Is An Ultrasound Guided Hip Injection Painful? At conduct.edu.vn, we explore this question by examining the procedure, its benefits, and the potential for discomfort. Understanding the procedure helps patients make informed decisions about pain management. Ultrasound guided hip injections, discomfort management, and recovery expectations are further explained below.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
- Anatomy and the Importance of the Hip Joint
- Why Choose Ultrasound Guidance?
- Conditions Treated with Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
- The Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injection Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Is an Ultrasound Guided Hip Injection Painful? What to Expect
- Managing Pain During the Injection: Techniques and Comfort Measures
- Post-Procedure Care and Recovery: Minimizing Discomfort
- Benefits of Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
- Risks and Complications of Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
- Long-Term Outcomes and Success Rates
- Alternatives to Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
- Preparing for Your Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injection
- Choosing a Qualified Specialist for Your Injection
- The Role of Imaging in Pain Management
- Innovations in Ultrasound Technology for Hip Injections
- Patient Testimonials and Real-Life Experiences
- Cost and Insurance Coverage for Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
- The Future of Hip Pain Treatment: Advances and Research
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
1. Understanding Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
Ultrasound-guided hip injections are a minimally invasive procedure used to both diagnose and treat hip pain. Utilizing real-time imaging, this technique allows medical professionals to accurately guide a needle into the hip joint. The injection typically contains a combination of a local anesthetic, to provide immediate pain relief, and a corticosteroid, which reduces inflammation over time. This dual-action approach can provide significant and lasting relief for individuals suffering from various hip conditions.
The accuracy of ultrasound guidance is a key factor in its effectiveness. By visualizing the underlying structures, physicians can ensure that the medication is delivered precisely where it is needed, maximizing its therapeutic effect and minimizing the risk of complications. This precision is particularly important in the hip joint, which is deep and surrounded by numerous muscles, ligaments, and nerves.
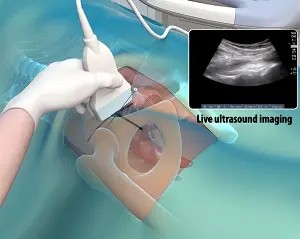 Ultrasound guided hip injection process visualized
Ultrasound guided hip injection process visualized
1.1 The Role of Ultrasound in Precision Medicine
Ultrasound technology has become an indispensable tool in modern medicine, particularly in the field of pain management. Its ability to provide real-time imaging without exposing patients to radiation makes it a safe and versatile option. In the context of hip injections, ultrasound guidance enhances the precision of the procedure, ensuring that the medication is delivered directly to the source of pain.
Precision medicine aims to tailor medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient. Ultrasound-guided hip injections align with this approach by allowing for a personalized treatment plan based on the patient’s specific anatomy and condition. This targeted approach can lead to better outcomes, reduced side effects, and improved patient satisfaction.
1.2 Comparing Ultrasound-Guided Injections to Blind Injections
Traditionally, hip injections were performed using a “blind” technique, where the physician relied on anatomical landmarks to guide the needle. However, this approach has limitations, as it does not account for individual variations in anatomy and may result in inaccurate needle placement. Studies have shown that ultrasound-guided injections are significantly more accurate than blind injections, leading to better pain relief and reduced risk of complications.
The advantages of ultrasound guidance include:
- Improved Accuracy: Real-time visualization ensures precise needle placement.
- Reduced Risk: Minimizes the chance of hitting surrounding structures, such as nerves and blood vessels.
- Enhanced Efficacy: Targeted delivery of medication maximizes its therapeutic effect.
- Non-Invasive: No radiation exposure.
1.3 The Science Behind Pain Relief: Anesthetic and Steroid Combination
The combination of a local anesthetic and a corticosteroid is a cornerstone of ultrasound-guided hip injections. The local anesthetic, such as lidocaine or bupivacaine, provides immediate pain relief by blocking nerve signals in the injected area. This effect is temporary, typically lasting for a few hours.
