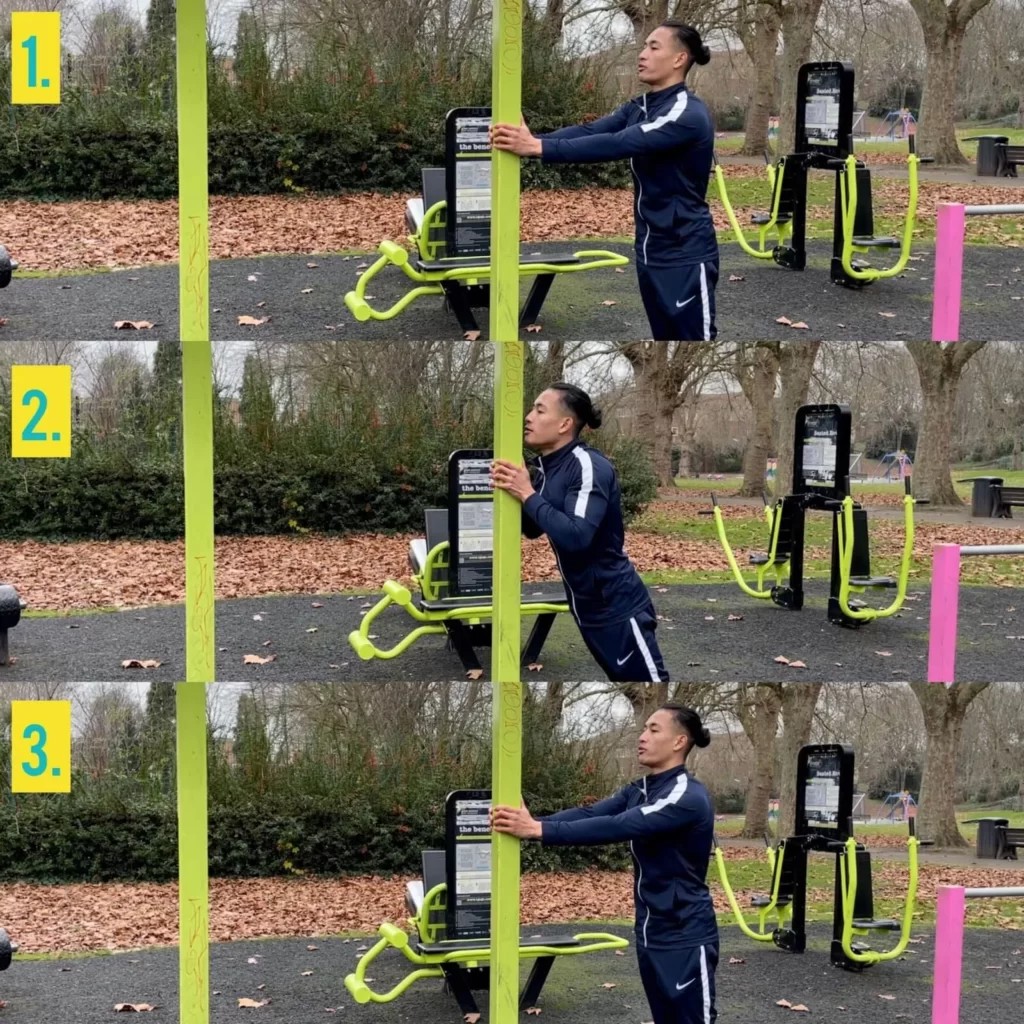
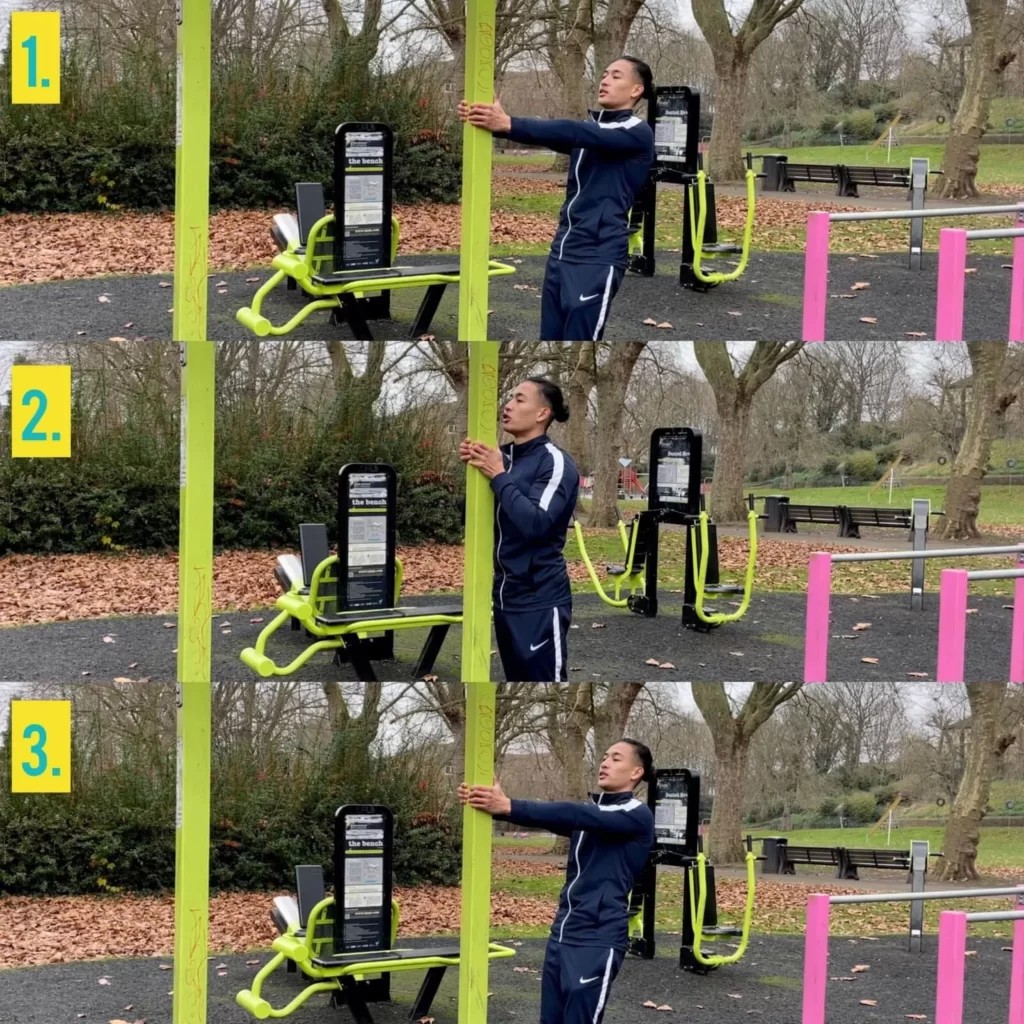
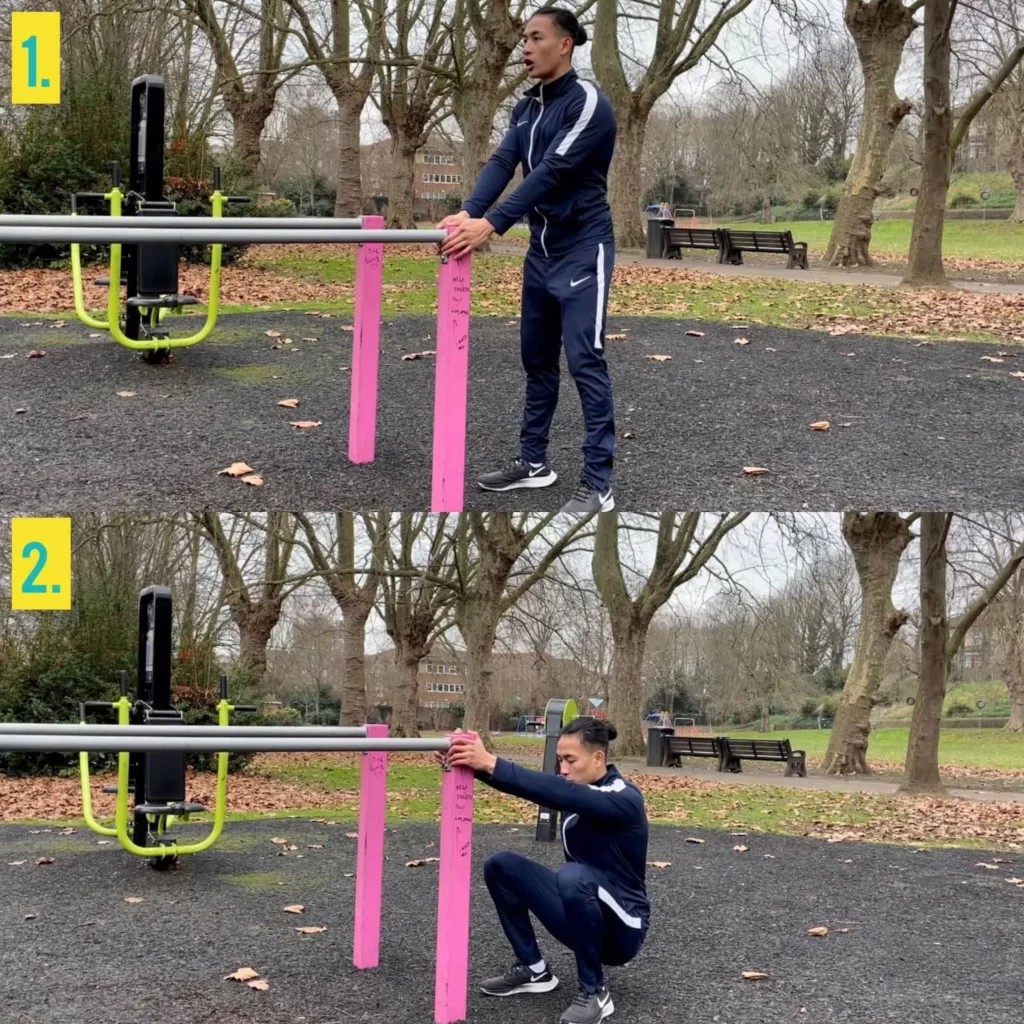
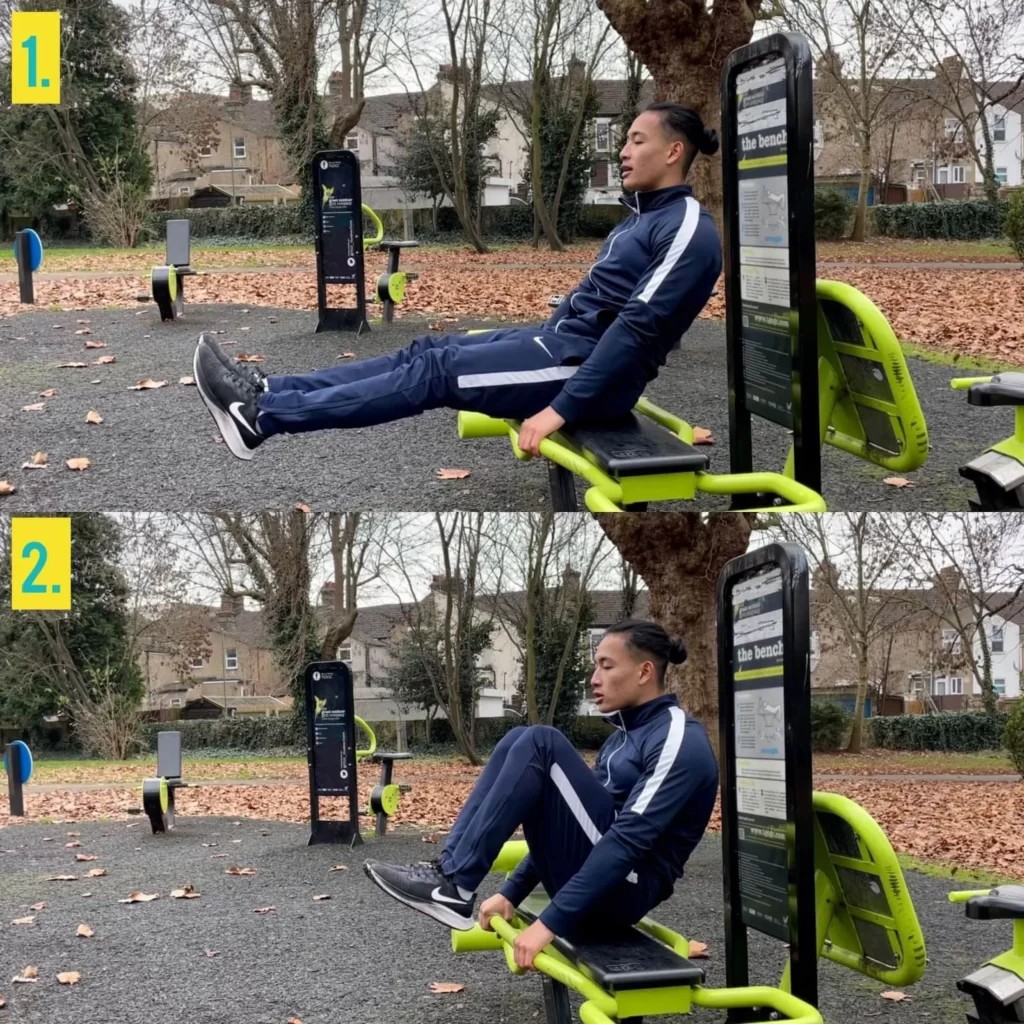
Calisthenics for beginners is a fantastic way to build strength, improve flexibility, and enhance body control using your own bodyweight. CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive resource to understand and implement the core principles of calisthenics. This beginner guide to calisthenics will help you get started safely and effectively, providing practical advice for calisthenics training split and calisthenics workout no equipment.
1. Understanding Calisthenics: An Introduction
Calisthenics is a form of exercise that uses your body weight for resistance. Unlike traditional weightlifting, calisthenics requires minimal or no equipment, making