WordPress, a leading content management system (CMS), empowers millions to create and manage their online presence. This how to use WordPress beginners guide provides an accessible pathway for individuals to master WordPress. CONDUCT.EDU.VN demystifies the platform, offering clear instructions and actionable advice for designing, building, and maintaining a successful website, ensuring a seamless transition into the world of web development and digital content management. By understanding WordPress basics and website creation, users unlock opportunities to craft engaging online experiences with confidence.
Table Of Contents
- Understanding WordPress
- Key Advantages of Choosing WordPress
- Selecting the Right Hosting Provider
- Setting Up WordPress: A Step-by-Step Approach
- Navigating the WordPress Dashboard
- Themes: Shaping Your Website’s Identity
- Plugins: Enhancing Functionality and Features
- Creating and Managing Content
- Customizing Your WordPress Site
- Launching Your WordPress Website
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Understanding WordPress
WordPress emerged in the late 1990s as a platform dedicated to blogging. Since then, it has evolved into a comprehensive CMS suitable for creating diverse websites, including membership sites, forums, and e-commerce platforms. WordPress is available in two primary versions: .com and .org. While both share a core platform, key distinctions arise in their hosting arrangements. The .org version is self-hosted, necessitating a separate hosting plan, while the .com version offers an all-inclusive platform with integrated hosting services.
For this guide, we’ll concentrate on the .org variant, primarily due to its enhanced benefits and flexibility, especially for beginners navigating the website development landscape.
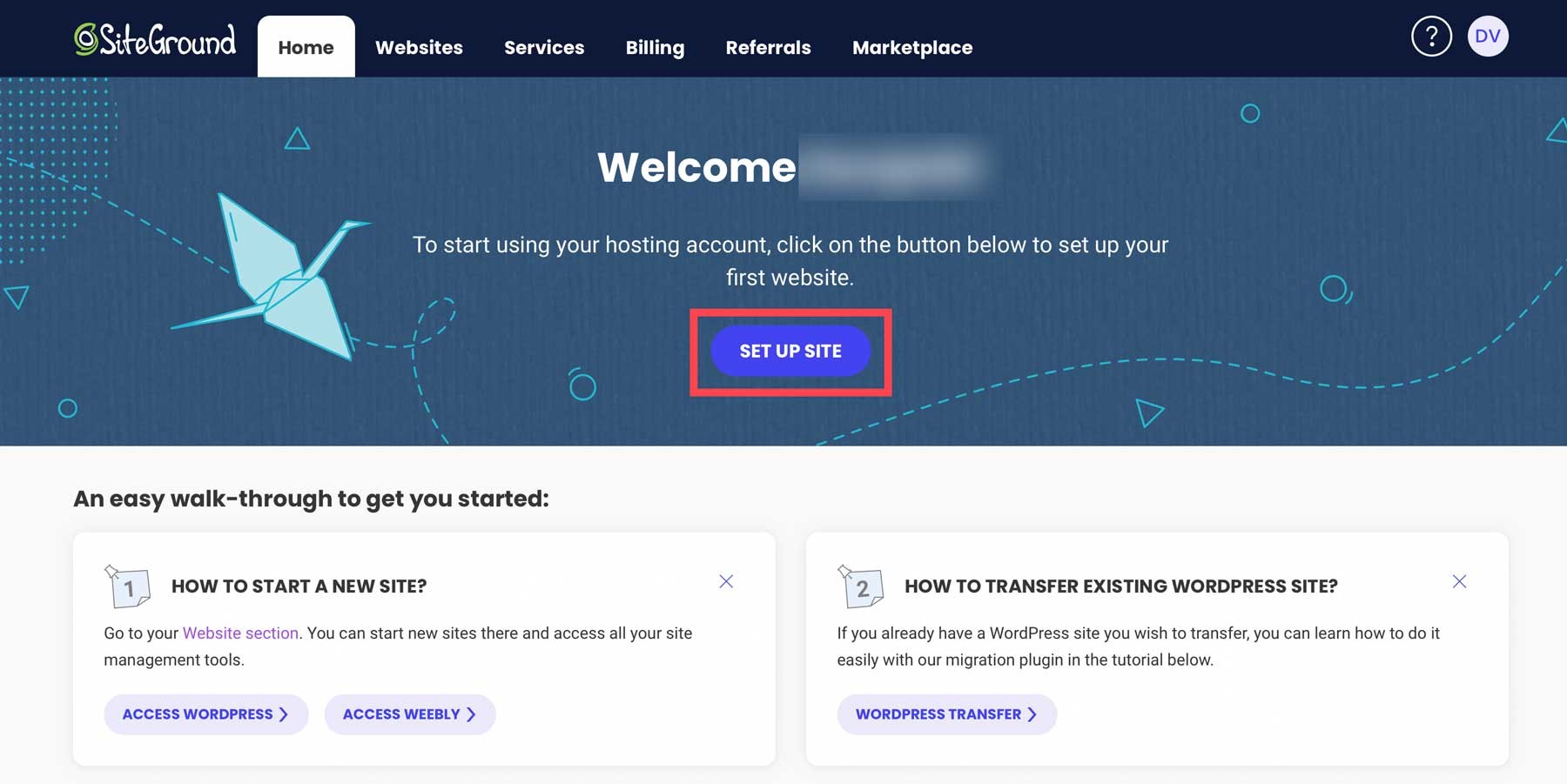
Image showing the setup site button to install WordPress on SiteGround, highlighting the first step in the WordPress installation process.
