Safety: FDA approved and free from harmful chemicals
Understanding these basics will help you choose the right tampon for your needs and ensure a comfortable and safe experience. For more detailed information and guidance, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, your trusted source for menstrual health education.
2. Preparing for Tampon Insertion: Hygiene and Comfort
Before you start, it’s important to ensure a clean and comfortable environment. Good hygiene practices are key to preventing infections and ensuring a smooth insertion process. Creating a relaxed atmosphere can also help ease any anxiety you may have. Here’s a guide to preparing for tampon insertion, focusing on hygiene and comfort.
2.1 Washing Your Hands: The First Step to Hygiene
Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling a tampon. This simple step can prevent the transfer of bacteria and reduce the risk of infection. Ensure your hands are clean and dry before proceeding.
2.2 Finding a Comfortable Position: Sitting, Squatting, or Standing
Finding a comfortable position is crucial for easy tampon insertion. Experiment with different positions to find what works best for you. Some common positions include:
- Sitting on the Toilet: This position allows you to relax your muscles and have easy access.
- Standing with One Leg Elevated: Place one leg on the toilet seat or edge of the tub to open up your hips.
- Squatting: This position can help relax your pelvic floor muscles.
2.3 Relaxing Your Muscles: Easing Tension for Smooth Insertion
Muscle tension can make tampon insertion difficult and uncomfortable. Take a few deep breaths to relax your muscles. If you’re feeling anxious, try listening to calming music or practicing a quick meditation exercise. Relaxing your pelvic floor muscles can also help ease the insertion process.
2.4 Knowing Your Anatomy: Understanding the Vaginal Opening
Understanding your anatomy can help you insert a tampon correctly. The vaginal opening is located between the urethra (where urine exits) and the anus. Use a mirror to familiarize yourself with the area if needed. Knowing the correct location will make insertion smoother and more comfortable.
2.5 Choosing the Right Time: When to Insert a Tampon
The best time to insert a tampon is when your flow is present. Inserting a tampon when you’re not menstruating can be uncomfortable and may cause irritation. If you’re unsure, wait until you see signs of your period before attempting insertion.
By following these preparation steps, you can create a comfortable and hygienic environment for tampon insertion. Remember, it’s okay to take your time and experiment to find what works best for you. For more tips and guidance on menstrual health, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Insert a Tampon with an Applicator
Using a tampon with an applicator can seem intimidating at first, but with practice, it becomes a straightforward process. This step-by-step guide will walk you through inserting a tampon with a plastic or cardboard applicator, ensuring a comfortable and successful experience. Follow these instructions carefully to master tampon insertion.
3.1 Unwrapping the Tampon: Preparing the Applicator
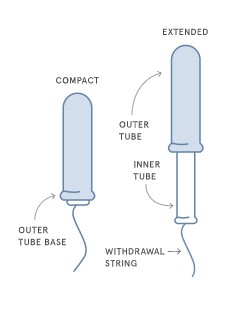
Start by unwrapping the tampon. Hold the applicator firmly in your dominant hand. Ensure that the applicator is fully extended if it’s a compact type. For cardboard applicators, slightly twist the inner and outer tubes to unlock them.
3.2 Holding the Applicator: Proper Grip for Control
Hold the applicator between your thumb and middle finger at the grip, which is usually located in the middle of the applicator. Place your index finger on the end of the inner tube, ready to push the tampon out.
3.3 Positioning the Applicator: Aiming Towards Your Back
Get into your chosen comfortable position. Gently insert the rounded tip of the applicator into your vaginal opening. Aim the applicator slightly upward and toward your back, following the natural angle of your vaginal canal.
3.4 Inserting the Applicator: How Far to Insert It
Continue inserting the applicator until your fingers holding the grip are just inside your vaginal opening. You should feel the outer tube almost completely inside you.
3.5 Pushing the Tampon: Deploying the Tampon Correctly
Using your index finger, push the inner tube of the applicator all the way into the outer tube. This will release the tampon from the applicator and position it correctly inside your vaginal canal.
3.6 Removing the Applicator: Discarding the Applicator Properly
Once the tampon is fully deployed, gently remove the applicator. Wrap the applicator in toilet paper and dispose of it in a wastebasket. Do not flush the applicator down the toilet, as it can cause plumbing issues.
3.7 Checking the String: Ensuring It’s Outside Your Body
Ensure that the tampon string is hanging outside your body. This string is essential for removing the tampon later. If the string is not visible, gently use your fingers to locate it.
By following these steps, you can confidently insert a tampon with an applicator. Remember to relax and take your time. If you experience any discomfort, remove the tampon and try again with a fresh one. For more detailed guidance and tips, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, your trusted resource for menstrual health information.