The corticosteroid, such as triamcinolone or betamethasone, is a potent anti-inflammatory agent. It works by reducing the production of inflammatory substances in the body, which can alleviate pain and swelling in the hip joint. The effects of the corticosteroid are typically seen within a few days and can last for several weeks or months.
The synergistic effect of these two medications provides both immediate and long-term pain relief, making ultrasound-guided hip injections an effective treatment option for various hip conditions.
2. Anatomy and the Importance of the Hip Joint
The hip joint is a complex and crucial structure in the human body, playing a vital role in movement, stability, and weight-bearing. Understanding its anatomy is essential for comprehending the causes of hip pain and the rationale behind ultrasound-guided hip injections.
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint, where the “ball” is the head of the femur (thigh bone) and the “socket” is the acetabulum, a cup-shaped cavity in the pelvis. This design allows for a wide range of motion, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation. The joint is stabilized by a network of ligaments, muscles, and tendons, which work together to maintain its integrity and function.
2.1 Key Structures of the Hip Joint
- Femoral Head: The rounded top of the femur that fits into the acetabulum.
- Acetabulum: The socket in the pelvis that articulates with the femoral head.
- Articular Cartilage: A smooth, protective layer that covers the surfaces of the bones, reducing friction and allowing for smooth movement.
- Labrum: A fibrocartilaginous rim that surrounds the acetabulum, providing stability and cushioning to the joint.
- Ligaments: Strong bands of connective tissue that connect bones to bones, providing stability to the hip joint. Key ligaments include the iliofemoral, pubofemoral, and ischiofemoral ligaments.
- Muscles: Numerous muscles surround the hip joint, including the gluteal muscles, hip flexors, and adductor muscles. These muscles provide movement and stability to the hip.
- Synovial Membrane: A thin layer of tissue that lines the joint capsule and produces synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint and provides nutrients to the cartilage.
2.2 Common Causes of Hip Pain: A Structural Perspective
Hip pain can arise from various sources, often related to the structural components of the hip joint. Understanding these causes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
- Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of articular cartilage. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
- Hip Labral Tears: Tears in the labrum can cause pain, clicking, and a feeling of instability in the hip joint.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the hip joint. This can cause pain and tenderness around the hip.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons that surround the hip joint. This can be caused by overuse or repetitive activities.
- Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI): A condition where the femoral head and acetabulum rub abnormally, leading to cartilage damage and pain.
- Hip Dysplasia: A condition where the hip socket is shallow, leading to instability and increased risk of dislocation.
2.3 The Interconnectedness of Hip Health: Muscles, Ligaments, and Bones
The health of the hip joint is dependent on the proper functioning of its interconnected components. Muscles, ligaments, and bones work together to provide stability, movement, and weight-bearing capacity. When one component is compromised, it can affect the entire system.
For example, weak hip muscles can lead to instability and increased stress on the ligaments and cartilage. Similarly, ligament injuries can compromise the stability of the joint, leading to increased risk of cartilage damage. Maintaining the health of all these components is essential for preventing hip pain and maintaining optimal function. Regular exercise, proper posture, and a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall hip health.
3. Why Choose Ultrasound Guidance?
Ultrasound guidance has revolutionized the field of joint injections, offering numerous advantages over traditional blind injection techniques. The ability to visualize the underlying structures in real-time allows for more accurate needle placement, reduced risk of complications, and improved patient outcomes.
3.1 Enhanced Accuracy and Precision
The primary advantage of ultrasound guidance is its ability to enhance accuracy and precision. By visualizing the hip joint and surrounding structures, physicians can ensure that the needle is placed precisely where it needs to be. This is particularly important in the hip joint, which is deep and surrounded by numerous muscles, ligaments, and nerves.
Studies have consistently shown that ultrasound-guided hip injections are significantly more accurate than blind injections. This improved accuracy can lead to better pain relief, reduced risk of complications, and improved patient satisfaction.
3.2 Minimizing Risks: Avoiding Nerves and Blood Vessels
Ultrasound guidance allows physicians to visualize nerves and blood vessels in real-time, reducing the risk of accidental injury during the injection. This is particularly important in the hip region, where the sciatic nerve and femoral vessels are located close to the joint.