it accessible to everyone, everywhere. It’s about mastering your body and achieving impressive feats of strength and agility.
Calisthenics is derived from the Greek words “Kallos” (beauty) and “Stenos” (strength). This method focuses on creating a harmonious blend of physical strength and aesthetic appeal through bodyweight exercises. Often referred to as “street workout,” calisthenics can be performed outdoors.
1.1 Benefits of Calisthenics
Calisthenics offers several benefits, making it an attractive option for fitness enthusiasts. Here are some key advantages:
- Accessibility: You can do calisthenics anywhere. Whether at home, in a park, or while traveling, you’re not limited by the need for a gym or specialized equipment.
- Full-Body Workout: Calisthenics exercises engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, promoting balanced strength and development.
- Improved Functional Strength: Calisthenics builds strength that translates directly into real-world activities. You’ll find everyday tasks becoming easier as your body adapts to these movements.
- Enhanced Flexibility and Mobility: Many calisthenics exercises require a full range of motion, which can improve your flexibility and joint mobility over time.
- Cost-Effective: Without the need for expensive gym memberships or equipment, calisthenics is an affordable way to stay fit.
- Versatility: From basic exercises like push-ups and squats to advanced movements like planches and muscle-ups, calisthenics can be adapted to suit all fitness levels.
- Mind-Body Connection: Calisthenics requires focus and body awareness, which helps develop a stronger mind-body connection.