4. Inserting a Tampon Without an Applicator: A Detailed Guide
Inserting a tampon without an applicator requires a bit more practice and confidence, but it’s a great option for those who prefer a more eco-friendly approach or find applicators uncomfortable. This detailed guide will walk you through each step, ensuring a comfortable and successful insertion.
4.1 Unwrapping the Tampon: Preparing for Insertion
Begin by unwrapping the tampon. Find the uneven place on the wrapper and tear it open. Ensure your hands are clean and dry to prevent contamination.
4.2 Preparing the Tampon: Positioning Your Fingers
Once unwrapped, pull down the strings at the base of the tampon. Place your forefinger at the base of the tampon and your thumb on the side facing you. This grip will give you control during insertion.
4.3 Finding a Comfortable Position: Relaxing Your Body
Choose a comfortable position, such as sitting on the toilet with your legs spread apart or standing with one leg elevated. Relax your muscles to ease the insertion process.
4.4 Inserting the Tampon: Aiming Towards Your Back
Gently insert the tampon into your vaginal opening. Aim slightly upward and toward your back, following the natural curve of your vaginal canal.
4.5 Pushing the Tampon In: How Far It Should Go
Push the tampon inside you about as far as the length of your forefinger. You should feel resistance, but no discomfort. If you feel resistance, adjust the angle slightly and continue pushing gently.
4.6 Ensuring Comfort: Checking the Tampon’s Position
Once the tampon is fully inserted, you shouldn’t feel it. If you feel any discomfort, the tampon may not be inserted far enough. Use your finger to gently push it further in until you no longer feel it.
4.7 Checking the String: Making Sure It’s Accessible
Ensure that the tampon string is hanging outside your body. This string is necessary for removing the tampon later. If the string is not visible, gently use your fingers to locate it.
Inserting a tampon without an applicator can be empowering and environmentally friendly. With practice, it will become a simple and comfortable part of your menstrual routine. For more guidance and tips on menstrual health, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, your trusted resource for comprehensive information.
5. Knowing It’s Right: Checking for Correct Tampon Insertion
One of the most common concerns when starting to use tampons is ensuring they are inserted correctly. A properly inserted tampon should be comfortable and unnoticeable. Knowing the signs of correct insertion can help alleviate anxiety and ensure effective protection. This section will guide you through checking for correct tampon insertion.
5.1 The Comfort Test: You Shouldn’t Feel It
The primary indicator of correct tampon insertion is comfort. Once inserted, you should not feel the tampon. If you experience discomfort, pressure, or a feeling that something is “there,” the tampon may not be inserted far enough or at the correct angle.
5.2 Checking for Leaks: Ensuring Proper Absorption
Another way to check for correct insertion is to monitor for leaks. If the tampon is positioned correctly, it should effectively absorb menstrual flow. If you experience leaks shortly after insertion, the tampon may not be fully expanded or properly placed.
5.3 Moving Around: Assessing Comfort During Activity
Move around and perform typical activities like walking, sitting, and bending over. If the tampon is correctly inserted, these movements should not cause any discomfort. If you feel discomfort during movement, readjust or replace the tampon.
5.4 Adjusting the Tampon: What to Do If It’s Uncomfortable
If you feel discomfort or detect leaks, try adjusting the tampon. Use your finger to gently push the tampon further into your vaginal canal. If adjustment doesn’t resolve the issue, remove the tampon and try again with a fresh one.
5.5 When to Seek Help: Addressing Persistent Discomfort
If you consistently experience discomfort or difficulty with tampon insertion, consult a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance and rule out any underlying issues.
Ensuring correct tampon insertion is crucial for comfort and effectiveness. By following these guidelines, you can confidently use tampons and manage your menstrual flow. For more information and support, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, your trusted source for menstrual health education.
6. Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them: Tips for Tampon Beginners
Starting to use tampons can be a learning process, and it’s common to make a few mistakes along the way. Knowing these common errors and how to avoid them can help you have a smoother and more comfortable experience. This section will highlight common mistakes and provide practical tips for tampon beginners.
6.1 Inserting at the Wrong Angle: Aiming for Comfort
One common mistake is inserting the tampon at the wrong angle. The vaginal canal curves upward and toward your back, not straight up. Aiming the tampon in the wrong direction can cause discomfort and make insertion difficult. Always aim slightly upward and toward your back for a more comfortable fit.
6.2 Not Inserting Far Enough: Ensuring Proper Placement
Another frequent error is not inserting the tampon far enough into the vaginal canal. If the tampon is not inserted far enough, you may feel it, and it may cause discomfort. Push the tampon in until you no longer feel it to ensure proper placement.