By avoiding these structures, ultrasound guidance can minimize the risk of complications such as nerve damage, bleeding, and hematoma formation. This can lead to a safer and more comfortable experience for patients.
3.3 Real-Time Visualization: A Clearer Picture for Better Outcomes
Real-time visualization is a key benefit of ultrasound guidance. The ability to see the needle as it advances towards the target allows physicians to make adjustments as needed, ensuring accurate placement. This is particularly helpful in patients with complex anatomy or previous hip surgery.
Real-time visualization also allows physicians to confirm that the medication is being delivered to the correct location. This can improve the effectiveness of the injection and lead to better pain relief.
3.4 Non-Invasive Imaging: No Radiation Exposure
Unlike other imaging modalities such as X-rays and CT scans, ultrasound does not involve radiation exposure. This makes it a safe and versatile option for guiding hip injections, particularly in patients who require repeated injections.
The absence of radiation exposure also makes ultrasound guidance a suitable option for pregnant women and children, where radiation exposure is a concern.
3.5 Cost-Effectiveness: A Smart Choice for Patients and Providers
Ultrasound guidance is a cost-effective option for hip injections. The equipment is relatively inexpensive, and the procedure can be performed in an outpatient setting, reducing the need for expensive hospital stays.
Moreover, the improved accuracy and reduced risk of complications associated with ultrasound guidance can lead to cost savings in the long run. By reducing the need for repeat injections and minimizing the risk of complications, ultrasound guidance can provide significant value to both patients and providers.
4. Conditions Treated with Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
Ultrasound-guided hip injections are used to treat a variety of conditions that cause hip pain and inflammation. These injections can provide significant relief for individuals suffering from osteoarthritis, hip labral tears, bursitis, and other hip-related problems.
4.1 Osteoarthritis: Easing the Pain of Joint Degeneration
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of articular cartilage. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion in the hip joint. Ultrasound-guided hip injections can help to alleviate these symptoms by reducing inflammation and providing pain relief.
The corticosteroid in the injection works by reducing the production of inflammatory substances in the body, which can alleviate pain and swelling in the hip joint. The local anesthetic provides immediate pain relief by blocking nerve signals in the injected area.
While ultrasound-guided hip injections cannot cure osteoarthritis, they can provide significant relief and improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from this condition.
4.2 Hip Labral Tears: Targeting the Source of Instability
Hip labral tears are tears in the labrum, a fibrocartilaginous rim that surrounds the acetabulum. These tears can cause pain, clicking, and a feeling of instability in the hip joint. Ultrasound-guided hip injections can help to alleviate these symptoms by reducing inflammation and providing pain relief.
The injection can help to reduce inflammation around the labrum, which can alleviate pain and improve stability. In some cases, ultrasound-guided hip injections can be used to guide the placement of regenerative medicine therapies, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP), to promote healing of the labrum.
4.3 Bursitis: Calming Inflammation in the Bursa
Bursitis is inflammation of the bursae, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the hip joint. This can cause pain and tenderness around the hip. Ultrasound-guided hip injections can help to alleviate these symptoms by reducing inflammation in the bursa.
The corticosteroid in the injection works by reducing the production of inflammatory substances in the bursa, which can alleviate pain and swelling. The local anesthetic provides immediate pain relief by blocking nerve signals in the injected area.
4.4 Tendinitis: Soothing Irritated Tendons
Tendinitis is inflammation of the tendons that surround the hip joint. This can be caused by overuse or repetitive activities. Ultrasound-guided hip injections can help to alleviate these symptoms by reducing inflammation in the tendons.
The injection can help to reduce inflammation around the tendons, which can alleviate pain and improve function. In some cases, ultrasound-guided hip injections can be used to guide the placement of regenerative medicine therapies, such as PRP, to promote healing of the tendons.