- Cardiovascular Health: Calisthenics workouts can be structured to elevate your heart rate and improve cardiovascular health.
- Progressive Overload: You can continuously challenge yourself by increasing the difficulty of exercises, adding repetitions, or reducing rest times.
- Injury Prevention: Strengthening your muscles, tendons, and ligaments through calisthenics can help prevent injuries.
- Mental Toughness: Mastering challenging calisthenics movements can build mental resilience and determination.
- Community: The calisthenics community is supportive and encouraging, offering a great way to stay motivated and learn from others.
1.2 Calisthenics vs. Weightlifting
While both calisthenics and weightlifting are effective forms of exercise, they differ significantly in their approach and benefits. Here’s a comparison:
| Feature | Calisthenics | Weightlifting |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance | Bodyweight | External weights (dumbbells, barbells, machines) |
| Equipment | Minimal or no equipment required | Requires weights, machines, and possibly a gym membership |
| Focus | Functional strength, body control, and coordination | Muscle hypertrophy (growth), maximal strength, and power |
| Accessibility | Can be done anywhere | Typically requires access to a gym or weight room |
| Muscle Engagement | Engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously | Can isolate specific muscle groups |
| Injury Risk | Lower risk of injury if performed correctly | Higher risk of injury if form is incorrect or weights are too heavy |
| Progression | Progress by increasing exercise difficulty (e.g., from push-ups to planche) | Progress by increasing the weight lifted |
| Cost | Low cost | High cost (gym memberships, equipment) |
| Flexibility | Improves flexibility and mobility | Can limit flexibility if not combined with stretching |
| Joint Health | Promotes joint health and stability | Can strain joints if proper form is not maintained |
| Example Exercises | Push-ups, pull-ups, squats, planks, dips | Bench press, squats, deadlifts, bicep curls |
Choosing between calisthenics and weightlifting depends on your fitness goals. If you aim for functional strength, body control, and convenience, calisthenics is an excellent choice. If you prioritize muscle growth and maximal strength, weightlifting might be more suitable. Many people find a combination of both to be the most effective approach.
2. Essential Calisthenics Exercises for Beginners
Starting calisthenics involves mastering fundamental exercises that build a solid foundation of strength and coordination. Here are the essential exercises every beginner should focus on:
2.1 Push-Ups
Push-ups are a cornerstone of calisthenics, working your chest, shoulders, triceps, and core. They are easily scalable, making them perfect for beginners.
How to Perform a Proper Push-Up:
- Start in a plank position with your hands shoulder-width apart and your body forming a straight line from head to heels.
- Lower your body until your chest nearly touches the ground, keeping your elbows close to your body.
- Push back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
- Maintain a straight line throughout the exercise, engaging your core to prevent sagging.
Modifications for Beginners:
- Wall Push-Ups: Stand facing a wall, place your hands on the wall at shoulder height, and perform push-ups against the wall.
- Incline Push-Ups: Place your hands on an elevated surface like a bench or box to make the exercise easier.
- Knee Push-Ups: Perform push-ups on your knees to reduce the amount of weight you’re lifting.
Progression:
- Decline Push-Ups: Place your feet on an elevated surface to increase the difficulty.
- Diamond Push-Ups: Bring your hands close together under your chest to target your triceps more.
- One-Arm Push-Ups: Perform push-ups with one arm to increase the challenge significantly.
2.2 Pull-Ups
Pull-ups are an excellent exercise for developing upper body strength, targeting your back, biceps, and forearms. They can be challenging for beginners, but with the right modifications, they are achievable.
How to Perform a Proper Pull-Up:
- Grip a pull-up bar with your hands shoulder-width apart and an overhand grip.
- Hang from the bar with your arms fully extended and your feet off the ground.
- Pull yourself up until your chin is above the bar, keeping your body straight.
- Lower yourself back down to the starting position with control.
Modifications for Beginners:
- Assisted Pull-Ups: Use an assisted pull-up machine or resistance band to reduce the amount of weight you’re lifting.
- Negative Pull-Ups: Jump or step up to the top position of a pull-up, then slowly lower yourself down to the starting position.
- Inverted Rows: Use a low bar or suspension trainer to perform rows with your body at an angle.
Progression:
- Weighted Pull-Ups: Add weight using a weight belt or by holding a dumbbell between your feet.
- Muscle-Ups: Combine a pull-up with a dip to lift your entire body over the bar.
- One-Arm Pull-Ups: Perform pull-ups with one arm to increase the challenge significantly.
2.3 Squats
Squats are a fundamental lower body exercise that works your quads, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. They are essential for building leg strength and improving overall athletic performance.
How to Perform a Proper Squat:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and your toes slightly pointing outward.
- Lower your body as if you’re sitting back into a chair, keeping your back straight and your chest up.
- Continue lowering until your thighs are parallel to the ground or as low as you can comfortably go.
- Push back up to the starting position, engaging your glutes and quads.
Modifications for Beginners:
- Chair Squats: Lower yourself until you gently touch a chair or bench, then push back up.
- Box Squats: Use a box or platform to ensure you’re reaching the correct depth.
- Assisted Squats: Hold onto a stable object for support as you squat.
