Guiding questions examples are prompts designed to stimulate deeper reflection and critical thinking, and CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources to help you master this technique. These questions encourage individuals to arrive at conclusions independently, fostering a more profound understanding. This article explores the definition, benefits, limitations, and practical applications of guiding questions, ensuring you are well-equipped to use them effectively. Masterful questioning, inquiry-based learning, and critical thinking skills are all enhanced through the strategic use of guiding questions.
1. Defining Guiding Questions: A Deep Dive
Guiding questions are carefully crafted inquiries intended to lead individuals or groups toward a specific learning outcome or solution without explicitly providing the answer. These questions serve as a cognitive scaffold, prompting learners to think critically, analyze information, and connect new knowledge with existing understandings. This approach encourages active participation and deeper engagement with the subject matter.
1.1 The Purpose of Guiding Questions
The primary purpose of guiding questions is to facilitate deeper learning and understanding. Unlike direct questions that seek specific answers, guiding questions encourage exploration, analysis, and critical thinking. They help individuals:
- Explore different perspectives: By prompting consideration of multiple viewpoints, guiding questions encourage a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Make connections: Guiding questions help learners relate new information to their existing knowledge and experiences.
- Develop critical thinking skills: By encouraging analysis and evaluation, guiding questions foster the development of critical thinking abilities.
- Promote self-discovery: Guiding questions allow individuals to arrive at conclusions independently, fostering a sense of ownership and deeper understanding.
- Enhance problem-solving abilities: They prompt individuals to consider various aspects of a problem, leading to more effective solutions.
1.2 Characteristics of Effective Guiding Questions
To be effective, guiding questions should possess certain characteristics that encourage meaningful exploration and reflection. Key characteristics include:
- Open-ended: Guiding questions should not have a simple yes or no answer. They should encourage elaboration and detailed responses.
- Thought-provoking: The questions should stimulate critical thinking and encourage individuals to delve deeper into the subject matter.
- Relevant: Guiding questions should be directly related to the topic or issue being explored.
- Clear and concise: The questions should be easy to understand and avoid ambiguity.
- Neutral: Guiding questions should not lead individuals toward a specific answer or viewpoint.
- Challenging: The questions should push individuals to think beyond their current understanding and explore new perspectives.
1.3 Examples of Guiding Questions Across Different Contexts
Guiding questions can be applied in various settings, including education, business, and personal development. Here are some examples:
- In Education:
- “How does this concept relate to what you already know?”
- “What are the potential implications of this theory?”
- “Can you provide an example of this concept in action?”
- “What are the strengths and weaknesses of this approach?”
- “How might different perspectives influence your understanding of this topic?”
- In Business:
- “What are the key challenges facing our organization?”
- “How can we improve our customer service?”
- “What are the potential risks and rewards of this strategy?”
- “How can we foster a more innovative work environment?”
- “What are the ethical considerations of this decision?”
- In Personal Development:
- “What are your core values and how do they influence your decisions?”
- “What are your strengths and weaknesses?”
- “What are your goals and how can you achieve them?”
- “What are the obstacles preventing you from reaching your full potential?”
- “How can you cultivate more positive relationships?”
2. Comprehensive List of Guiding Questions Examples
Here’s an extended list of guiding questions, categorized by the specific purpose they serve.
2.1 Questions to Clarify Understanding
These questions help to ensure that individuals have a solid grasp of the fundamental concepts.
- “Can you explain this concept in your own words?”
- “What are the key components of this theory?”
- “How does this relate to previous concepts we’ve discussed?”
- “What are the defining characteristics of this phenomenon?”
- “Can you provide a real-world example of this concept?”
- “What are the potential misconceptions about this topic?”
- “How can we break this down into simpler terms?”
- “What are the essential elements to remember?”
- “How does this differ from similar concepts?”
- “What are the prerequisites for understanding this concept?”
2.2 Questions to Encourage Critical Thinking
These questions push individuals to think beyond the surface level and analyze the information presented.
- “What are the potential implications of this?”
- “What are the strengths and weaknesses of this approach?”
- “What evidence supports this claim?”
- “What are the alternative perspectives on this issue?”
- “How can we evaluate the validity of this argument?”
- “What assumptions are being made?”
- “How might this be interpreted differently?”
- “What are the potential biases influencing this perspective?”
- “How does this fit into the larger context?”
- “What are the ethical considerations involved?”
