What Is Science Study Guide is your essential resource for test preparation and mastering scientific concepts. CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides comprehensive guidance, practical tips, and detailed explanations to help you excel in your science studies, covering everything from fundamental principles to advanced topics, ensuring you are well-prepared for any scientific challenge. Explore our resources to enhance your understanding of scientific theories, methodologies, and applications.
1. Frequently Asked Questions About Science Study
1.1 Is Science Study Difficult?
Science can seem daunting, but effective preparation makes it manageable. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers strategies to simplify complex topics. According to a study by the National Science Teachers Association (NSTA), students who engage in hands-on activities and real-world applications demonstrate better understanding and retention of scientific concepts. Here are a few tips to make science study easier:
- Focus on Core Concepts: Understand fundamental principles before moving to more advanced material.
- Use Visual Aids: Diagrams, charts, and videos can help clarify complex ideas.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice reinforces learning and improves retention.
- Seek Clarification: Don’t hesitate to ask teachers or peers for help when you encounter difficulties.
1.2 What Areas Does Science Study Cover?
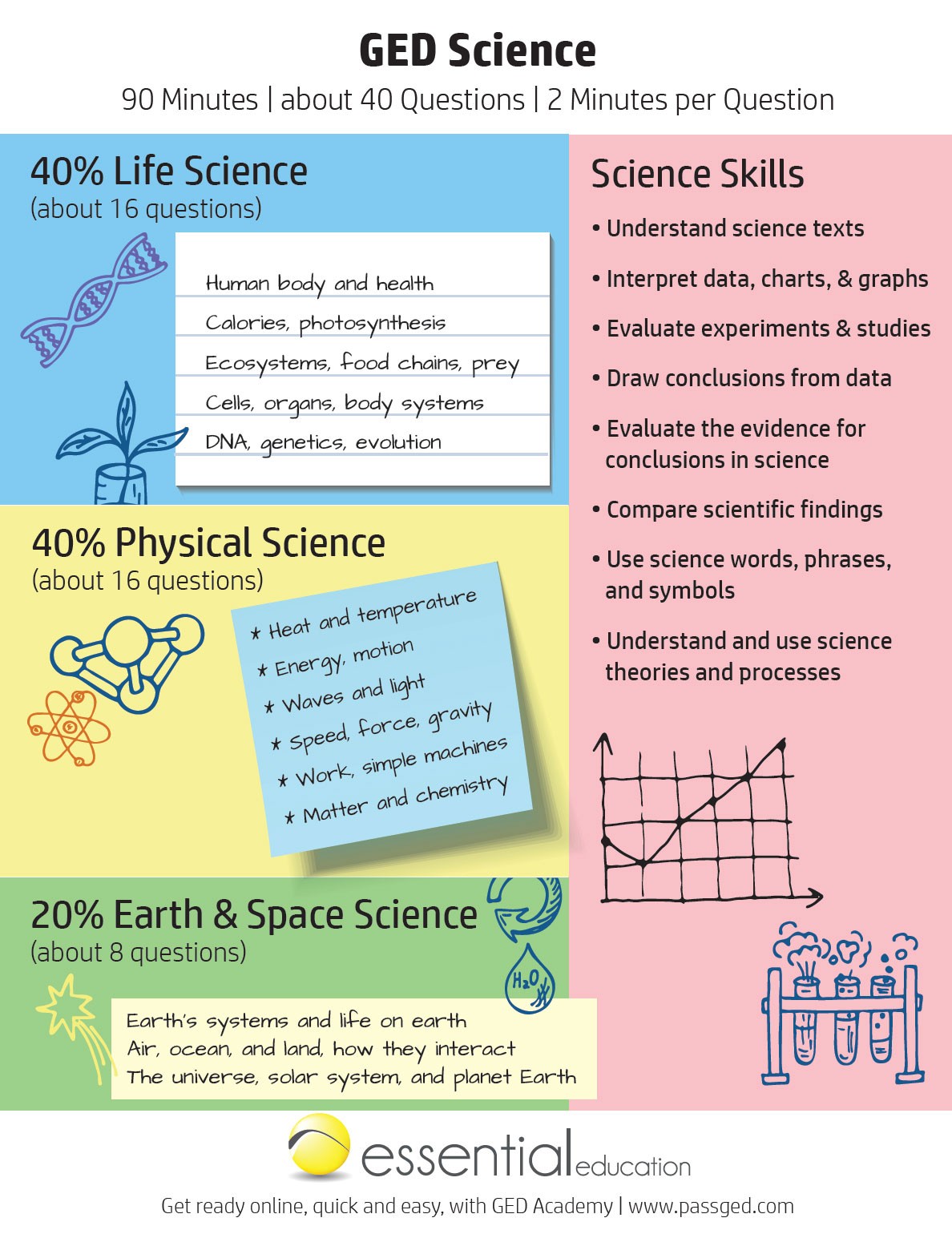
Science encompasses diverse fields, each exploring different aspects of the natural world. Science study can be broken down into three primary areas:
- Life Science: This includes biology, zoology, botany, and genetics. Life science covers the study of living organisms, their structure, function, growth, evolution, and interactions with each other and their environment.