Progression:
- Jump Squats: Perform squats and explode upward into a jump.
- Pistol Squats: Perform squats on one leg to increase the difficulty significantly.
- Weighted Squats: Hold a dumbbell or wear a weight vest to add resistance.
2.4 Dips
Dips are a great exercise for developing your chest, shoulders, and triceps. They can be performed on parallel bars or using dip bars.
How to Perform a Proper Dip:
- Grip the parallel bars with your hands shoulder-width apart and your arms fully extended.
- Lower your body by bending your elbows, keeping them close to your body.
- Continue lowering until your shoulders are below your elbows or as low as you can comfortably go.
- Push back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
Modifications for Beginners:
- Bench Dips: Use a bench or chair to support your hands, and lower your body towards the ground.
- Assisted Dips: Use an assisted dip machine or resistance band to reduce the amount of weight you’re lifting.
Progression:
- Weighted Dips: Add weight using a weight belt or by holding a dumbbell between your feet.
- Ring Dips: Perform dips on gymnastic rings to increase the instability and challenge.
2.5 Planks
Planks are an excellent exercise for strengthening your core, including your abs, obliques, and lower back. They also improve your posture and stability.
How to Perform a Proper Plank:
- Start in a push-up position, but instead of placing your hands on the ground, rest on your forearms.
- Keep your body in a straight line from head to heels, engaging your core to prevent sagging.
- Hold the position for as long as you can maintain good form.
Modifications for Beginners:
- Knee Planks: Perform planks on your knees to reduce the amount of weight you’re supporting.
- Incline Planks: Place your forearms on an elevated surface to make the exercise easier.
Progression:
- Side Planks: Perform planks on your side, supporting your body with one forearm.
- Plank with Leg Lift: Lift one leg off the ground while maintaining a plank position.
- Plank with Arm Lift: Lift one arm off the ground while maintaining a plank position.
2.6 Leg Raises
Leg raises are an effective exercise for targeting your lower abs and hip flexors. They can be performed hanging from a bar or lying on the ground.
How to Perform Hanging Leg Raises:
- Hang from a pull-up bar with your arms fully extended.
- Raise your legs by flexing at your hips, bringing your knees towards your chest.
- Lower your legs back down to the starting position with control.
How to Perform Lying Leg Raises:
- Lie on your back with your legs extended and your hands by your sides or under your glutes for support.
- Raise your legs off the ground, keeping them straight or slightly bent.
- Lower your legs back down to the starting position with control, but don’t let them touch the ground.
Modifications for Beginners:
- Knee Raises: Perform leg raises by bringing your knees towards your chest instead of keeping your legs straight.
- Incline Leg Raises: Perform leg raises on an inclined bench to make the exercise easier.
Progression:
- Hanging Straight Leg Raises: Perform leg raises while keeping your legs straight.
- Lying Straight Leg Raises: Perform leg raises while lying on the ground and keeping your legs straight.
- Weighted Leg Raises: Hold a dumbbell between your feet to add resistance.
3. Creating Your First Calisthenics Workout Routine
Designing a beginner-friendly calisthenics routine involves selecting exercises that match your current fitness level and progressively increasing the challenge as you improve. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating your first calisthenics workout routine:
3.1 Assess Your Current Fitness Level
Before starting any workout routine, it’s important to assess your current fitness level. This will help you choose exercises that are appropriate for you and avoid injuries.
- Strength Test: How many push-ups, pull-ups, squats, and dips can you perform with good form?
- Flexibility Test: Can you touch your toes? How easily can you move your joints through their full range of motion?
- Endurance Test: How long can you hold a plank? How long can you perform bodyweight exercises without getting fatigued?
3.2 Select Your Exercises
Choose exercises that target all major muscle groups and align with your fitness goals. For beginners, it’s best to focus on the fundamental exercises listed above.
- Upper Body: Push-ups, pull-ups, dips
- Lower Body: Squats, lunges
- Core: Planks, leg raises
3.3 Determine Your Sets and Reps
The number of sets and reps you perform will depend on your fitness level and goals. Here are some general guidelines for beginners:
- Sets: 3-4 sets per exercise
- Reps: 8-12 reps per set
If you can’t perform 8 reps with good form, modify the exercise to make it easier. If you can easily perform 12 reps, consider progressing to a more difficult variation.
3.4 Plan Your Workout Schedule
Consistency is key to seeing results with calisthenics. Plan your workout schedule to ensure you’re training regularly.
- Frequency: 3-4 workouts per week
- Rest: Allow at least one day of rest between workouts to allow your muscles to recover.
Here’s an example of a beginner calisthenics workout schedule:
- Monday: Workout A
- Tuesday: Rest
- Wednesday: Workout B
- Thursday: Rest
- Friday: Workout A
- Saturday: Rest
- Sunday: Workout B
3.5 Example Beginner Calisthenics Workout Routines
Here are two example beginner calisthenics workout routines you can follow:
Workout A
- Push-ups: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Squats: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Planks: 3 sets of 30-60 seconds
- Leg Raises: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Inverted Rows: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
Workout B
- Dips: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Lunges: 3 sets of 8-12 reps per leg
- Side Planks: 3 sets of 30-60 seconds per side
- Knee Raises: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Wall Push-ups: 3 sets of 15-20 reps
3.6 Warm-Up and Cool-Down
Always start your workout with a warm-up and end with a cool-down to prevent injuries and improve recovery.