2. Key Advantages of Choosing WordPress
There are numerous reasons to favor WordPress, and its accessibility is one of its most appealing features. The platform itself is free, but it is important to consider associated costs like hosting, domain registration, plugins, and themes. Despite these expenses, the ease of learning WordPress offers significant value. The platform is intuitive, particularly after the initial learning curve. A wide array of tutorials and documentation are readily available to assist users.
WordPress’s customizability is another significant benefit. With a plethora of themes and plugins, users can tailor their sites, whether for blogging, e-commerce, or community building, to provide a unique browsing experience. Beginners can easily modify layouts, colors, fonts, and other design elements. Experienced developers can further customize functionality through custom code and webhooks.
WordPress is also scalable, capable of handling increased traffic and content as your website grows. Its SEO-friendly nature aids in achieving higher search engine rankings, attracting more organic traffic.
3. Selecting the Right Hosting Provider
Choosing a reliable web hosting service is crucial for the success of your WordPress website. Your web host should offer speed, reliability, scalability, and robust security measures, all within your budget. While this might seem demanding, many excellent WordPress hosting providers are available.
CONDUCT.EDU.VN recommends SiteGround as a top choice.
SiteGround offers three plans tailored to both beginners and experts, with prices ranging from $15 to $40 per month. Regular specials provide opportunities for cost savings. Beyond affordability, SiteGround provides features like free emails, SSL, CDN, and migration support, ensuring smooth website operation.
Security is a priority with SiteGround, featuring a web application firewall (WAF) to protect against hackers and prevent malware and DDoS attacks.
While SiteGround is recommended, other reputable options exist, including Hostinger, Pressable, Cloudways, and Flywheel.
Image showcasing SiteGround WordPress hosting, highlighting its features and benefits as a recommended hosting provider.
4. Setting Up WordPress: A Step-by-Step Approach
The following steps will guide you through installing WordPress, navigating the dashboard, creating content, styling your site, and launching it live, underscoring why WordPress is beginner-friendly.
4.1. Installing WordPress
WordPress can be installed through various methods, including using a hosting provider, manual installation, or local setup via Local by Flywheel or MAMP Pro. This tutorial focuses on installing WordPress using SiteGround’s Site Tools dashboard.
4.1.1. Install WordPress via SiteGround
After signing up for a SiteGround account, installing WordPress requires just a few clicks. Begin by selecting the set up site button.
Next, specify whether to set up your site on a new, existing, or temporary domain. Select temporary domain and click continue. SiteGround will assign a temporary domain for your WordPress installation. Proceed by clicking continue.
Then, click start new website and choose WordPress.
The following step involves creating your login credentials for accessing your WordPress dashboard. Ensure you save this information for future reference. Click continue to proceed.
Finally, click the finish button to install WordPress. You can access the WordPress dashboard directly through SiteGround by clicking the log in admin button. Alternatively, you can log in via your browser by navigating to www.yoursite.com/wp-admin, replacing www.yoursite.com with your domain.
Image showing the option to choose a temporary domain on SiteGround, illustrating the domain setup process during WordPress installation.
5. Navigating the WordPress Dashboard
Upon logging in for the first time, you’ll find the WordPress toolbar on the left side of your screen. This is the central hub for managing your site, offering access to all necessary tools and settings. The dashboard’s main screen provides quick links for viewing and managing pages, editing your site’s design, accessing useful resources, and exploring WordPress-related blog posts.
The Updates tab allows you to manage updates for plugins, themes, or core files, crucial for maintaining functionality and security. Regularly updating your software is essential to prevent vulnerabilities and potential breaches. Before performing any updates, back up your website to prevent data loss. Most hosting providers offer free backup services, or you can use a plugin like UpdraftPlus to schedule daily or weekly backups.
Image of the WordPress updates section, emphasizing the importance of keeping plugins, themes, and core files up to date for security and functionality.
5.1. Posts
The posts tab allows you to create and manage blog entries. You can create new posts, edit existing ones, and organize your content using categories and tags. This helps with SEO and improves user navigation.