6.3 Using the Wrong Absorbency: Choosing the Right Size
Using the wrong absorbency level can lead to discomfort and leaks. If the tampon is too absorbent for your flow, it can cause dryness and irritation. If it’s not absorbent enough, it can lead to leaks. Choose the lowest absorbency level that meets your needs and adjust as necessary.
6.4 Forgetting to Remove the Applicator: Discarding Properly
It’s essential to remember to remove and discard the applicator after inserting the tampon. Leaving the applicator inside can cause discomfort and increase the risk of infection. Always double-check that the applicator is removed before finishing.
6.5 Leaving a Tampon in Too Long: Avoiding Risks
Leaving a tampon in for longer than the recommended 4-8 hours can increase the risk of Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS). Always change your tampon regularly and never leave it in for more than 8 hours.
6.6 Flushing Tampons: Disposing Responsibly
Flushing tampons down the toilet can cause plumbing issues and environmental damage. Always wrap used tampons in toilet paper and dispose of them in a wastebasket.
By being aware of these common mistakes and following these tips, you can avoid potential issues and have a more positive experience with tampons. For more guidance and resources on menstrual health, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, your trusted source for comprehensive information.
7. Removing a Tampon: A Simple Guide
Removing a tampon is a straightforward process, but it’s important to do it correctly to avoid discomfort or injury. This simple guide will walk you through the steps of removing a tampon safely and easily.
7.1 Washing Your Hands: Maintaining Hygiene
As with insertion, start by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water before removing a tampon. This helps prevent the transfer of bacteria and reduces the risk of infection.
7.2 Relaxing Your Muscles: Easing Removal
Relax your muscles to make the removal process easier. Taking a few deep breaths can help ease any tension. If you’re feeling anxious, try to focus on relaxing your pelvic floor muscles.
7.3 Gently Pulling the String: Removing the Tampon
Locate the tampon string and gently pull it downward. The tampon should slide out easily. Avoid pulling forcefully, as this can cause discomfort.
7.4 Disposing of the Tampon: Responsible Disposal
Once the tampon is removed, wrap it in toilet paper and dispose of it in a wastebasket. Do not flush tampons down the toilet, as they can cause plumbing issues and environmental damage.
7.5 Checking the Tampon: Ensuring Complete Removal
After removing the tampon, check to make sure it is intact. If you notice any pieces missing, consult a healthcare professional.
7.6 Washing Your Hands Again: Final Hygiene Step
Wash your hands again after disposing of the tampon. This final step ensures that your hands are clean and free from bacteria.
Removing a tampon is a simple and essential part of using tampons. By following these steps, you can remove a tampon safely and responsibly. For more guidance and information on menstrual health, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, your trusted resource for comprehensive support.
8. Tampon Hygiene: Maintaining Cleanliness and Health
Maintaining proper hygiene when using tampons is essential for preventing infections and ensuring overall health. This section will provide comprehensive guidelines on tampon hygiene, including when to change tampons, how to dispose of them, and tips for staying clean and healthy.
8.1 Changing Tampons Regularly: Preventing Infections
Change your tampon every 4-8 hours to prevent bacterial growth and reduce the risk of Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS). Never leave a tampon in for more than 8 hours. Regular changes help maintain cleanliness and promote good health.
8.2 Using the Lowest Absorbency: Minimizing Risks
Use the lowest absorbency level that meets your needs. Higher absorbency tampons increase the risk of TSS. Choosing the right absorbency helps minimize risks and ensures comfort.
8.3 Washing Your Hands: Before and After
Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before inserting or removing a tampon. This simple step is crucial for preventing the transfer of bacteria and reducing the risk of infection.
8.4 Storing Tampons Properly: Maintaining Cleanliness
Store tampons in a clean, dry place to prevent contamination. Avoid storing them in damp or humid environments, such as the bathroom, as this can promote bacterial growth.
8.5 Disposing of Tampons Responsibly: Protecting the Environment
Wrap used tampons in toilet paper and dispose of them in a wastebasket. Do not flush tampons down the toilet, as they can cause plumbing issues and environmental damage.
8.6 Recognizing Signs of Infection: Seeking Medical Attention
Be aware of the signs of infection, such as fever, rash, dizziness, or muscle aches. If you experience any of these symptoms, remove the tampon and seek medical attention immediately.
8.7 Considering Organic Options: Reducing Chemical Exposure
Consider using organic tampons made from 100% organic cotton to reduce exposure to synthetic materials and chemicals. Organic tampons are a healthier and more environmentally friendly option.
Maintaining proper tampon hygiene is crucial for preventing infections and ensuring overall health. By following these guidelines, you can confidently use tampons and manage your menstrual flow safely and responsibly. For more information and resources on menstrual health, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, your trusted source for comprehensive support.
