In computer networks, data zips between devices through various pathways known as transmission media. These pathways can be broadly categorized into two types: guided and unguided. This article dives deep into What Is Guided Media, exploring its characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and different types.
A transmission medium is the physical pathway between a transmitter and a receiver. It’s the channel through which data journeys from one device to another.
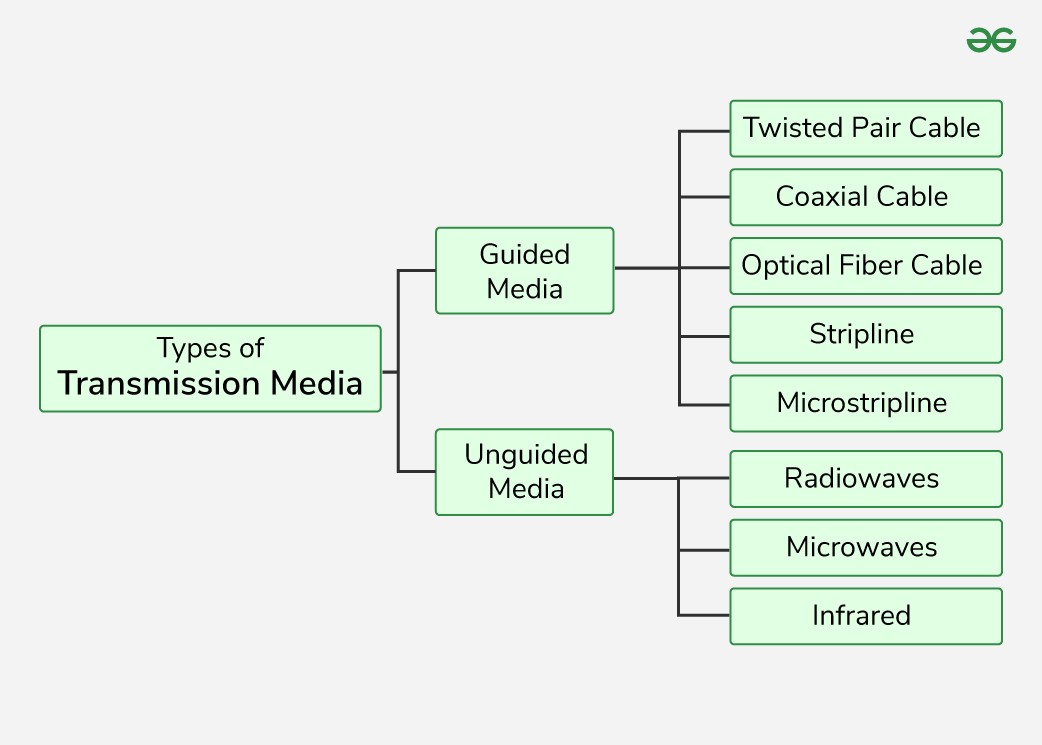
Guided media, also called wired or bounded transmission media, uses physical links to confine signals to a narrow pathway, ensuring directed and secure transmission.
Features of Guided Media
Guided media boasts several key features:
- High Speed: Wired connections generally offer higher data transfer speeds compared to wireless alternatives.
- Secure: The physical connection makes it more difficult for unauthorized access and interception of data.
- Shorter Distances: Typically used for shorter distances due to signal degradation over longer cable lengths.
Types of Guided Media
There are several types of guided media, each with unique properties and applications:
Twisted Pair Cable
Twisted pair cable consists of two insulated copper wires twisted together. This twisting helps reduce interference (crosstalk) from other wires. These cables are commonly bundled together within a protective sheath.
There are two main types of twisted pair cables:
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
UTP is the most common and least expensive type of twisted pair cable. It’s widely used in Ethernet networks and telephone systems.
Advantages of UTP:
- Least Expensive: UTP cables are affordable and readily available.
- Easy to Install: They are relatively easy to install and terminate.
- High-Speed Capacity: Modern UTP cables can support high data transfer rates.
Disadvantages of UTP:
- Lower Performance: Compared to STP (Shielded Twisted Pair), UTP is more susceptible to interference.
- Shorter Distance Transmission: Signal attenuation limits the maximum cable length.
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
STP cables include a copper braid or foil shield around the twisted wires to provide better protection against interference.
Advantages of STP:
- Better Performance: STP offers better performance at higher data rates due to reduced interference.
- Eliminates Crosstalk: The shielding minimizes crosstalk between adjacent wires.
- Faster Data Rate: Supports faster data transfer speeds compared to UTP.
Disadvantages of STP:
- Difficult Installation: STP cables are more difficult to install and terminate.
- More Expensive: STP cables are more costly than UTP cables.
- Bulky: The shielding adds to the bulk and weight of the cable.
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable consists of a central conductor surrounded by an insulating layer, a conductive shield, and an outer plastic jacket. It’s used for transmitting radio frequency signals.
Advantages of Coaxial Cable:
- High Bandwidth: Coaxial cables offer high bandwidth capabilities.
- Easy to Install: Relatively easy to install.
- Reliable and Durable: More reliable and durable than twisted pair cables.
- Less Affected by Interference: Less susceptible to noise, crosstalk, and electromagnetic interference.
- Supports Multiple Channels: Can support multiple channels of data transmission.
Disadvantages of Coaxial Cable:
- Expensive: More expensive than twisted pair cables.
- Grounding Required: Requires proper grounding to prevent crosstalk.
- Bulky: The multiple layers make coaxial cables bulky.
- Security Risk: Vulnerable to tapping with “t-joints,” potentially compromising data security.
Optical Fiber Cable
Optical fiber cable transmits data as light pulses through thin strands of glass or plastic. It offers very high bandwidth and is ideal for long-distance communication.
Advantages of Optical Fiber Cable:
- Increased Capacity and Bandwidth: Offers extremely high bandwidth and data transfer rates.
- Lightweight: Lighter than copper cables.
- Less Signal Attenuation: Minimal signal loss over long distances.
- Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference: Not susceptible to electromagnetic interference.
- Resistance to Corrosive Materials: Resistant to corrosion.
Disadvantages of Optical Fiber Cable:
- Difficult Installation and Maintenance: More challenging to install and maintain.
- High Cost: More expensive than copper cables.
Applications of Optical Fiber Cable:
- Medical Purpose: Used in medical instruments for imaging and diagnostics.
- Defense Purpose: Used in aerospace for data transmission.
- Communication: Widely used in internet cables for high-speed data transmission.
- Industrial Purpose: Used for lighting and safety measures in automobiles.
Stripline
Stripline is a type of transmission line used to transmit high-frequency signals. It consists of a conducting strip sandwiched between two ground planes.
Microstripline
Microstripline is another type of transmission line used for high-frequency signals. It consists of a conducting strip on top of a dielectric substrate with a ground plane on the other side. Microstriplines are commonly found in microwave and radio frequency circuits.
Conclusion
Guided media plays a critical role in computer networks, providing secure and high-speed data transmission. Understanding the characteristics and types of guided media is essential for designing and maintaining efficient and reliable network infrastructure. The choice of guided media depends on factors like bandwidth requirements, distance, budget, and the level of security needed.