4.5 Post-Surgical Pain: Managing Discomfort After Hip Procedures
Ultrasound-guided hip injections can be used to manage pain after hip surgery. The injection can help to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief, allowing patients to recover more comfortably.
The corticosteroid in the injection works by reducing the production of inflammatory substances in the surgical area, which can alleviate pain and swelling. The local anesthetic provides immediate pain relief by blocking nerve signals in the injected area.
Ultrasound-guided hip injections can be a valuable tool in the management of post-surgical pain, allowing patients to recover more quickly and comfortably.
5. The Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injection Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
The ultrasound-guided hip injection procedure is a relatively simple and straightforward process. It typically takes about 15-30 minutes to complete and is performed in an outpatient setting. Here is a step-by-step guide to what you can expect during the procedure:
5.1 Preparation: What to Expect Before the Injection
Before the procedure, you will be asked to provide your medical history and undergo a physical examination. Your physician will explain the procedure in detail and answer any questions you may have. You may be asked to sign a consent form before the procedure.
You may be advised to stop taking blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or warfarin, for a few days before the procedure. You should also inform your physician if you have any allergies to medications or contrast dyes.
On the day of the procedure, you should wear comfortable clothing and avoid wearing jewelry or other accessories that may interfere with the ultrasound imaging.
5.2 Positioning and Sterilization: Ensuring a Safe Environment
You will be asked to lie on your back on an examination table. The injection site will be cleaned with an antiseptic solution, such as iodine or chlorhexidine, to reduce the risk of infection.
A sterile drape will be placed over the injection site to maintain a sterile environment. The physician will wear sterile gloves and a mask during the procedure.
5.3 Ultrasound Imaging: Guiding the Needle with Precision
The physician will use an ultrasound machine to visualize the hip joint and surrounding structures. A small amount of gel will be applied to the skin over the injection site to improve contact between the ultrasound probe and the skin.
The ultrasound probe will be used to guide the needle towards the target area in the hip joint. The physician will monitor the needle’s progress in real-time on the ultrasound screen, ensuring accurate placement.
5.4 Injection: Delivering the Medication to the Source of Pain
Once the needle is in the correct position, the physician will inject a combination of a local anesthetic and a corticosteroid into the hip joint. The local anesthetic will provide immediate pain relief by blocking nerve signals in the injected area. The corticosteroid will reduce inflammation over time, providing longer-lasting pain relief.
The physician may inject a small amount of contrast dye into the hip joint to confirm that the medication is being delivered to the correct location.
5.5 Post-Injection Monitoring: Ensuring Stability and Comfort
After the injection, the needle will be removed, and a bandage will be applied to the injection site. You will be monitored for a short period of time to ensure that you are stable and comfortable.
You may be advised to avoid strenuous activities for the rest of the day. You can typically resume your normal activities the following day.
6. Is an Ultrasound Guided Hip Injection Painful? What to Expect
One of the primary concerns for patients considering ultrasound-guided hip injections is the level of pain they might experience during the procedure. While pain perception varies from person to person, understanding what to expect can help alleviate anxiety and prepare you for the process.
6.1 The Sensation During Injection: A Range of Experiences
Most patients report experiencing minimal to moderate discomfort during the injection. The sensation is often described as a brief sting or pressure as the needle is inserted into the hip joint. The use of a local anesthetic at the injection site helps to numb the area, reducing the level of pain.
Some factors that can influence the level of pain include:
- Individual Pain Tolerance: People have different thresholds for pain.
- Anxiety Levels: High anxiety can amplify pain perception.
- Inflammation: The degree of inflammation in the hip joint can affect the level of discomfort.
- Technique: The skill and experience of the physician performing the injection can impact the level of pain.
6.2 Immediate Post-Injection Discomfort: What’s Normal?
Immediately after the injection, you may experience some soreness or aching in the hip area. This is normal and is usually caused by the needle insertion and the injection of fluid into the joint. The discomfort is typically mild and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
In some cases, patients may experience a temporary increase in pain after the injection. This is often due to the local anesthetic wearing off and the corticosteroid not yet taking effect. This flare-up usually subsides within a few days.