2.3 Questions to Promote Problem-Solving
These questions guide individuals through the process of identifying and resolving issues.
- “What is the core problem we’re trying to solve?”
- “What are the potential causes of this issue?”
- “What are the possible solutions?”
- “What are the pros and cons of each solution?”
- “How can we evaluate the effectiveness of each solution?”
- “What resources do we need to implement the best solution?”
- “What are the potential challenges we might face?”
- “How can we mitigate these challenges?”
- “How will we measure our success?”
- “What are the long-term implications of our solution?”
2.4 Questions to Foster Creativity
These questions encourage individuals to think outside the box and generate innovative ideas.
- “What if we approached this from a completely different angle?”
- “What are the unconventional solutions we haven’t considered?”
- “How can we combine existing ideas in new and innovative ways?”
- “What are the potential opportunities we’re overlooking?”
- “How can we challenge the status quo?”
- “What are the most audacious ideas we can come up with?”
- “How can we make this more engaging and exciting?”
- “What are the potential applications beyond the obvious?”
- “How can we leverage emerging technologies to solve this problem?”
- “What if we had unlimited resources?”
2.5 Questions to Encourage Reflection
These questions prompt individuals to consider their own thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- “How does this make you feel?”
- “What are your initial reactions to this?”
- “What assumptions are you making?”
- “How has your perspective changed?”
- “What have you learned from this experience?”
- “How can you apply this to your own life?”
- “What are the key takeaways for you?”
- “How has this challenged your beliefs?”
- “What are you still wondering about?”
- “How can you continue to learn and grow from this?”
2.6 Questions to Encourage Goal Setting
These questions help individuals to identify their goals and develop strategies for achieving them.
- “What do you want to achieve?”
- “Why is this goal important to you?”
- “What are the steps you need to take to achieve this goal?”
- “What resources do you need?”
- “What are the potential obstacles you might face?”
- “How will you measure your progress?”
- “What are the rewards for achieving this goal?”
- “What are the consequences of not achieving this goal?”
- “How can you stay motivated along the way?”
- “What support do you need from others?”
 Guiding Questions Encourage Reflection
Guiding Questions Encourage Reflection
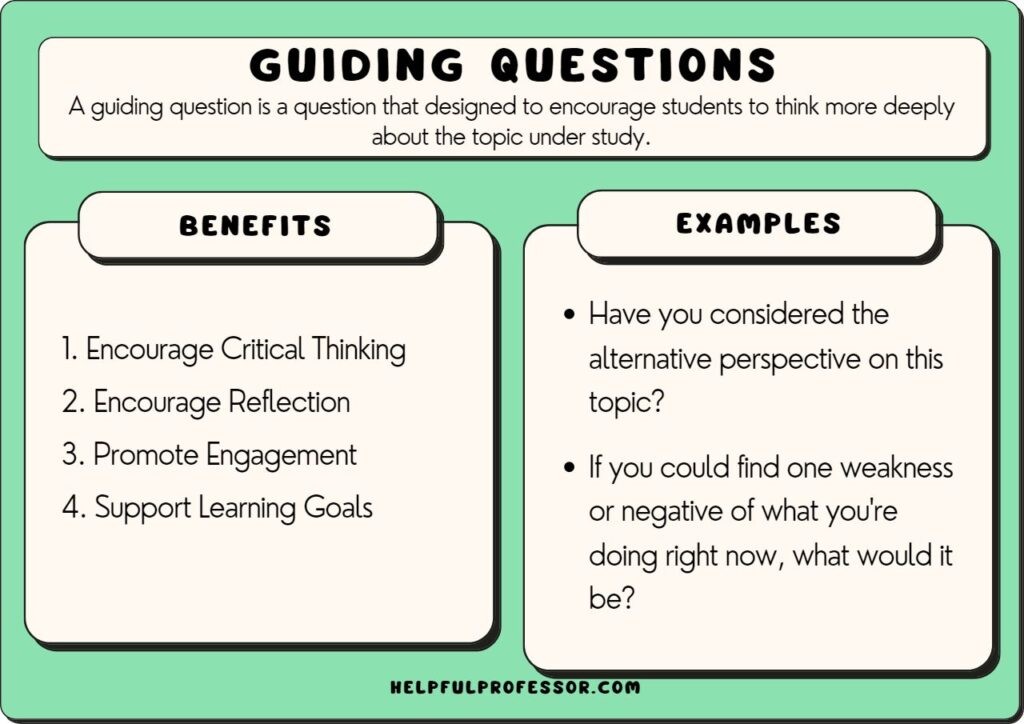
3. The Benefits of Using Guiding Questions
Utilizing guiding questions offers numerous advantages in various contexts. Here are some key benefits:
3.1 Enhanced Learning and Understanding
Guiding questions promote deeper engagement with the subject matter, leading to improved retention and comprehension. By actively exploring the material and connecting it to their existing knowledge, learners develop a more profound understanding.
