Navigating menstrual hygiene can be empowering, and How To Use A Tampon Visual Guide from CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides a clear and comprehensive understanding of tampon insertion and usage. This guide aims to demystify the process with easy-to-follow instructions and visual aids, ensuring a comfortable and confident experience. Whether you’re a beginner or seeking to refine your technique, this detailed resource will help you manage your period with ease and assurance, promoting safer period practices and menstrual health awareness.
1. Understanding the Benefits of Tampons
Tampons offer a range of benefits that make them a popular choice for menstrual management. Their compact size and portability make them ideal for active lifestyles, allowing you to participate in activities such as swimming, running, and other sports without discomfort or inconvenience. Unlike pads, tampons are discreet and virtually invisible under clothing, providing confidence in any outfit, even tight-fitting ones.
Moreover, many tampons are now made with eco-friendly materials like 100% organic cotton, which reduces environmental impact. The absence of synthetic materials also minimizes the risk of irritation and allergic reactions, making them a healthier option for many users. Choosing organic tampons and recyclable applicators can significantly lessen your ecological footprint while ensuring comfort and safety during your period.
2. Tampon Types: A Comprehensive Overview
Tampons are designed to absorb menstrual flow internally and come in various types to suit different preferences and needs. Understanding the different options available can help you choose the best tampon for your body and lifestyle.
2.1. Applicator Tampons
Applicator tampons are the most common type and come with either a plastic or cardboard applicator to facilitate insertion.
- Plastic Applicator Tampons: These applicators are smooth and easy to use, providing a comfortable grip and precise insertion. They are particularly useful for beginners or those who prefer a more hygienic option.
- Cardboard Applicator Tampons: These are an eco-friendly alternative to plastic applicators. Made from biodegradable cardboard, they reduce plastic waste while still providing a convenient way to insert the tampon.
2.2. Non-Applicator Tampons
Non-applicator tampons are inserted directly using your fingers. They are compact and produce less waste, making them a sustainable choice for environmentally conscious users. While they may require a bit more practice to insert correctly, many find them just as effective and comfortable as applicator tampons.
2.3. Absorbency Levels
Tampons come in various absorbency levels to match different flow intensities. It’s essential to choose the right absorbency to avoid discomfort and reduce the risk of Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS).
The FDA provides clear guidelines on absorbency levels:
- Light: For very light flow
- Regular: For light to moderate flow
- Super: For moderate to heavy flow
- Super Plus: For very heavy flow
Always use the lowest absorbency necessary to manage your flow and change your tampon every 4-8 hours.
| Tampon Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Plastic Applicator | Tampon with a smooth plastic applicator for easy insertion | Hygienic, easy to grip, precise insertion |
| Cardboard Applicator | Tampon with a biodegradable cardboard applicator | Eco-friendly, reduces plastic waste, convenient |
| Non-Applicator | Tampon inserted directly with fingers | Compact, less waste, sustainable |
| Absorbency Levels | Light, Regular, Super, Super Plus | Matches different flow intensities, reduces discomfort, minimizes TSS risk |

Choosing the right tampon type and absorbency level ensures a comfortable and safe menstrual experience. Understanding your body’s needs and preferences will guide you in making the best choice for your individual requirements.
3. Preparing for Tampon Insertion: Essential Steps
Before inserting a tampon, proper preparation is key to ensuring a comfortable and hygienic experience. Here are the essential steps to follow:
3.1. Hand Hygiene
Begin by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water. This prevents the transfer of bacteria to the tampon and reduces the risk of infection. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), proper hand hygiene is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of germs.
3.2. Choosing the Right Absorbency
Select the appropriate tampon absorbency level based on your menstrual flow. Using a tampon with higher absorbency than needed can lead to dryness and irritation. It’s advisable to start with a lower absorbency, especially if you are new to using tampons, and adjust as necessary. Remember, using the lightest absorbency tampon for your flow reduces the risk of Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS).
3.3. Getting Comfortable
Find a comfortable position to insert the tampon. Many women find it easiest to sit on the toilet with their knees apart or stand with one leg propped up on the edge of the tub or toilet seat. Experiment to find the position that works best for you.
3.4. Understanding Your Anatomy
Familiarize yourself with your vaginal opening. Knowing the location and angle of your vagina can make insertion smoother and more comfortable. If you are unsure, you can use a mirror to help guide you.