5.2. Media
WordPress includes its own media library for uploading and managing images and other media files. This tool simplifies adding images to your website.
Image displaying the WordPress media library, illustrating how to add and manage images and media files for your website.
5.3. Pages
This section allows you to add and manage static pages on your website, such as an “About Us” or “Contact” page. These pages are typically displayed in your site’s main navigation menu. Pages differ from posts in that they do not support categories and tags.
5.4. Comments
WordPress provides a built-in commenting system for your posts, allowing visitors to engage with your content. You can moderate comments to ensure they are appropriate and relevant. Effective comment moderation can boost user engagement and community interaction.
Image highlighting the WordPress comments section, showing how to moderate and manage comments to boost engagement and foster community interaction.
5.5. Appearance
The Appearance tab contains essential customization tools, including themes, customization options, widgets, and navigation menus. The available tools may vary depending on the theme you are using. Premium themes like Divi typically offer more extensive options, including the ability to edit theme files.
5.6. Plugins
WordPress plugins extend the functionality of your website, allowing you to add features like contact forms, SEO tools, and e-commerce capabilities. The plugins tab lists currently installed plugins, which you can manage or delete as needed. You can also add new plugins from the WordPress repository.
Image displaying the WordPress plugins section, illustrating how to view, manage, and install new plugins to extend your website’s functionality.
5.7. Users
The users section lets you manage user accounts on your site, including adding, editing, and deleting users. You can also assign roles and permissions, controlling what each user can do on your site. Membership plugins can extend user management, allowing you to restrict content based on membership level.
5.8. Tools
This section offers tools to manage and maintain your site, including importing and exporting content, monitoring site security and performance, and managing user data for GDPR compliance.
Image of the WordPress tools section, highlighting features for managing and maintaining your website, including import/export options and site health monitoring.
5.9. Settings
The WordPress settings section allows you to configure your site’s title, tagline, home page, media settings, privacy options, and more.
6. Themes: Shaping Your Website’s Identity
A WordPress theme dictates the visual appearance of your website. It’s crucial to select a theme that is visually appealing and effectively presents the information users seek. The ideal WordPress theme should align with your website’s objectives and provide an engaging user experience. You can install themes either by searching for free themes in the WordPress directory or by uploading a premium theme like Divi.
conduct.edu.vn highly suggests Divi due to its versatility and extensive array of features.
Divi provides over 2000 pre-made layouts and a Theme Builder for creating custom headers, footers, and templates for e-commerce and search results pages.
To install a theme, navigate to Appearance > Themes in the WordPress dashboard and click Add New Theme. From there, you can choose from recommended themes, browse the WordPress directory, or upload a theme. After selecting a theme, click install and then activate to make it live.
Image showing the process of choosing a WordPress theme, with options to browse recommended themes, search the WP directory, or upload a custom theme.
7. Plugins: Enhancing Functionality and Features
Plugins extend the functionality of your WordPress website. The right plugins can enhance user experience, improve SEO, and add essential features. Thousands of plugins are available through the WordPress repository and third-party vendors like the Divi Marketplace.
For Divi users, the Divi Marketplace offers extensions like child themes, layouts, and plugins designed specifically for the Divi theme. Popular options include Divi Plus, Divi Supreme Pro, and Divi Essential, each adding unique design modules, extensions, and templates.
In addition to Divi-specific plugins, every website should include essential plugins for security and customer safety. Consider installing plugins like WP Forms for creating forms, All In One SEO for search engine optimization, WP Rocket for speed optimization, and EWWW for image optimization.
7.1. Installing a WordPress Plugin
Similar to themes, plugins can be installed by searching within WordPress or uploading a premium plugin. Navigate to Plugins > Add New in your WordPress dashboard.
To install a plugin from the WordPress directory, search or browse for the plugin, then click install to download it. Alternatively, click the upload plugin tab to upload a plugin from your computer. After uploading, click install now and then activate to complete the installation.
Image illustrating how to search for and install plugins in WordPress, either by browsing the WordPress directory or uploading a plugin file.
8. Creating and Managing Content
With your theme and plugins installed, you’re ready to add content to your WordPress site. Content creation primarily involves working with posts, pages, and media.
8.1. Add a Post to WordPress
Posts are typically used for blog articles and news updates. You can create posts using the Gutenberg block editor or a page builder plugin like Divi.
To create a new post, click Add New in the Posts section of the dashboard. Give your post a title and add content using the block editor or Divi. You can assign the post to a category, add tags, and then click publish to make it live.
Image showing how to add a title to a new post in WordPress, highlighting the first step in creating blog content.
8.2. Add a Page to WordPress
Pages are used for static content like “About Us” or “Contact” information. To add a new page, navigate to Pages > Add New in the dashboard. Give your page a title and add content. Click publish to make your page live.