3.2 Development of Critical Thinking Skills
Guiding questions encourage individuals to analyze information, evaluate arguments, and form their own opinions. This process cultivates critical thinking skills that are essential for success in academic and professional settings.
3.3 Increased Engagement and Motivation
By actively participating in the learning process, individuals become more invested in the outcome. Guiding questions can spark curiosity, challenge assumptions, and inspire a desire to learn more.
3.4 Improved Problem-Solving Abilities
Guiding questions help individuals to approach problems systematically, identify potential solutions, and evaluate their effectiveness. This approach enhances problem-solving abilities and fosters a more proactive mindset.
3.5 Promotion of Self-Reflection and Awareness
Guiding questions prompt individuals to consider their own thoughts, feelings, and experiences. This process promotes self-reflection and awareness, leading to personal growth and development.
3.6 Fostering Collaboration and Communication
Guiding questions can be used in group settings to facilitate discussion, encourage diverse perspectives, and promote collaborative problem-solving. This approach enhances communication skills and fosters a more inclusive environment.
3.7 Encouraging Autonomy and Responsibility
By allowing individuals to arrive at conclusions independently, guiding questions foster a sense of ownership and responsibility for their learning outcomes. This approach promotes autonomy and empowers individuals to take control of their own development.
4. Addressing the Limitations of Guiding Questions
While guiding questions offer numerous benefits, it’s important to acknowledge their limitations and potential drawbacks.
4.1 Risk of Restricting Creativity
If not carefully crafted, guiding questions can inadvertently limit the scope of exploration and stifle creativity. It’s essential to ensure that the questions are open-ended enough to allow for diverse perspectives and innovative solutions.
4.2 Potential for Bias
Guiding questions can reflect the biases of the questioner, leading individuals toward a particular viewpoint. It’s important to be aware of this potential and strive to formulate questions that are neutral and unbiased.
4.3 Time-Consuming Nature
Using guiding questions effectively can be a time-consuming process, particularly in group settings. It requires careful planning, facilitation, and patience to ensure that everyone has the opportunity to participate and contribute.
4.4 Dependence on Facilitation Skills
The success of guiding questions depends heavily on the skills of the facilitator. A skilled facilitator can create a safe and supportive environment, encourage participation, and guide the discussion in a productive direction.
4.5 Possibility of Incomplete Understanding
If not carefully designed, guiding questions may only address certain aspects of a topic, leading to an incomplete understanding. It’s important to ensure that the questions cover all relevant areas and encourage a comprehensive exploration of the subject matter.
5. Real-World Applications: Case Studies
To illustrate the practical application of guiding questions, let’s examine a few case studies across different domains.
5.1 Case Study 1: Enhancing Student Engagement in a History Class
A history teacher wanted to improve student engagement and critical thinking skills. Instead of lecturing, she began using guiding questions to explore historical events. For example, when studying the American Revolution, she asked:
- “What were the key factors that led to the American Revolution?”
- “How did different groups (e.g., colonists, British government, enslaved people) experience the revolution?”
- “What were the long-term consequences of the American Revolution?”
- “How does the American Revolution relate to contemporary issues?”
By prompting students to analyze primary sources, consider different perspectives, and connect historical events to the present day, the teacher fostered a more engaging and meaningful learning experience.
5.2 Case Study 2: Improving Team Performance in a Business Setting
A project manager wanted to improve team collaboration and problem-solving abilities. He implemented a strategy of using guiding questions during team meetings. For example, when facing a project challenge, he asked:
- “What is the core problem we’re trying to solve?”
- “What are the potential causes of this issue?”
- “What are the possible solutions?”
- “What are the pros and cons of each solution?”
- “How can we evaluate the effectiveness of each solution?”
By encouraging team members to analyze the problem, generate solutions, and evaluate their options, the project manager fostered a more collaborative and effective problem-solving process.