3.5. Staying Relaxed
Relaxation is crucial for easy tampon insertion. Tensing your muscles can make the process more difficult and uncomfortable. Take a few deep breaths to relax your body and mind before you begin.
| Preparation Step | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Hand Hygiene | Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water | Prevents transfer of bacteria and reduces infection risk |
| Choosing Right Absorbency | Select tampon absorbency level based on menstrual flow | Avoids dryness and irritation, reduces risk of TSS |
| Getting Comfortable | Find a comfortable position (sitting or standing) | Makes insertion smoother and more comfortable |
| Understanding Anatomy | Familiarize yourself with vaginal opening | Guides insertion and reduces discomfort |
| Staying Relaxed | Take deep breaths to relax body and mind | Prevents muscle tension, making insertion easier |
4. Step-by-Step Visual Guide to Tampon Insertion
Inserting a tampon can seem daunting at first, but with the right technique, it becomes a simple and routine part of menstrual hygiene. Here’s a detailed visual guide for each type of tampon applicator.
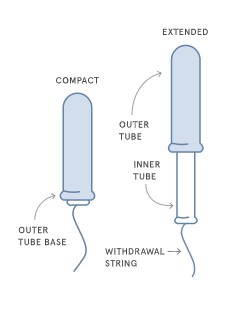
4.1. Inserting a Tampon with a Compact Plastic Applicator
- Extend the Applicator: Before inserting, fully extend the applicator by gently pulling the inner tube until it stops.
- Grip the Applicator: Hold the extended applicator between your thumb and middle finger at the grip, usually located at the wider end of the applicator.
- Position Yourself: Find a comfortable position, such as sitting on the toilet or standing with one leg elevated.
- Insert the Applicator: Gently insert the rounded tip of the applicator into your vaginal opening. Angle it slightly upward towards your back, as this follows the natural curve of your vaginal canal.
- Slide the Applicator: Continue to slide the applicator in until your fingers touch your body.
- Push the Inner Tube: Use your index finger to push the inner tube completely into the outer tube. This releases the tampon into your vagina.
- Remove the Applicator: Gently remove the applicator, leaving the string hanging outside your body.
- Dispose of the Applicator: Wrap the applicator in toilet paper and dispose of it in a wastebasket. Do not flush it down the toilet. Recycle the wrapper if possible.
4.2. Inserting a Tampon with a Cardboard Applicator
- Prepare the Applicator: Slightly twist the outer and inner tubes in opposite directions to unlock the tabs holding the applicator together.
- Grip the Applicator: Hold the applicator between your thumb and middle finger at the grip.
- Position Yourself: Find a comfortable position.
- Insert the Applicator: Gently insert the rounded tip of the applicator into your vaginal opening, angling it slightly upward towards your back.
- Slide the Applicator: Continue to slide the applicator in until your fingers touch your body.
- Push the Inner Tube: Use your index finger to push the inner tube completely into the outer tube, releasing the tampon.
- Remove the Applicator: Gently remove the applicator, leaving the string hanging outside your body.
- Dispose of the Applicator: Dispose of the cardboard applicator in a wastebasket. Check with your local recycling facility to see if they accept cardboard applicators for recycling, as some may classify them as biohazards.
4.3. Inserting a Non-Applicator Tampon
- Unwrap the Tampon: Remove the tampon from its wrapper.
- Prepare the String: Pull down the strings at the base of the tampon.
- Position Your Finger: Place your forefinger at the base of the tampon and your thumb on the side facing you.
- Position Yourself: Find a comfortable position.
- Insert the Tampon: Aiming towards your back, push the tampon inside you about as far as the length of your forefinger.
- Ensure Proper Placement: The tampon should be inserted deep enough that you cannot feel it. If you feel discomfort, it may not be inserted far enough.
- Check the String: Ensure the string is hanging outside your body for easy removal.