9. Addressing Concerns: Common Questions About Tampons
Using tampons can bring up many questions, especially for beginners. Addressing these concerns can help alleviate anxiety and provide a better understanding of tampon usage. This section will answer common questions about tampons, providing clarity and confidence.
9.1 Can I Swim with a Tampon In?
Yes, you can swim with a tampon in. Tampons are a convenient option for swimming during your period, as they provide discreet protection. Be sure to change your tampon after swimming to maintain hygiene.
9.2 Can I Sleep with a Tampon In?
Yes, you can sleep with a tampon in, but it’s important to use the lowest absorbency level needed and change it before going to bed and as soon as you wake up. Never leave a tampon in for more than 8 hours to reduce the risk of TSS.
9.3 Will a Tampon Get Lost Inside Me?
No, a tampon cannot get lost inside you. The vaginal canal is a closed space, and the tampon string ensures that you can always remove it.
9.4 Can a Tampon Break My Hymen?
Using tampons can stretch the hymen but will not break it. The hymen is a flexible membrane that naturally has openings, and tampon use is unlikely to cause significant changes.
9.5 What is Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)?
Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS) is a rare but serious bacterial infection associated with tampon use. Symptoms include fever, rash, dizziness, and muscle aches. Prevent TSS by changing tampons regularly and using the lowest absorbency level needed.
9.6 Can I Use Tampons If I’m a Virgin?
Yes, you can use tampons if you’re a virgin. Tampons do not affect your virginity. The hymen is flexible and has natural openings, so tampon use is safe and acceptable.
9.7 How Do I Know Which Absorbency to Use?
Start with the lowest absorbency level (light) and adjust as necessary. If you experience leaks, try a higher absorbency. If the tampon feels dry and uncomfortable, try a lower absorbency.
9.8 What If I Can’t Get the Tampon In?
If you’re having trouble inserting a tampon, relax your muscles and try a different position. Use a lubricant if needed. If you continue to have difficulty, consult a healthcare professional.
9.9 Can Tampons Cause Yeast Infections?
Tampon use can sometimes disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina, potentially leading to yeast infections. To minimize this risk, change tampons regularly and avoid using scented products.
9.10 Are Tampons Bad for the Environment?
Conventional tampons contain plastic and synthetic materials that are not biodegradable. Consider using organic cotton tampons or reusable menstrual products to reduce your environmental impact.
Addressing these common concerns can help you feel more confident and informed about using tampons. For more detailed information and support, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, your trusted source for menstrual health education.
10. Exploring Alternatives: Other Menstrual Products to Consider
While tampons are a popular choice for managing menstrual flow, they are not the only option available. Exploring alternatives can help you find the best fit for your lifestyle and preferences. This section will introduce other menstrual products to consider, offering a comprehensive overview of your options.
10.1 Menstrual Pads: A Classic Choice
Menstrual pads are absorbent products worn inside your underwear to collect menstrual flow. They are available in various sizes and absorbency levels, making them a versatile option. Pads are a good choice for those who prefer external protection or are new to managing their periods.
10.2 Menstrual Cups: Reusable and Eco-Friendly
Menstrual cups are flexible, bell-shaped cups made of silicone or rubber that are inserted into the vagina to collect menstrual flow. They are reusable and can be worn for up to 12 hours, making them an eco-friendly and cost-effective option.
10.3 Period Underwear: Comfortable and Convenient
Period underwear are absorbent underwear designed to be worn during your period. They come in various styles and absorbency levels, providing comfortable and discreet protection. Period underwear are a great option for light to moderate flow days or as backup protection with other products.
10.4 Menstrual Discs: Similar to Menstrual Cups
Menstrual discs are similar to menstrual cups but are flatter and sit higher in the vaginal canal. They collect menstrual flow and can be worn for up to 12 hours. Menstrual discs are a good option for those who find menstrual cups uncomfortable.
10.5 Choosing the Right Product: Factors to Consider
When choosing a menstrual product, consider factors such as:
- Flow Level: Match the product’s absorbency to your flow.
- Comfort: Choose a product that feels comfortable and doesn’t cause irritation.
- Lifestyle: Consider your activity level and daily routine.
- Environmental Impact: Opt for reusable or eco-friendly options.
- Cost: Compare the cost of disposable vs. reusable products.
Exploring alternatives to tampons can help you find the perfect fit for your menstrual needs. Each product offers unique benefits, and the best choice depends on your individual preferences and lifestyle. For more information and guidance on menstrual health, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, your trusted resource for comprehensive support.
At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of reliable information when it comes to personal health and hygiene. If you’re still unsure or have specific concerns about tampon usage, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 555-1234. Our website, conduct.edu.vn, offers a wealth of resources to guide you through every step, ensuring a confident and comfortable experience with menstrual care products.