- Physical Science: This includes physics, chemistry, and astronomy. Physical science explores the fundamental laws and principles governing the behavior of matter and energy.
- Earth Science: This includes geology, meteorology, and oceanography. Earth science focuses on the study of the Earth, its structure, composition, processes, and its place in the solar system.
1.3 How to Plan Your Science Study?
Effective planning is crucial for successful science study. Begin by identifying your goals and the specific topics you need to cover. Here’s a step-by-step approach to help you create a solid study plan:
- Set Specific Goals: Determine what you want to achieve, such as mastering a particular concept or passing an exam.
- Break Down the Material: Divide large topics into smaller, manageable sections.
- Create a Timeline: Allocate specific time slots for each topic, ensuring you cover everything before your deadline.
- Use a Variety of Resources: Utilize textbooks, online resources, and study guides for a comprehensive understanding.
- Review Regularly: Schedule regular review sessions to reinforce your learning.
- Take Practice Tests: Use practice tests to identify areas where you need more work.
1.4 How Much Time Should You Dedicate to Science Study?
The amount of time needed for science study depends on your goals, the complexity of the subject matter, and your current level of understanding. However, consistency is key. Aim for at least 1-2 hours of focused study each day. Remember to include time for:
- Reading and note-taking
- Practice problems and exercises
- Reviewing and summarizing material
- Seeking help when needed
1.5 How Can I Effectively Learn Science Formulas?
Formulas are essential tools in science. They provide a concise way to express relationships between different variables and make quantitative predictions. Mastering formulas requires understanding their meaning, application, and limitations. Here’s a guide:
- Understand the Meaning: Grasp the underlying concepts behind each formula.
- Identify the Variables: Know what each symbol in the formula represents.
- Practice Application: Work through numerous practice problems to apply the formula in different contexts.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards with the formula on one side and its explanation on the other.
- Relate to Real-World Examples: Connect the formula to real-world phenomena to make it more tangible.
1.6 What Role Do Experiments Play in Science Study?
Experiments are fundamental to science study as they provide empirical evidence to support or refute scientific hypotheses. They help students understand the scientific method, develop critical thinking skills, and apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations. The steps of an experiment include:
- Formulating a Hypothesis: Developing a testable statement about the relationship between variables.
- Designing the Experiment: Planning the procedure, including identifying variables, controls, and sample sizes.
- Conducting the Experiment: Following the procedure and collecting data accurately.
- Analyzing the Data: Using statistical methods to interpret the data and draw conclusions.
- Communicating the Results: Presenting the findings in a clear and concise manner, usually in a written report.
1.7 Where Can I Find Science Worksheets?
Science worksheets are valuable tools for reinforcing learning and practicing problem-solving skills. They provide structured exercises that help students apply their knowledge and identify areas where they need more work. You can find science worksheets at the following places:
- Educational Websites: Many websites offer free or subscription-based science worksheets for various topics and grade levels.
- Textbooks and Study Guides: Textbooks often include worksheets and practice problems at the end of each chapter.
- Teacher Resources: Teachers may provide worksheets as part of their lesson plans.
1.8 Is there a science cheat sheet to help me understand the test?
Yes, science cheat sheets can be valuable tools for quickly reviewing key concepts and formulas. They provide a concise summary of the most important information. These cheat sheets are best used to:
- Review Key Concepts: Quickly refresh your memory on important definitions, formulas, and theories.
- Identify Knowledge Gaps: Spot areas where you need to focus your study efforts.
- Prepare for Exams: Use them as a last-minute study aid to reinforce your knowledge.