5.3 Case Study 3: Promoting Personal Growth and Self-Awareness
A life coach used guiding questions to help clients identify their goals, overcome obstacles, and achieve personal growth. For example, when working with a client who felt stuck in their career, the coach asked:
- “What do you truly want to achieve in your career?”
- “What are your strengths and how can you leverage them?”
- “What are the obstacles preventing you from reaching your goals?”
- “What steps can you take to overcome these obstacles?”
- “How can you stay motivated and accountable?”
By prompting clients to reflect on their values, identify their strengths, and develop a plan of action, the coach helped them to take control of their lives and achieve their full potential.
6. Best Practices for Formulating Effective Guiding Questions
Creating guiding questions that stimulate critical thinking and facilitate deeper understanding requires careful consideration. Here are some best practices to follow:
6.1 Start with Clear Objectives
Before formulating any questions, it’s important to define the specific learning objectives or desired outcomes. What do you want individuals to learn, understand, or achieve? Having a clear sense of purpose will help you to craft questions that are relevant and effective.
6.2 Use Open-Ended Language
Guiding questions should be open-ended, encouraging elaboration and detailed responses. Avoid questions that can be answered with a simple yes or no. Instead, use phrases like “How,” “Why,” “What,” and “In what ways.”
6.3 Encourage Exploration of Multiple Perspectives
Formulate questions that prompt individuals to consider different viewpoints and challenge their assumptions. This will help them to develop a more comprehensive understanding of the topic and avoid narrow thinking.
6.4 Promote Analysis and Evaluation
Craft questions that encourage individuals to analyze information, evaluate arguments, and form their own opinions. This will help them to develop critical thinking skills and become more discerning learners.
6.5 Foster Reflection and Self-Awareness
Include questions that prompt individuals to consider their own thoughts, feelings, and experiences. This will help them to develop self-awareness and connect the learning material to their own lives.
6.6 Ensure Clarity and Relevance
Use language that is clear, concise, and easy to understand. Avoid jargon or technical terms that may confuse or intimidate individuals. Make sure that the questions are directly related to the topic or issue being explored.
6.7 Create a Safe and Supportive Environment
Encourage participation by creating a safe and supportive environment where individuals feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and ideas. Avoid criticism or judgment and focus on fostering a culture of curiosity and exploration.
7. How to Integrate Guiding Questions into Your Teaching or Training Sessions
Integrating guiding questions into your teaching or training sessions can significantly enhance the learning experience. Here’s how to do it effectively:
7.1 Prepare Your Questions in Advance
Before the session, carefully plan the guiding questions you want to use. Align them with your learning objectives and ensure they cover key concepts and themes.
7.2 Set the Stage
At the beginning of the session, explain the purpose of using guiding questions and emphasize that there are no right or wrong answers. Encourage everyone to participate and share their thoughts openly.
7.3 Present Questions at Strategic Moments
Introduce guiding questions at key points during the session to stimulate discussion, encourage critical thinking, and check for understanding.
7.4 Facilitate Discussion
As individuals respond to the questions, facilitate a discussion by asking follow-up questions, encouraging different perspectives, and summarizing key points.
7.5 Provide Feedback
Offer constructive feedback on individuals’ responses, highlighting their insights and encouraging them to delve deeper into the subject matter.
7.6 Encourage Reflection
At the end of the session, encourage individuals to reflect on what they have learned and how they can apply it to their own lives.
7.7 Use Visual Aids
Displaying the questions visually (e.g., on a whiteboard or slide) can help to keep everyone focused and engaged.
8. Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Guiding Questions
Implementing guiding questions effectively is not without its challenges. Here are some common obstacles and how to overcome them:
8.1 Resistance to Participation
Some individuals may be hesitant to participate in discussions or share their thoughts openly. To overcome this, create a safe and supportive environment, emphasize that there are no right or wrong answers, and encourage everyone to contribute at their own pace.
8.2 Dominating Voices
In group settings, some individuals may dominate the discussion, preventing others from having a chance to speak. To address this, use techniques like round-robin discussions, small group activities, or anonymous feedback mechanisms to ensure that everyone has an opportunity to participate.
8.3 Superficial Responses
Some individuals may provide superficial responses that lack depth or critical thinking. To encourage deeper engagement, ask follow-up questions, challenge assumptions, and prompt individuals to provide evidence or examples to support their claims.
8.4 Time Constraints
Using guiding questions effectively can be time-consuming, especially in group settings. To manage time effectively, prioritize the most important questions, set time limits for responses, and use techniques like brainstorming or mind mapping to generate ideas quickly.