| Step | Compact Plastic Applicator | Cardboard Applicator | Non-Applicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Extend applicator fully | Twist outer and inner tubes to unlock | Unwrap tampon, pull down strings |
| 2. Grip | Hold between thumb and middle finger at grip | Hold between thumb and middle finger at grip | Place forefinger at base of tampon, thumb on side |
| 3. Position | Comfortable position (sitting or standing) | Comfortable position (sitting or standing) | Comfortable position (sitting or standing) |
| 4. Insertion | Insert rounded tip into vaginal opening, angling slightly upward | Insert rounded tip into vaginal opening, angling slightly upward | Aim towards back, push tampon in as far as forefinger length |
| 5. Depth | Slide in until fingers touch body | Slide in until fingers touch body | Ensure tampon is inserted deep enough that you cannot feel it |
| 6. Release | Push inner tube completely into outer tube to release tampon | Push inner tube completely into outer tube to release tampon | N/A |
| 7. Removal | Gently remove applicator, leaving string outside body | Gently remove applicator, leaving string outside body | Ensure string is hanging outside body for easy removal |
| 8. Disposal | Wrap applicator in toilet paper and dispose in wastebasket; recycle wrapper | Dispose of cardboard applicator in wastebasket; check local recycling guidelines | N/A |
5. Common Mistakes and Tips for First-Time Tampon Users
Starting to use tampons can come with a learning curve. Here are some common mistakes beginners make and tips to help you avoid them:
5.1. Incorrect Angle
One of the most common mistakes is pointing the tampon upward toward your stomach instead of angling it towards your back. The vaginal canal curves slightly, so aiming towards your back follows the natural curve of your reproductive system and provides optimal comfort. If you experience discomfort, try adjusting the angle.
5.2. Not Inserting Deep Enough
If you can feel the tampon after insertion, it’s likely not inserted far enough. Gently push the tampon in further until you no longer feel it. The tampon should be positioned deep enough in the vaginal canal that it doesn’t cause any discomfort.
5.3. Using the Wrong Absorbency
Using a tampon with too high absorbency when your flow is light can cause dryness and irritation. Start with a lower absorbency and increase if needed. Conversely, using a tampon with too low absorbency can lead to leaks. Change your tampon every 4-8 hours, or more frequently if needed.
5.4. Forgetting to Remove the Applicator
The applicator is only meant to aid in insertion and should be removed and discarded after the tampon is in place. Leaving the applicator inside can cause discomfort and increase the risk of infection.
5.5. Tensing Up
Tensing your muscles can make insertion difficult and uncomfortable. Try to relax your body and mind before inserting the tampon. Taking deep breaths can help you relax.
5.6. Helpful Tips for Beginners
- Read the Instructions: Always read the instructions that come with your tampons before using them.
- Practice: It may take a few tries to get the hang of inserting a tampon. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t get it right the first time.
- Use Lubricant: If you are experiencing dryness, try applying a small amount of water-based lubricant to the tip of the applicator.
- Change Regularly: Change your tampon every 4-8 hours to prevent odor and reduce the risk of TSS.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any discomfort or unusual symptoms and consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns.
| Mistake | Solution |
|---|---|
| Incorrect Angle | Aim tampon towards your back, following natural curve of vaginal canal |
| Not Inserting Deep Enough | Gently push tampon in further until you no longer feel it |
| Using Wrong Absorbency | Start with lower absorbency, increase if needed; change tampon every 4-8 hours |
| Forgetting to Remove Applicator | Remove and discard applicator after tampon is in place |
| Tensing Up | Relax body and mind before insertion; take deep breaths |
6. Aftercare and Hygiene: Maintaining Tampon Safety
Proper aftercare and hygiene are crucial for maintaining tampon safety and preventing potential health issues. Here’s what you need to know:
6.1. How Often to Change a Tampon
The FDA recommends changing your tampon every 4-8 hours. Leaving a tampon in for longer than 8 hours increases the risk of bacterial overgrowth and Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS). Always use the lightest absorbency tampon possible for your flow and change it regularly.
6.2. Removing a Tampon
To remove a tampon, gently pull on the string. The tampon should slide out easily. If you experience resistance or pain, the tampon may not be fully saturated, or you may be experiencing dryness. In this case, try removing it gently or waiting a bit longer until it is easier to remove.
6.3. Disposing of Used Tampons
Never flush used tampons down the toilet, as they can cause blockages in your plumbing or septic systems. Wrap the used tampon in toilet paper or the tampon wrapper and dispose of it in a wastebasket.
6.4. Managing Odor
Tampons can help minimize menstrual odor by absorbing blood internally. However, if you notice an unusual or foul odor, it could be a sign of infection. Consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns.
6.5. Understanding Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS) is a rare but serious condition caused by bacterial toxins. It is associated with tampon use, particularly with high-absorbency tampons and prolonged use. Symptoms of TSS include:
- Sudden high fever
- Flu-like symptoms (muscle aches, headache, sore throat)
- Rash resembling a sunburn
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Dizziness or fainting
If you experience any of these symptoms while using tampons, remove the tampon immediately and seek medical attention.