- Warm-Up: 5-10 minutes of light cardio and dynamic stretching, such as arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists.
- Cool-Down: 5-10 minutes of static stretching, holding each stretch for 30 seconds.
4. Progressing in Calisthenics: Intermediate and Advanced Exercises
Once you’ve mastered the fundamental exercises, it’s time to progress to more challenging variations and new movements. Here’s how to continue advancing in calisthenics:
4.1 Increase Exercise Difficulty
The simplest way to progress in calisthenics is to increase the difficulty of your exercises. Here are some examples:
- Push-Ups: Progress from knee push-ups to regular push-ups to decline push-ups to diamond push-ups to one-arm push-ups.
- Pull-Ups: Progress from assisted pull-ups to negative pull-ups to regular pull-ups to weighted pull-ups to muscle-ups.
- Squats: Progress from chair squats to regular squats to jump squats to pistol squats to weighted squats.
- Dips: Progress from bench dips to assisted dips to regular dips to weighted dips to ring dips.
- Planks: Progress from knee planks to regular planks to side planks to plank with leg lift to plank with arm lift.
- Leg Raises: Progress from knee raises to lying leg raises to hanging leg raises to hanging straight leg raises.
4.2 Learn New Exercises
As you get stronger, you can start learning new and more advanced calisthenics exercises. Here are some examples:
- Handstand Push-Ups: Perform push-ups while in a handstand position against a wall.
- Front Lever: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your arms extended in front of you.
- Back Lever: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your arms extended behind you.
- Planche: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your arms fully extended and your feet off the ground.
- Muscle-Ups: Combine a pull-up with a dip to lift your entire body over the bar.
4.3 Increase Training Volume
Another way to progress in calisthenics is to increase your training volume. This can be done by:
- Increasing Sets: Add more sets to your workouts.
- Increasing Reps: Increase the number of reps you perform per set.
- Reducing Rest Time: Reduce the amount of rest time between sets.
- Increasing Frequency: Add more workouts per week.
4.4 Calisthenics Training Split
To optimize your training and allow for adequate recovery, consider using a calisthenics training split. Here are some popular options:
- Full Body: Train all major muscle groups in each workout (3-4 workouts per week).
- Upper/Lower: Alternate between upper body and lower body workouts (4-6 workouts per week).
- Push/Pull/Legs: Divide your workouts into push exercises (chest, shoulders, triceps), pull exercises (back, biceps, forearms), and leg exercises (4-6 workouts per week).
4.5 Listen to Your Body
As you progress in calisthenics, it’s important to listen to your body and avoid overtraining. Pay attention to signs of fatigue, soreness, and injury, and adjust your training accordingly. Make sure to rest and recover properly, and don’t be afraid to take a break when needed.
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid in Calisthenics
To maximize your results and prevent injuries, it’s important to avoid common mistakes in calisthenics. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for:
5.1 Neglecting Proper Form
Proper form is crucial for preventing injuries and maximizing the effectiveness of your exercises. Avoid rushing through your reps and focus on maintaining good form throughout each exercise.
5.2 Skipping the Warm-Up and Cool-Down
Warming up and cooling down are essential for preparing your body for exercise and promoting recovery. Don’t skip these steps, as they can help prevent injuries and improve your performance.
5.3 Overlooking Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is the key to seeing results with calisthenics. Make sure you’re continuously challenging yourself by increasing the difficulty of your exercises, adding repetitions, or reducing rest times.
5.4 Ignoring Rest and Recovery
Rest and recovery are just as important as training. Make sure you’re getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and allowing your muscles to recover between workouts.
5.5 Comparing Yourself to Others
Everyone progresses at their own pace, so don’t compare yourself to others. Focus on your own journey and celebrate your own achievements.
5.6 Training Through Pain
Pain is a sign that something is wrong. Don’t train through pain, as this can lead to injuries. If you experience pain during an exercise, stop immediately and consult with a healthcare professional.
5.7 Lack of Consistency
Consistency is key to seeing results with calisthenics. Make sure you’re training regularly and sticking to your workout schedule.
6. Staying Motivated and Consistent
Staying motivated and consistent with your calisthenics training can be challenging, but there are several strategies you can use to stay on track:
6.1 Set Realistic Goals
Set realistic goals that are achievable and measurable. This will help you stay motivated and track your progress.
6.2 Find a Training Partner
Training with a partner can provide accountability and motivation. You can encourage each other, share tips, and make the workouts more enjoyable.
6.3 Join a Calisthenics Community
Joining a calisthenics community can provide support, encouragement, and inspiration. You can connect with other calisthenics enthusiasts, share your experiences, and learn from others.
6.4 Track Your Progress
Tracking your progress can help you stay motivated and see how far you’ve come. Keep a workout journal, take progress photos, or use a fitness app to track your workouts and results.
6.5 Reward Yourself
Reward yourself for achieving your goals. This could be anything from buying new workout gear to treating yourself to a massage.
6.6 Make It Fun
Find ways to make your workouts more enjoyable. This could be anything from listening to music to training outdoors.