6.3 Long-Term Pain Relief: The Goal of the Procedure
The primary goal of ultrasound-guided hip injections is to provide long-term pain relief. The local anesthetic provides immediate pain relief, which can last for a few hours. The corticosteroid reduces inflammation over time, providing longer-lasting pain relief that can last for several weeks or months.
The degree of pain relief varies from person to person, depending on the underlying condition and the severity of the inflammation. Some patients experience complete pain relief, while others experience a significant reduction in pain.
6.4 Addressing Patient Fears: Open Communication is Key
It is important to address any fears or concerns you may have about the procedure with your physician. Open communication can help to alleviate anxiety and ensure that you are comfortable throughout the process.
Your physician can explain the procedure in detail, answer your questions, and provide reassurance. They can also discuss pain management options and strategies for minimizing discomfort.
Remember, the goal of ultrasound-guided hip injections is to provide pain relief and improve your quality of life. By understanding what to expect and communicating openly with your physician, you can approach the procedure with confidence and optimism.
7. Managing Pain During the Injection: Techniques and Comfort Measures
While ultrasound-guided hip injections are generally well-tolerated, there are several techniques and comfort measures that can be employed to minimize pain and anxiety during the procedure.
7.1 Local Anesthesia: Numbing the Injection Site
The use of a local anesthetic is a standard practice in ultrasound-guided hip injections. The anesthetic is injected into the skin and tissues surrounding the injection site, numbing the area and reducing the level of pain.
The local anesthetic typically takes effect within a few minutes and can last for several hours. This provides immediate pain relief during the injection and in the immediate post-injection period.
7.2 Relaxation Techniques: Calming the Nerves
Anxiety can amplify pain perception, so it is important to stay relaxed during the procedure. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and visualization, can help to calm the nerves and reduce anxiety.
Before the procedure, practice these techniques at home to become familiar with them. During the injection, focus on your breathing and visualize a peaceful scene.
7.3 Distraction: Shifting Focus Away from the Procedure
Distraction techniques can help to shift your focus away from the procedure and reduce anxiety. Listening to music, watching a video, or engaging in conversation can help to take your mind off the injection.
Bring your favorite music or a relaxing video to the appointment. If you prefer to talk, engage in conversation with the physician or a member of the medical staff.
7.4 Communication: Keeping Your Physician Informed
It is important to communicate with your physician throughout the procedure. Let them know if you are experiencing any pain or discomfort. They can adjust the technique or administer additional local anesthetic to help manage the pain.
Do not hesitate to ask questions or express your concerns. Open communication can help to ensure that you are comfortable and confident throughout the process.
7.5 Topical Anesthetics: Preparing the Skin for Needle Insertion
Topical anesthetics, such as creams or patches, can be applied to the skin before the injection to numb the area. These anesthetics contain medications like lidocaine or prilocaine, which block nerve signals in the skin.
Topical anesthetics can help to reduce the pain associated with needle insertion. They are typically applied 30-60 minutes before the procedure to allow enough time for the medication to take effect.
8. Post-Procedure Care and Recovery: Minimizing Discomfort
Proper post-procedure care is essential for minimizing discomfort and promoting optimal recovery after an ultrasound-guided hip injection.
8.1 Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding Overexertion
After the injection, it is important to rest and avoid overexertion. Avoid strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting, running, and jumping, for at least 24-48 hours.
You can typically resume your normal activities the following day, but listen to your body and avoid any activities that cause pain or discomfort.
8.2 Ice and Heat Therapy: Managing Swelling and Pain
Ice and heat therapy can be used to manage swelling and pain after the injection. Ice can help to reduce inflammation and swelling, while heat can help to soothe sore muscles and improve circulation.
Apply ice to the injection site for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. After 24-48 hours, you can switch to heat therapy, using a warm compress or a heating pad.
8.3 Pain Medication: Over-the-Counter Relief
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can be used to manage pain and discomfort after the injection. Follow the instructions on the label and consult your physician if you have any questions or concerns.