8.5 Lack of Facilitation Skills
Effectively facilitating discussions using guiding questions requires specific skills, such as active listening, questioning techniques, and conflict resolution. If you lack these skills, consider seeking training or mentorship to improve your facilitation abilities.
9. The Role of Technology in Enhancing Guiding Questions
Technology can play a significant role in enhancing the effectiveness of guiding questions. Here are some ways to leverage technology:
9.1 Online Discussion Forums
Create online discussion forums where individuals can respond to guiding questions, share their thoughts, and engage with others asynchronously.
9.2 Interactive Whiteboards
Use interactive whiteboards to display guiding questions, capture responses, and facilitate real-time collaboration.
9.3 Polling and Survey Tools
Use polling and survey tools to gather quick feedback on guiding questions and assess understanding.
9.4 Video Conferencing
Utilize video conferencing platforms to conduct virtual discussions using guiding questions, enabling remote participants to engage in the learning process.
9.5 Collaborative Document Tools
Use collaborative document tools (e.g., Google Docs) to create shared workspaces where individuals can respond to guiding questions, share ideas, and co-create content.
9.6 Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Integrate guiding questions into learning management systems to provide a structured learning experience and track individual progress.
10. Ethical Considerations When Using Guiding Questions
Using guiding questions ethically is paramount to ensure a fair and unbiased learning or problem-solving environment.
10.1 Avoid Leading Questions
Ensure that your questions do not lead participants to a predetermined answer. The aim is to stimulate thought, not to steer opinions.
10.2 Respect Diverse Perspectives
Acknowledge and respect the diverse perspectives that may arise from guiding questions. Create an inclusive environment where all viewpoints are valued.
10.3 Maintain Confidentiality
When using guiding questions in a personal or coaching context, maintain confidentiality and respect the privacy of the individuals involved.
10.4 Be Mindful of Power Dynamics
Be aware of power dynamics in group settings and ensure that all participants have an equal opportunity to share their thoughts and ideas.
10.5 Promote Critical Thinking
Encourage participants to think critically about the information presented and to form their own opinions based on evidence and reasoning.
11. Integrating Guiding Questions into Different Learning Styles
Different individuals learn in different ways. Integrating guiding questions into various learning styles can enhance their effectiveness.
11.1 Visual Learners
Use visual aids like diagrams, charts, and videos to complement guiding questions. Display the questions visually to keep them engaged.
11.2 Auditory Learners
Encourage discussion and verbal responses to guiding questions. Facilitate group discussions where they can learn from their peers.
11.3 Kinesthetic Learners
Incorporate hands-on activities or simulations that relate to the guiding questions. Allow them to explore concepts through experience.
11.4 Read/Write Learners
Provide written versions of the guiding questions and encourage them to write down their responses. Offer reading materials that support their understanding.
12. Guiding Questions in Leadership and Management
Guiding questions are powerful tools for leaders and managers to foster critical thinking, innovation, and problem-solving within their teams.
12.1 Strategic Planning
Use guiding questions to help teams develop strategic plans, identify goals, and define success metrics.
12.2 Decision-Making
Employ guiding questions to ensure that decisions are well-informed, ethical, and aligned with organizational values.
12.3 Performance Management
Utilize guiding questions during performance reviews to encourage self-reflection, identify areas for improvement, and set goals.
12.4 Conflict Resolution
Use guiding questions to facilitate constructive dialogue, explore different perspectives, and find mutually agreeable solutions.
12.5 Innovation and Creativity
Foster a culture of innovation by using guiding questions to challenge assumptions, generate new ideas, and explore unconventional solutions.
13. Examples of Guiding Questions in Different Industries
Guiding questions can be tailored to specific industries to address unique challenges and opportunities.
13.1 Healthcare
“How can we improve patient outcomes while reducing costs?”
“What are the ethical considerations of this medical procedure?”
“How can we enhance the patient experience?”
13.2 Education
“How can we make learning more engaging and relevant for students?”
“What are the most effective teaching strategies for different learning styles?”
“How can we promote equity and inclusion in education?”
13.3 Technology
“How can we use technology to solve pressing social problems?”
“What are the potential risks and rewards of this new technology?”
“How can we ensure that technology is used ethically and responsibly?”
13.4 Finance
“How can we help our clients achieve their financial goals?”