- Organize Information: Help structure and organize information in a way that is easy to understand and remember.
1.9 What are the key areas to focus on when studying for a science test?
When preparing for a science test, it’s crucial to focus on several key areas to ensure comprehensive coverage of the material. These include:
- Understand Core Concepts: Focus on grasping the fundamental principles and theories in each topic.
- Review Vocabulary: Familiarize yourself with key scientific terms and their definitions.
- Practice Problem Solving: Work through various examples and exercises to apply your knowledge.
- Analyze Data: Practice interpreting and analyzing data from graphs, charts, and tables.
- Apply the Scientific Method: Understand and apply the scientific method in experimental scenarios.
1.10 How to integrate CONDUCT.EDU.VN Resources Into My Science Study?
Integrating CONDUCT.EDU.VN resources into your science study can greatly enhance your understanding and preparation. Here’s how:
- Access Comprehensive Guides: Use CONDUCT.EDU.VN’s detailed guides for in-depth explanations of scientific concepts.
- Utilize Practice Questions: Test your knowledge with practice questions to identify areas for improvement.
- Review Real-World Examples: Explore real-world case studies to see how scientific principles are applied in practical situations.
- Engage with Ethical Discussions: Consider the ethical implications of scientific advancements through thought-provoking discussions.
- Seek Expert Advice: Connect with experts through CONDUCT.EDU.VN to get personalized guidance and clarification.
2. Science Topics Breakdown
Understanding the breadth of science topics is essential for effective science study. Here is a breakdown of the major areas:
2.1 Life Science (Biology)
Life science, or biology, is the study of living organisms, their structure, function, growth, evolution, and interactions with each other and their environment. Life science is an expansive field, covering everything from the microscopic world of cells and molecules to the vast complexity of ecosystems and biomes. Understanding the core concepts in life science is crucial for anyone interested in pursuing a career in healthcare, environmental science, or biotechnology. Key sub-disciplines include:
- Anatomy: The study of the structure of living organisms.
- Physiology: The study of the function of living organisms and their parts.
- Genetics: The study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics.
- Ecology: The study of the interactions between living organisms and their environment.
- Evolution: The study of the processes by which living organisms change over time.
- Microbiology: The study of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa.
2.2 Physical Science (Physics and Chemistry)
Physical science encompasses the study of non-living matter and energy. It includes disciplines such as physics, chemistry, and astronomy, which seek to explain the fundamental laws and principles that govern the behavior of the universe. Physical science is essential for understanding the world around us and for developing new technologies and innovations.
- Physics: The study of the fundamental laws of nature, including motion, energy, force, and matter.
- Chemistry: The study of the composition, structure, properties, and reactions of matter.
- Astronomy: The study of celestial objects, such as planets, stars, galaxies, and the universe as a whole.
2.3 Earth Science (Geology and Environmental Science)
Earth science is an interdisciplinary field that studies the Earth, its structure, composition, processes, and its place in the solar system. It includes disciplines such as geology, meteorology, oceanography, and environmental science, which seek to understand the complex interactions between the Earth’s systems and the impact of human activities on the environment. Earth science is crucial for addressing some of the most pressing challenges facing humanity, such as climate change, resource management, and natural hazards.
- Geology: The study of the Earth’s structure, composition, and processes, including rocks, minerals, and landforms.
- Meteorology: The study of the atmosphere, weather, and climate.
- Oceanography: The study of the oceans, including their physical, chemical, and biological properties.
- Environmental Science: The study of the interactions between humans and the environment, including pollution, conservation, and sustainability.
3. Key Science Skills for Success
Developing key science skills is essential for achieving success in science study and future career endeavors. These skills enable you to think critically, solve problems, and apply scientific knowledge effectively.
3.1 How To Understand Science Texts Effectively?
Understanding science texts requires active reading strategies that help you grasp complex concepts and retain information. Effective reading habits include:
- Preview the Text: Skim the headings, subheadings, and images to get an overview of the topic.
- Read Actively: Annotate the text by highlighting key points, writing notes in the margins, and summarizing the main ideas.
- Look Up Unfamiliar Terms: Use a dictionary or online resources to define unfamiliar words and phrases.
- Make Connections: Relate the information to what you already know and think about how it applies to real-world situations.
- Summarize the Text: Write a summary of the main points in your own words to check your understanding.