Avoid taking aspirin or other blood-thinning medications, as these can increase the risk of bleeding.
8.4 Monitoring for Infection: Recognizing Warning Signs
It is important to monitor the injection site for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, warmth, and drainage. If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your physician immediately.
Infection is a rare complication of ultrasound-guided hip injections, but it is important to seek prompt medical attention if it occurs.
8.5 Physical Therapy: Restoring Function and Mobility
Physical therapy can be an important part of the recovery process after an ultrasound-guided hip injection. A physical therapist can help you to restore function and mobility in your hip joint.
They can teach you exercises to strengthen your hip muscles, improve your range of motion, and reduce your pain. They can also provide guidance on proper posture and body mechanics to prevent future problems.
9. Benefits of Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
Ultrasound-guided hip injections offer a multitude of benefits for patients suffering from hip pain and inflammation.
9.1 Accurate Diagnosis: Pinpointing the Source of Pain
Ultrasound-guided hip injections can be used to diagnose the source of hip pain. By injecting a local anesthetic into the hip joint, physicians can determine whether the pain is originating from the joint itself or from surrounding structures, such as muscles, ligaments, or tendons.
If the injection provides significant pain relief, it is likely that the pain is originating from the hip joint. If the injection does not provide relief, it is likely that the pain is originating from a different source.
9.2 Effective Pain Relief: Reducing Discomfort and Improving Function
Ultrasound-guided hip injections can provide effective pain relief for various hip conditions, such as osteoarthritis, hip labral tears, bursitis, and tendinitis. The combination of a local anesthetic and a corticosteroid can reduce inflammation and block nerve signals, providing both immediate and long-lasting pain relief.
This pain relief can improve function and mobility, allowing patients to participate in activities they previously had to avoid.
9.3 Minimally Invasive: A Gentle Approach to Treatment
Ultrasound-guided hip injections are a minimally invasive procedure, meaning that they do not require a large incision or extensive surgery. This reduces the risk of complications, such as infection and scarring.
The procedure is typically performed in an outpatient setting and takes about 15-30 minutes to complete. Patients can usually return to their normal activities the following day.
9.4 Improved Quality of Life: Regaining Enjoyment in Daily Activities
By reducing pain and improving function, ultrasound-guided hip injections can significantly improve the quality of life for patients suffering from hip pain. Patients can regain enjoyment in daily activities, such as walking, running, and playing sports.
They can also experience improved sleep, reduced reliance on pain medication, and enhanced overall well-being.
9.5 Avoiding or Delaying Surgery: A Conservative Treatment Option
Ultrasound-guided hip injections can be used as a conservative treatment option to avoid or delay surgery. In some cases, injections can provide enough pain relief to allow patients to avoid surgery altogether. In other cases, injections can delay the need for surgery, allowing patients to maintain their function and mobility for a longer period of time.
10. Risks and Complications of Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
While ultrasound-guided hip injections are generally safe, there are some potential risks and complications associated with the procedure.
10.1 Infection: A Rare but Serious Concern
Infection is a rare but serious complication of ultrasound-guided hip injections. The risk of infection can be minimized by following strict sterile techniques during the procedure.
Symptoms of infection include redness, swelling, warmth, and drainage at the injection site. If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your physician immediately.
10.2 Bleeding: Bruising and Hematoma Formation
Bleeding can occur at the injection site, resulting in bruising or hematoma formation. This is more common in patients who are taking blood-thinning medications.
The risk of bleeding can be minimized by avoiding blood-thinning medications before the procedure and applying pressure to the injection site after the procedure.
10.3 Nerve Damage: A Remote Possibility
Nerve damage is a remote possibility with ultrasound-guided hip injections. The risk of nerve damage can be minimized by using ultrasound guidance to visualize the nerves and avoid them during the injection.
Symptoms of nerve damage include numbness, tingling, or weakness in the leg or foot. If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your physician immediately.