6.7 Be Patient
Progress takes time, so be patient and don’t get discouraged if you don’t see results immediately. Stick with your training and trust the process.
7. Nutrition and Calisthenics
Nutrition plays a crucial role in your calisthenics journey. Eating a healthy diet can help you build muscle, lose fat, and improve your overall performance. Here are some nutrition tips for calisthenics enthusiasts:
7.1 Eat a Balanced Diet
Eat a balanced diet that includes plenty of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
- Protein: Essential for building and repairing muscle tissue. Good sources include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, and plant-based sources like beans, lentils, and tofu.
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy for your workouts. Good sources include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Healthy Fats: Important for hormone production and overall health. Good sources include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish.
7.2 Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, muscle cramps, and decreased performance.
7.3 Time Your Meals
Time your meals to optimize your energy levels and recovery.
- Pre-Workout: Eat a meal or snack that’s high in carbohydrates and moderate in protein about 1-2 hours before your workout.
- Post-Workout: Eat a meal or snack that’s high in protein and carbohydrates within 1-2 hours after your workout to replenish your glycogen stores and repair muscle tissue.
7.4 Consider Supplements
Consider taking supplements to support your training and nutrition. Some popular supplements for calisthenics enthusiasts include:
- Creatine: Helps increase strength and power.
- Protein Powder: Helps with muscle recovery and growth.
- BCAAs: Help reduce muscle soreness and fatigue.
- Vitamin D: Important for bone health and immune function.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Important for heart health and brain function.
7.5 Avoid Processed Foods
Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of unhealthy fats. These foods can hinder your progress and negatively impact your health.
8. Safety Tips for Calisthenics
Safety should always be a top priority when practicing calisthenics. Here are some safety tips to keep in mind:
8.1 Consult with a Healthcare Professional
Before starting any new exercise program, consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it’s safe for you.
8.2 Start Slowly
Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
8.3 Use Proper Form
Use proper form for all exercises to prevent injuries.
8.4 Warm-Up and Cool-Down
Always warm up before your workouts and cool down afterward.
8.5 Listen to Your Body
Listen to your body and stop if you experience pain.
8.6 Use Spotters
Use spotters when performing difficult exercises, such as dips and pull-ups.
8.7 Train in a Safe Environment
Train in a safe environment that is free from hazards.
8.8 Use Proper Equipment
Use proper equipment, such as a sturdy pull-up bar and exercise mat.
8.9 Stay Hydrated
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water before, during, and after your workouts.
8.10 Get Enough Rest
Get enough rest to allow your body to recover.
9. Calisthenics for Different Body Types
Calisthenics can be adapted to suit different body types and fitness goals. Here’s how to tailor your training to your individual needs:
9.1 Ectomorph (Naturally Lean)
Ectomorphs typically have a fast metabolism and find it difficult to gain weight. For ectomorphs, focus on:
- High-Calorie Diet: Consume a high-calorie diet with plenty of protein and carbohydrates.
- Compound Exercises: Focus on compound exercises like push-ups, pull-ups, and squats to build muscle.
- Progressive Overload: Continuously challenge yourself to stimulate muscle growth.
- Rest and Recovery: Prioritize rest and recovery to allow your muscles to rebuild and grow.
9.2 Mesomorph (Naturally Muscular)
Mesomorphs tend to gain muscle easily and have a naturally athletic build. For mesomorphs, focus on:
- Balanced Diet: Consume a balanced diet with a moderate amount of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
- Variety of Exercises: Incorporate a variety of exercises to challenge your muscles from different angles.
- High-Intensity Workouts: Focus on high-intensity workouts to maximize muscle growth and fat loss.
- Maintenance: Maintain a consistent training routine to preserve muscle mass and strength.
9.3 Endomorph (Naturally Curvy)
Endomorphs typically have a slower metabolism and find it easier to gain weight. For endomorphs, focus on:
- Calorie Deficit: Consume a calorie deficit to promote fat loss.
- High-Protein Diet: Eat a high-protein diet to preserve muscle mass.
- Cardio: Incorporate cardio exercises to burn calories and improve cardiovascular health.
- Interval Training: Focus on high-intensity interval training (HIIT) to maximize fat loss.
9.4 Adapting Calisthenics to Specific Goals
Whether your goal is to build muscle, lose fat, or improve your overall fitness, calisthenics can be tailored to your specific needs.
- Building Muscle: Focus on compound exercises, progressive overload, and a high-protein diet.
- Losing Fat: Focus on a calorie deficit, high-intensity workouts, and cardio exercises.
- Improving Fitness: Focus on a balanced routine that includes a variety of exercises and a healthy diet.
10. Advanced Calisthenics Skills and Drills
Once you’ve mastered the basics and intermediate exercises, you can start working towards advanced calisthenics skills. These require a high level of strength, coordination, and body control. Here are some advanced skills and drills to consider:
10.1 Handstand
The handstand is a foundational skill for many advanced calisthenics movements. It requires balance, strength, and coordination.
Drills for Handstand:
- Wall Handstands: Practice holding a handstand against a wall to build strength and balance.
- Handstand Push-Ups: Perform push-ups while in a handstand position against a wall.