3.2 How To Interpret Data, Charts, and Graphs?
Interpreting data, charts, and graphs is a crucial skill in science. These visual representations provide valuable information about relationships, trends, and patterns. To interpret them effectively:
- Identify the Variables: Determine what the axes represent and what units are being used.
- Look for Trends: Identify any patterns or relationships in the data, such as increasing or decreasing trends, correlations, or outliers.
- Read the Labels: Pay attention to the labels, captions, and legends to understand the context and meaning of the data.
- Draw Conclusions: Use the data to draw conclusions and make inferences about the phenomena being studied.
- Consider Limitations: Be aware of any limitations or biases in the data and how they might affect your interpretations.
3.3 How To Evaluate Experiments and Studies Critically?
Evaluating experiments and studies critically involves assessing the validity, reliability, and significance of the research findings.
- Purpose of the Experiment: Understand the research question or hypothesis being tested. What are the researchers trying to find out or prove?
- Experimental Design: Assess the experimental design to see if it is appropriate for addressing the research question. Was there a control group? Were variables controlled?
- Sample Size: Determine if the sample size is large enough to provide reliable results.
- Data Analysis: Examine the data analysis methods to see if they are appropriate and accurate.
- Conclusions: Assess whether the conclusions are supported by the data and if there are any limitations or biases in the interpretation.
3.4 Drawing Conclusions from Data
Drawing conclusions from data is a fundamental skill in science. It involves using evidence to support or refute a hypothesis, make predictions, and gain insights into the natural world. You should:
- Examine the Data: Carefully analyze the data to identify any patterns, trends, or relationships.
- Consider the Context: Take into account the experimental design, sample size, and any limitations or biases.
- Support Your Conclusions: Base your conclusions on the evidence and avoid making unsupported claims.
- Communicate Clearly: Present your conclusions in a clear and concise manner, using appropriate language and terminology.
3.5 Evaluating the Evidence for Conclusions in Science
Evaluating the evidence for conclusions in science requires a critical assessment of the data, methods, and interpretations used in a study. To evaluate evidence effectively:
- Examine the Data: Assess the quality, reliability, and validity of the data used to support the conclusions.
- Consider Alternative Explanations: Think about other possible explanations for the findings and if the evidence adequately rules them out.
- Look for Biases: Identify any potential biases or limitations in the study design or interpretation.
- Compare to Other Studies: Compare the findings to those of other studies to see if they are consistent and supported by multiple lines of evidence.
3.6 Comparing Scientific Findings
Comparing scientific findings involves examining similarities, differences, and relationships between different studies, theories, or models. This process helps to identify areas of agreement, disagreement, and uncertainty, and to refine and improve scientific knowledge.
- Identify the Key Findings: Determine the main results or conclusions of each study, theory, or model.
- Look for Similarities: Identify any areas of agreement or overlap between the findings.
- Highlight Differences: Identify any areas of disagreement or contradiction between the findings.
- Assess the Evidence: Evaluate the evidence used to support each set of findings and consider any limitations or biases.
- Draw Conclusions: Use the comparison to draw conclusions about the state of scientific knowledge and identify areas for further research or clarification.
3.7 Using Science Words, Phrases, and Symbols
Using science words, phrases, and symbols accurately is essential for communicating scientific information effectively.
- Learn Key Terms: Familiarize yourself with the vocabulary used in different areas of science.
- Use Precise Language: Avoid using vague or ambiguous terms and use precise language to convey your meaning.
- Understand Symbols: Learn the symbols and abbreviations used to represent scientific concepts and quantities.
- Check Your Work: Review your writing to ensure that you have used the correct terminology and symbols.
3.8 How to Understand and Use Science Theories and Processes
Understanding and using science theories and processes involves grasping the underlying principles and applying them to solve problems, make predictions, and gain insights into the natural world.
- Learn the Basics: Familiarize yourself with the basic concepts and definitions related to the theory or process.
- Understand the Assumptions: Identify any assumptions or limitations that underpin the theory or process.
- Apply to Examples: Work through examples and case studies to see how the theory or process is applied in different situations.
- Make Connections: Relate the theory or process to other areas of science and consider its implications for real-world problems.
4. Effective Science Study Tips
To excel in science study, adopting effective study habits and strategies is crucial. Here are some tips to help you:
4.1 Integrate Reading and Math Skills
Integrating reading and math skills into your science study can enhance your understanding and retention of scientific concepts.