Image demonstrating how to add content to a new page in WordPress, emphasizing the steps to create static content like an “About Us” page.
8.3. Add Content With Divi AI
Divi users can leverage Divi AI to generate layouts effortlessly. Divi AI allows both WordPress novices and seasoned developers to create attractive, professional-looking layouts quickly.
To create a page with Divi AI, click Use Divi Builder on the new page. Then, select Generate Layout to use Divi AI. Describe the type of page you want to create, provide any additional information, and choose fonts and colors. Divi AI will generate the page, adding design modules, writing copy, and generating images. After the page is created, you can use the Visual Builder to edit, add design modules, or regenerate content as needed.
Image displaying the option to use the Divi Builder, which leads to using Divi AI for generating layouts and enhancing the web design process.
9. Customizing Your WordPress Site
Before launching your site, perform final customizations, including adding custom CSS, configuring SEO, adding social media links, and adjusting theme settings. These options vary based on your installed theme.
9.1. Adding Custom CSS
Custom CSS allows you to style various elements of your website. You can add CSS through the WordPress customizer (Appearance > Customize) or, for premium themes like Divi, through the theme options (Divi > Theme Options).
9.2. Auto-Update Plugins
WordPress allows you to enable automatic plugin updates. Using an activity log plugin like WP Activity Log can help you troubleshoot any issues that arise during updates.
To enable auto-updates, go to the plugins section of the WordPress dashboard and click enable auto-updates on any plugin you want to update automatically.
Image showing how to enable auto-updates for plugins in WordPress, ensuring that plugins are automatically updated for security and performance.
9.3. Configure Your SEO
Configuring SEO settings is essential before launching your website. An SEO plugin like Rank Math can guide you in optimizing your site for search engines, providing helpful tips and suggestions to improve your SEO scores.
9.4. Add a Site Title and Tagline
Your site’s title and tagline help visitors identify your website. Navigate to Settings > General to input your desired title and tagline.
9.5. WordPress Reading Settings
In the reading settings, ensure you set a home page and that the Discourage search engines from indexing this site checkbox is unchecked. This ensures that search engines can index your site.
9.6. Configure Theme Settings
Customize your theme settings to properly represent your business. Add your logo, social media accounts, colors, and fonts. In Divi, navigate to Divi > Theme Options to add necessary branding elements and make other changes.
9.7. Back Up Your Site
Backing up your website before launching is crucial. This preserves your site’s files in case any issues occur during the launch process. Many managed hosting providers like SiteGround offer backups in their hosting plans, or you can use a backup plugin.
10. Launching Your WordPress Website
The final step is taking your website live. If you built your site on a temporary domain using SiteGround, you’ll need to add a domain first.
Regardless of your hosting provider, ensure you check the following items once your site is live:
- Verify that all pages are loading correctly.
- Test all forms and interactive elements.
- Ensure your site is mobile-responsive.
- Check your site speed and performance.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
11.1. Is WordPress beginner-friendly?
Yes, WordPress is considered beginner-friendly due to its user-friendly interface, extensive selection of pre-designed themes and plugins (such as Divi), and comprehensive documentation and support resources.
11.2. Can I learn WordPress for free?
Yes, you can learn WordPress for free through various online resources such as WordPress.org’s documentation and YouTube tutorials.
11.3. Can you learn WordPress by yourself?
Yes, learning WordPress independently through online resources is possible, but it may take time and effort.
11.4. How long does it take to learn how to make a WordPress website?
The time to learn how to make a WordPress website varies, but you can learn the basics in a few weeks with dedication and practice.
11.5. Does learning WordPress require coding skills?
No, learning WordPress does not necessarily require coding skills. You can achieve many features and designs without writing code through plugins and themes.
11.6. What are the best resources to learn about WordPress?
The best resources include the official WordPress website, online tutorials, forums, and popular WordPress blogs.
11.7. Why should I learn WordPress?
You should learn WordPress because it is the most popular CMS used to create websites, user-friendly, customizable, and supported by a large community of developers.
11.8. What other skills should I learn with WordPress?
Beneficial skills include HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SEO optimization, content creation, and website security.
11.9. Is WordPress still relevant?
Yes, WordPress is still relevant, powering over 40% of websites on the internet and continuing to evolve with new features and updates.
11.10. Is WordPress a viable source to make a living?
Yes, WordPress offers numerous opportunities for developers, designers, content creators, and entrepreneurs to earn a living through website-related services.
Need more tutorials? If you’d like a more comprehensive look into WordPress, check out our complete guide on how to make a website from scratch.
For additional support and resources, contact CONDUCT.EDU.VN at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (707) 555-1234. Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN for more information.
Image showcasing Divi Layouts AI, highlighting its features for AI-assisted design and layout generation, making website building more efficient.