- Freestanding Handstands: Practice holding a handstand away from the wall, gradually increasing the duration.
10.2 Front Lever
The front lever is a challenging skill that requires tremendous back and core strength.
Drills for Front Lever:
- Tuck Front Lever: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your knees tucked towards your chest.
- Advanced Tuck Front Lever: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your knees slightly extended.
- Straddle Front Lever: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your legs straddled.
- Full Front Lever: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your legs fully extended.
10.3 Back Lever
The back lever is another challenging skill that requires significant back and core strength.
Drills for Back Lever:
- Tuck Back Lever: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your knees tucked towards your chest.
- Advanced Tuck Back Lever: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your knees slightly extended.
- Straddle Back Lever: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your legs straddled.
- Full Back Lever: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your legs fully extended.
10.4 Planche
The planche is one of the most impressive and difficult calisthenics skills, requiring incredible strength and body control.
Drills for Planche:
- Tuck Planche: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your knees tucked towards your chest and your arms fully extended.
- Advanced Tuck Planche: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your knees slightly extended and your arms fully extended.
- Straddle Planche: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your legs straddled and your arms fully extended.
- Full Planche: Hold your body parallel to the ground with your legs fully extended and your arms fully extended.
10.5 Muscle-Up
The muscle-up is a dynamic movement that combines a pull-up with a dip to lift your entire body over the bar.
Drills for Muscle-Up:
- Explosive Pull-Ups: Perform pull-ups with as much force and speed as possible.
- Transition Work: Practice transitioning from the pull-up to the dip position.
- Assisted Muscle-Ups: Use an assisted muscle-up machine or resistance band to reduce the amount of weight you’re lifting.
- Full Muscle-Ups: Perform muscle-ups without assistance.
11. Calisthenics and Mental Health
Calisthenics offers numerous physical benefits, but it also has a positive impact on mental health. Regular exercise can:
- Reduce Stress: Calisthenics can help lower stress hormones and promote relaxation.
- Improve Mood: Exercise releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects.
- Increase Self-Esteem: Achieving fitness goals and mastering new skills can boost your self-esteem and confidence.
- Reduce Anxiety and Depression: Exercise has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Improve Sleep: Regular exercise can improve your sleep quality.
- Enhance Cognitive Function: Exercise can improve cognitive function and memory.
To maximize the mental health benefits of calisthenics:
- Be Mindful: Focus on your body and breath during your workouts.
- Set Realistic Goals: Avoid setting unrealistic expectations and focus on progress, not perfection.
- Celebrate Your Achievements: Acknowledge and celebrate your progress, no matter how small.
- Practice Gratitude: Take time to appreciate your body and its capabilities.
- Connect with Others: Join a calisthenics community and connect with other enthusiasts.
12. Calisthenics Resources and Communities
To further enhance your calisthenics journey, here are some valuable resources and communities to explore:
12.1 Online Resources
- conduct.edu.vn: Offers detailed guides and insights into calisthenics principles and techniques.
- YouTube Channels: Channels like THENX, Calisthenics Movement, and FitnessFAQs provide tutorials, workout routines, and tips.
- Websites and Blogs: Websites like BarBend, Bodybuilding.com, and Nerd Fitness offer articles, workout plans, and nutrition advice.
12.2 Social Media Groups
- Facebook Groups: Join calisthenics groups on Facebook to connect with other enthusiasts, share your progress, and ask questions.
- Instagram: Follow calisthenics athletes and trainers on Instagram for inspiration and tips.
- Reddit: Check out the r/calisthenics subreddit for discussions, advice, and resources.
12.3 Mobile Apps
- Madbarz: Offers customizable calisthenics workouts and progress tracking.
- Freeletics: Provides personalized training plans and a supportive community.
- Thenx: Features workout programs and tutorials from experienced calisthenics athletes.
12.4 Books
- “Complete Calisthenics” by Ashley Kalym: A comprehensive guide to calisthenics exercises and training principles.
- “Convict Conditioning” by Paul Wade: A minimalist calisthenics program based on old-school prison workouts.
- “You Are Your Own Gym” by Mark Lauren: A bodyweight training program designed for busy people.
13. Calisthenics for Women
Calisthenics is a great form of exercise for women, offering numerous benefits such as increased strength, improved body composition, and enhanced overall fitness. Here are some considerations for women starting calisthenics:
13.1 Focus on Proper Form
Proper form is crucial for preventing injuries, especially for women who may be more prone to certain types of injuries. Focus on maintaining good form throughout each exercise and avoid rushing through your reps.
13.2 Modify Exercises as Needed
Don’t be afraid to modify exercises to suit your fitness level and body type. Start with easier variations and gradually progress to more difficult ones as you get stronger.
13.3 Incorporate Variety
Incorporate a variety of exercises to target all major muscle groups and prevent boredom.
13.4 Prioritize Nutrition
Eat a healthy diet that includes plenty of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
13.5 Don’t Be Afraid to Lift Weights
Calisthenics can be combined with weightlifting to create a well-rounded fitness routine. Don’t be afraid to lift weights to build muscle and increase your strength.
13.6 Listen to Your Body
Listen to your body and rest when you need to. Don’t push yourself too hard, especially when starting