- Use Reading Strategies: Apply active reading strategies to science texts, such as previewing, annotating, and summarizing.
- Practice Math Problems: Work through practice problems and exercises that involve mathematical concepts, such as calculations, equations, and graphs.
- Connect to Real-World Examples: Relate scientific concepts to real-world examples and applications to make them more tangible and meaningful.
4.2 Take Science Practice Tests
Taking practice tests is an effective way to assess your knowledge, identify areas for improvement, and prepare for exams.
- Use Official Practice Tests: Use official practice tests from reputable sources, such as textbooks, study guides, or online resources.
- Simulate Exam Conditions: Take the practice tests under realistic exam conditions, including time limits and no distractions.
- Review Your Answers: Review your answers carefully to identify any errors or misconceptions.
- Focus on Your Weaknesses: Spend more time studying the topics and concepts that you struggled with on the practice tests.
4.3 Optimize Your Study Sessions
Optimizing your study sessions involves creating a structured and focused learning environment that maximizes your productivity and retention.
- Set Clear Goals: Define what you want to achieve during each study session.
- Create a Schedule: Develop a study schedule that allocates specific time slots for different topics and activities.
- Minimize Distractions: Find a quiet and comfortable place to study, free from distractions such as noise, social media, or email.
- Use Active Learning Techniques: Engage in active learning techniques, such as summarizing, explaining, or teaching the material to someone else.
- Take Breaks: Take short breaks every hour to avoid burnout and maintain your focus.
4.4 Learn Essential Science Formulas
Learning essential science formulas involves understanding their meaning, application, and limitations.
- Understand the Meaning: Grasp the underlying concepts behind each formula.
- Identify the Variables: Know what each symbol in the formula represents.
- Practice Application: Work through numerous practice problems to apply the formula in different contexts.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards with the formula on one side and its explanation on the other.
- Relate to Real-World Examples: Connect the formula to real-world phenomena to make it more tangible.
4.5 Understand Science Studies and Experiments
Understanding science studies and experiments involves grasping the key concepts and procedures used to investigate phenomena and draw conclusions.
- Identify the Purpose: Determine the research question or hypothesis being tested.
- Examine the Design: Assess the experimental design to see if it is appropriate for addressing the research question.
- Analyze the Data: Examine the data analysis methods to see if they are appropriate and accurate.
- Evaluate the Conclusions: Assess whether the conclusions are supported by the data and if there are any limitations or biases in the interpretation.
4.6 Extract Key Points From Text and Graphics
Extracting key points from text and graphics is a valuable skill for summarizing and synthesizing scientific information.
- Read the Question First: Understand what you need to look for before you start reading the text or examining the graphic.
- Read Actively: Annotate the text by highlighting key points, writing notes in the margins, and summarizing the main ideas.
- Look for Trends: Identify any patterns or relationships in the data, such as increasing or decreasing trends, correlations, or outliers.
- Relate to Real-World Examples: Connect the information to what you already know and think about how it applies to real-world situations.
4.7 Implement Effective Test-Taking Strategies
Implementing effective test-taking strategies can improve your performance on science exams and reduce test anxiety. Here are some habits for taking the test:
- Stop Studying: Don’t study the night before or the day of the test.
- Get a Good Night’s Sleep: Go to bed early and wake up refreshed.
- Eat a Good Breakfast: Eat a good breakfast, including protein and water.
- Arrive Early: Make sure you know where and when the test is, and arrive early so you’re not too stressed.
- Don’t Focus on Worry: Focus on positive thoughts instead of worries.
- Don’t Focus on What You Don’t Know: Don’t worry if a question seems totally foreign, there’s a lot of room for error, so just pick an answer and move on.
- Eliminate Wrong Answers: If you’re not sure of an answer, eliminate all the wrong answers first.
- Have a System for Guessing: If you need to guess, choose an answer for every question. You will never lose points for guessing. It can only help!
4.8 Create Helpful Diagrams
Creating helpful diagrams can enhance your understanding and retention of scientific concepts.
- Choose a Topic: Select a topic that is complex or challenging to understand.
- Gather Information: Collect information about the topic from textbooks, study guides, or online resources.
- Organize Your Thoughts: Organize your thoughts and ideas into a logical structure.
- Draw the Diagram: Create a diagram that visually represents the key concepts, relationships, and processes.
- Label the Diagram: Label the diagram clearly and concisely.
- Review and Revise: Review the diagram to ensure that it is accurate, complete, and easy to understand.