10.4 Allergic Reaction: Responding to Medication Sensitivity
Allergic reactions to the local anesthetic or corticosteroid are possible, although rare. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can range from mild to severe and may include rash, hives, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing, and anaphylaxis.
Inform your physician if you have any known allergies to medications before the procedure.
10.5 Post-Injection Flare: Temporary Increase in Pain
Some patients may experience a temporary increase in pain after the injection, known as a post-injection flare. This is often due to the local anesthetic wearing off and the corticosteroid not yet taking effect.
The flare-up usually subsides within a few days. Over-the-counter pain relievers, ice, and rest can help to manage the pain.
11. Long-Term Outcomes and Success Rates
The long-term outcomes and success rates of ultrasound-guided hip injections vary depending on the underlying condition being treated and the individual patient’s response to the injection.
11.1 Osteoarthritis: Managing Chronic Pain and Improving Function
For patients with osteoarthritis, ultrasound-guided hip injections can provide significant pain relief and improve function. However, the effects of the injection are typically temporary, lasting for several weeks or months.
Repeated injections may be necessary to maintain pain relief and function. In some cases, injections can delay the need for hip replacement surgery.
11.2 Hip Labral Tears: Addressing Instability and Pain
For patients with hip labral tears, ultrasound-guided hip injections can help to reduce pain and inflammation. However, injections do not repair the torn labrum.
In some cases, injections can provide enough pain relief to allow patients to avoid surgery. In other cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the torn labrum and restore stability to the hip joint.
11.3 Bursitis: Resolving Inflammation and Reducing Tenderness
For patients with bursitis, ultrasound-guided hip injections can effectively resolve inflammation and reduce tenderness. The effects of the injection are typically long-lasting, with many patients experiencing significant pain relief for several months or years.
In some cases, additional treatments, such as physical therapy or activity modification, may be necessary to prevent recurrence of bursitis.
11.4 Factors Influencing Success: A Holistic Approach
Several factors can influence the success of ultrasound-guided hip injections, including:
- Underlying Condition: The type and severity of the underlying condition being treated can affect the outcome of the injection.
- Patient Compliance: Following post-procedure instructions, such as rest, activity modification, and physical therapy, can improve the outcome of the injection.
- Injection Technique: The skill and experience of the physician performing the injection can impact the accuracy and effectiveness of the injection.
- Overall Health: The patient’s overall health and lifestyle can affect their response to the injection.
11.5 When to Consider Alternative Treatments: A Comprehensive Evaluation
If ultrasound-guided hip injections do not provide adequate pain relief or improve function, it may be necessary to consider alternative treatments, such as physical therapy, medication, or surgery. A comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional can help to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your individual needs.
12. Alternatives to Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections
While ultrasound-guided hip injections can be an effective treatment option for hip pain, they are not the only option available. Several alternative treatments can provide pain relief and improve function.
12.1 Physical Therapy: Strengthening Muscles and Improving Flexibility
Physical therapy can be an effective treatment option for various hip conditions. A physical therapist can help you to strengthen your hip muscles, improve your range of motion, and reduce your pain.
They can also provide guidance on proper posture and body mechanics to prevent future problems.
12.2 Oral Medications: Managing Pain and Inflammation
Oral medications, such as over-the-counter pain relievers and prescription anti-inflammatory drugs, can be used to manage pain and inflammation in the hip.
However, these medications can have side effects, such as stomach upset, liver damage, and kidney damage. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of oral medications with your physician.
12.3 Topical Medications: Targeted Pain Relief
Topical medications, such as creams and gels, can be applied to the skin over the hip to provide targeted pain relief. These medications typically contain anti-inflammatory or pain-relieving ingredients.
Topical medications are generally safe and have fewer side effects than oral medications.
12.4 Assistive Devices: Reducing Stress on the Hip Joint
Assistive devices, such as canes, crutches, and walkers, can help to reduce stress on the hip joint and improve mobility. These devices can be particularly helpful for patients with osteoarthritis or other conditions that cause pain and instability in the hip.