6.6. Tips for Reducing TSS Risk
- Change tampons every 4-8 hours.
- Use the lowest absorbency tampon necessary for your flow.
- Alternate between tampons and pads.
- Avoid using tampons overnight.
- Be aware of the symptoms of TSS and seek medical attention immediately if they occur.
| Aftercare/Hygiene Aspect | Recommendation | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency of Change | Change tampon every 4-8 hours | Prevents bacterial overgrowth, reduces TSS risk |
| Removal | Gently pull on string; avoid forcing | Ensures comfortable and safe removal |
| Disposal | Wrap in toilet paper/wrapper; dispose in wastebasket | Prevents plumbing blockages, maintains hygiene |
| Managing Odor | Change regularly; consult healthcare professional for unusual odor | Minimizes odor, detects potential infections |
| Understanding TSS | Be aware of symptoms (fever, rash, flu-like symptoms) | Enables prompt medical attention, reduces severity of condition |
| Reducing TSS Risk | Use lowest absorbency; alternate with pads; avoid overnight use | Minimizes risk of bacterial overgrowth and TSS |
7. Conclusion: Empowering Your Period Experience
Mastering tampon usage can significantly enhance your comfort and confidence during menstruation. By understanding the different types of tampons, following proper insertion techniques, and adhering to hygiene guidelines, you can manage your period with greater ease and assurance.
Remember, every woman’s body is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Experiment with different tampon types and absorbency levels to find what suits you best. If you encounter any difficulties or have concerns, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional.
At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing reliable and comprehensive information to empower you to make informed decisions about your health and well-being. We believe that understanding your body and menstrual cycle is essential for maintaining overall health and enjoying a comfortable, confident life.
For more detailed information and additional resources on menstrual hygiene and related topics, visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN. Our mission is to provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to navigate your health journey with confidence.
Contact Information:
- Address: 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (707) 555-1234
- Website: CONDUCT.EDU.VN
Empower yourself with the right knowledge and take control of your menstrual health today.
FAQ: Common Questions About Tampon Use
Here are some frequently asked questions about using tampons, designed to help you feel more informed and confident:
1. How do I know what tampon absorbency to use?
Start with the lowest absorbency tampon for your flow. If it becomes soaked in less than 4 hours, try a higher absorbency. If it’s uncomfortable to remove after 4-8 hours, use a lower absorbency.
2. Can I sleep with a tampon in?
It’s generally recommended to avoid using tampons overnight. If you do, insert a fresh tampon just before bed and remove it as soon as you wake up, ensuring it’s within the 4-8 hour timeframe. Alternatively, use a pad overnight.
3. What should I do if I can feel the tampon after inserting it?
If you can feel the tampon, it likely isn’t inserted far enough. Try pushing it in a bit further. If it’s still uncomfortable, remove it and try again with a fresh tampon, ensuring you’re angling it towards your back.
4. How often should I change my tampon?
Change your tampon every 4-8 hours, or more frequently if needed, to prevent odor and reduce the risk of Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS).
5. What are the signs of Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)?
Signs of TSS include sudden high fever, flu-like symptoms (muscle aches, headache, sore throat), rash resembling a sunburn, vomiting or diarrhea, and dizziness or fainting. Seek medical attention immediately if you experience these symptoms.
6. Can I go swimming with a tampon in?
Yes, you can swim with a tampon in. Just be sure to insert a fresh tampon before swimming and change it afterward to maintain hygiene.
7. Is it okay to use tampons if I have a sensitive vagina?
Yes, but choose tampons made from 100% organic cotton and avoid those with added fragrances or chemicals. If you experience irritation, discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional.
8. Can tampons get lost inside my body?
No, tampons cannot get lost inside your body. The vaginal canal is a closed passage, and the tampon string ensures it can be easily removed.
9. What should I do if the tampon string breaks?
If the tampon string breaks, try to remove the tampon with your fingers. If you cannot reach it, consult a healthcare professional for assistance.
10. Are tampons bad for the environment?
Traditional tampons with plastic applicators can contribute to environmental waste. Opt for tampons with cardboard applicators or non-applicator tampons to reduce your environmental impact.
By addressing these common questions, we hope to provide you with the knowledge and confidence to use tampons safely and comfortably. Remember, CONDUCT.EDU.VN is here to support your health journey with reliable information and practical guidance.
Remember to visit conduct.edu.vn for more information and guidance.