4.9 Memorize Your Elements
Memorizing your elements and molecules can enhance your understanding of chemical reactions and properties.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards with the symbol on one side and the name on the other.
- Make Connections: Relate the elements to real-world examples and applications.
- Practice Regularly: Review the periodic table regularly to reinforce your knowledge.
4.10 Focus on Evidence and Data
Focusing on evidence and data can improve your critical thinking and problem-solving skills in science.
- Read Carefully: Read the text or examine the graphic carefully.
- Identify the Variables: Determine what the axes represent and what units are being used.
- Look for Trends: Identify any patterns or relationships in the data, such as increasing or decreasing trends, correlations, or outliers.
- Draw Conclusions: Use the data to draw conclusions and make inferences about the phenomena being studied.
5. Checklist: Key Areas to Focus On
This checklist highlights the key areas to focus on to ensure comprehensive coverage of the material and effective science study.
5.1 Essential Science Topics
- Life Science:
- Basics about the human body and health
- Relationships between life and energy
- Energy in ecosystems
- Organization of life
- Heredity
- Evolution
- Physical Science:
- Energy
- Work, motion, and forces
- Chemistry and living systems
- Earth and Space Science:
- Earth’s systems and how they interact with living things
- The Earth and its components
- The structure and organization of the cosmos
5.2 Essential Science Skills
- Interpret and use science texts, charts, diagrams, and data
- Understand and evaluate science experiments and studies
- Reason from data
- Evaluate conclusions or theories
- Compare scientific findings
- Use words, phrases, and symbols to express scientific information
- Understand and apply scientific models, theories, processes, and formulas
6. Online Resources for Science Study
Leveraging online resources can provide comprehensive support for your science study efforts. Here are some recommended platforms:
- Khan Academy: Offers free video lessons and practice exercises on various science topics.
- Coursera: Provides access to courses from top universities and institutions worldwide.
- edX: Features courses, programs, and degrees in science from leading universities.
- CONDUCT.EDU.VN: Comprehensive guides, practice questions, and real-world examples to help you grasp key concepts.
7. Ethical Considerations in Science Study
Ethical considerations are integral to science study and practice, influencing how research is conducted and how scientific knowledge is applied.
7.1 Responsible Research Practices
- Honesty and Integrity: Maintain honesty and integrity in all aspects of research, including data collection, analysis, and reporting.
- Objectivity: Avoid bias in the design, conduct, and interpretation of research.
- Careful Data Management: Properly manage and store data to ensure its integrity and accessibility.
- Respect for Intellectual Property: Give proper credit to the work of others and avoid plagiarism.
7.2 Ethical Use of Scientific Knowledge
- Consider Consequences: Think about the potential consequences of scientific discoveries and innovations before they are implemented.
- Promote Social Good: Use scientific knowledge to promote social good and address global challenges such as poverty, disease, and environmental degradation.
- Engage in Public Dialogue: Engage in public dialogue about the ethical implications of scientific advancements and involve diverse stakeholders in decision-making processes.
7.3 Animal Welfare
- Minimize Harm: Minimize harm to animals used in research and ensure their welfare is protected.
- Use Alternatives: Explore alternatives to animal experimentation whenever possible, such as computer simulations or in vitro studies.
- Follow Ethical Guidelines: Adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations for the care and use of animals in research, such as the principles of the “3Rs” (Replacement, Reduction, Refinement).
7.4 Human Subjects Research
- Informed Consent: Obtain informed consent from human subjects before they participate in research.
- Confidentiality: Protect the privacy and confidentiality of human subjects by keeping their personal information secure.
- Minimize Risk: Minimize the risks to human subjects and ensure that the benefits of the research outweigh the risks.
- Ethical Review: Seek ethical review and approval from an institutional review board (IRB) before conducting research involving human subjects.
Navigating the complexities of science study requires dedication, effective strategies, and a commitment to ethical principles. At CONDUCT.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing you with the tools and guidance necessary for success.
Do you find yourself struggling with complex scientific concepts or unsure how to apply ethical principles in your studies? Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive resources, connect with experts, and gain the knowledge you need to excel. Our detailed guides, practice questions, and real-world examples are designed to help you master scientific concepts and make informed decisions.
Take the next step towards your academic and professional success. Contact us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 555-1234. Start your journey towards scientific mastery with conduct.edu.vn.