12.5 Surgical Options: Addressing Structural Issues
Surgical options, such as hip arthroscopy and hip replacement, may be necessary to address structural issues in the hip joint. Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that can be used to repair torn cartilage, remove bone spurs, and address other problems in the hip joint. Hip replacement is a more extensive procedure that involves replacing the damaged hip joint with an artificial joint.
The choice of treatment depends on the underlying condition, the severity of the pain, and the individual patient’s needs and preferences.
13. Preparing for Your Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injection
Proper preparation can help to ensure a smooth and successful ultrasound-guided hip injection.
13.1 Medical History Review: Informing Your Physician
Before the procedure, your physician will review your medical history and ask about any medications you are taking, allergies you have, and medical conditions you have. It is important to provide accurate and complete information to your physician.
13.2 Medication Management: Adjusting Blood Thinners
If you are taking blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or warfarin, your physician may advise you to stop taking them for a few days before the procedure. This can help to reduce the risk of bleeding.
Follow your physician’s instructions carefully regarding medication management.
13.3 Day-of Instructions: What to Wear and Expect
On the day of the procedure, wear comfortable clothing and avoid wearing jewelry or other accessories that may interfere with the ultrasound imaging.
You may be asked to arrive at the clinic or hospital a few minutes early to complete paperwork and prepare for the procedure.
13.4 Mental Preparation: Reducing Anxiety
Anxiety can amplify pain perception, so it is important to stay relaxed during the procedure. Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and visualization, to help calm your nerves.
13.5 Questions for Your Doctor: Ensuring Clarity and Comfort
Prepare a list of questions to ask your doctor before the procedure. This can help to ensure that you understand the procedure and are comfortable with it.
Some questions you may want to ask include:
- What are the potential risks and complications of the procedure?
- What type of medication will be injected?
- How long will the pain relief last?
- What should I do after the procedure?
14. Choosing a Qualified Specialist for Your Injection
Choosing a qualified specialist is essential for ensuring a safe and effective ultrasound-guided hip injection.
14.1 Credentials and Expertise: Verifying Qualifications
Look for a physician who is board-certified in a relevant specialty, such as pain management, radiology, or orthopedics. Verify that the physician has extensive experience performing ultrasound-guided hip injections.
14.2 Experience with Ultrasound Guidance: Seeking Proficiency
Ensure that the physician has specific training and experience in using ultrasound guidance for hip injections. This can help to improve the accuracy and safety of the procedure.
14.3 Patient Reviews and Testimonials: Assessing Satisfaction
Read patient reviews and testimonials to assess the physician’s reputation and patient satisfaction. This can provide valuable insights into the physician’s skills, bedside manner, and overall quality of care.
14.4 Facility Accreditation: Ensuring Safety and Standards
Choose a facility that is accredited by a recognized organization, such as the American Association for Accreditation of Ambulatory Surgery Facilities (AAAASF) or the Accreditation Association for Ambulatory Health Care (AAAHC). This can help to ensure that the facility meets high standards of safety and quality.
14.5 Communication and Comfort: Building Trust
Choose a physician with whom you feel comfortable communicating. The physician should be willing to answer your questions, address your concerns, and explain the procedure in detail.
15. The Role of Imaging in Pain Management
Imaging plays a crucial role in pain management, helping physicians to diagnose the source of pain, guide injections, and monitor treatment outcomes.
15.1 Ultrasound: Real-Time Visualization
Ultrasound is a valuable imaging modality for pain management because it provides real-time visualization of the soft tissues and joints. This allows physicians to accurately guide needles and other instruments during injections and other procedures.
Ultrasound is also non-invasive and does not involve radiation exposure, making it a safe option for patients who require repeated imaging.
15.2 X-Ray: Assessing Bone Structure
X-ray imaging is used to assess the bone structure and identify any abnormalities, such as fractures, arthritis, or bone spurs. X-rays are often used in conjunction with other imaging modalities, such as ultrasound or MRI, to provide a comprehensive assessment of the musculoskeletal system.