“What are the ethical considerations of this investment strategy?”
“How can we mitigate financial risks?”
13.5 Manufacturing
“How can we improve efficiency and reduce waste in our manufacturing processes?”
“What are the sustainability implications of our products?”
“How can we ensure the safety of our workers?”
14. The Future of Guiding Questions: Trends and Innovations
As technology and learning methodologies evolve, the use of guiding questions is also adapting.
14.1 AI-Powered Guiding Questions
Artificial intelligence can be used to generate personalized guiding questions based on individual learning needs and preferences.
14.2 Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR can create immersive learning experiences that incorporate guiding questions to enhance engagement and understanding.
14.3 Adaptive Learning Platforms
Adaptive learning platforms can adjust the difficulty and content of guiding questions based on individual performance, providing a customized learning experience.
14.4 Gamification
Gamification techniques can be used to make answering guiding questions more engaging and rewarding, motivating individuals to participate actively.
14.5 Collaborative Online Platforms
Collaborative online platforms can facilitate group discussions using guiding questions, enabling remote participants to engage in real-time problem-solving.
15. Actionable Steps to Implement Guiding Questions Effectively
To ensure that you effectively implement guiding questions in your personal or professional life, follow these actionable steps:
15.1 Identify Your Goals
Clearly define what you want to achieve by using guiding questions. What specific outcomes are you seeking?
15.2 Plan Your Questions
Carefully plan the guiding questions you will use, aligning them with your goals and considering the context in which they will be used.
15.3 Practice Your Facilitation Skills
If you will be facilitating group discussions, practice your facilitation skills to ensure that you can create a safe and supportive environment, encourage participation, and manage time effectively.
15.4 Gather Feedback
After using guiding questions, gather feedback from participants to assess their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
15.5 Reflect and Adapt
Reflect on your experiences using guiding questions and adapt your approach based on what you have learned. Continuously refine your questions and facilitation techniques to maximize their impact.
By following these steps, you can harness the power of guiding questions to foster critical thinking, promote deeper learning, and achieve your desired outcomes.
16. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Guiding Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about guiding questions:
16.1 What is the difference between guiding questions and direct questions?
Guiding questions are open-ended inquiries designed to stimulate critical thinking and exploration, while direct questions seek specific answers.
16.2 How do I create effective guiding questions?
To create effective guiding questions, start with clear objectives, use open-ended language, encourage exploration of multiple perspectives, and promote analysis and evaluation.
16.3 What are the benefits of using guiding questions?
The benefits of using guiding questions include enhanced learning and understanding, development of critical thinking skills, increased engagement and motivation, improved problem-solving abilities, and promotion of self-reflection and awareness.
16.4 What are the limitations of using guiding questions?
The limitations of using guiding questions include the risk of restricting creativity, the potential for bias, the time-consuming nature, and the dependence on facilitation skills.
16.5 How can I integrate guiding questions into my teaching or training sessions?
To integrate guiding questions into your teaching or training sessions, prepare your questions in advance, set the stage, present questions at strategic moments, facilitate discussion, provide feedback, and encourage reflection.
16.6 How can I overcome challenges in implementing guiding questions?
To overcome challenges in implementing guiding questions, address resistance to participation, manage dominating voices, encourage deeper engagement, manage time effectively, and improve your facilitation skills.
16.7 What role does technology play in enhancing guiding questions?
Technology can enhance guiding questions through online discussion forums, interactive whiteboards, polling and survey tools, video conferencing, collaborative document tools, and learning management systems.
16.8 What are the ethical considerations when using guiding questions?
Ethical considerations when using guiding questions include avoiding leading questions, respecting diverse perspectives, maintaining confidentiality, being mindful of power dynamics, and promoting critical thinking.
16.9 How can I integrate guiding questions into different learning styles?
To integrate guiding questions into different learning styles, use visual aids for visual learners, encourage discussion for auditory learners, incorporate hands-on activities for kinesthetic learners, and provide written materials for read/write learners.
16.10 How can I use guiding questions in leadership and management?
You can use guiding questions in leadership and management for strategic planning, decision-making, performance management, conflict resolution, and innovation and creativity.
In conclusion, guiding questions are powerful tools that can enhance learning, promote critical thinking, and foster innovation. By understanding their benefits, limitations, and best practices, you can effectively implement them in various settings and achieve your desired outcomes. For more information and resources on guiding questions and ethical conduct, visit conduct.edu.vn at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 555-1234.