Garment construction relies heavily on guides to ensure accuracy, consistency, and efficiency. What is used as a guide in garment construction? Patterns, manuals, and detailed instructions serve as crucial guides, ensuring precision and quality in the finished product. CONDUCT.EDU.VN provides in-depth resources on garment construction, offering clarity and practical solutions for both beginners and professionals. Understanding sewing specifications, technical documentation, and best practices enhances the overall garment production process.
1. Understanding the Core of Garment Construction Guides
Garment construction guides are essential for anyone involved in the clothing manufacturing process, from hobbyists to industry professionals. These guides provide a structured approach to creating garments, ensuring consistency, quality, and efficiency. A garment construction guide typically includes patterns, sewing instructions, and technical specifications that serve as a roadmap for the entire process.
1.1 The Role of Patterns in Guiding Construction
Patterns are fundamental guides in garment construction. They provide a template for cutting fabric pieces to the correct size and shape, which are then sewn together to form the garment.
- Types of Patterns: Patterns can be purchased commercially from pattern companies, drafted from scratch using measurements, or created through draping on a mannequin.
- Pattern Markings: Patterns include various markings such as cutting lines, seam allowances, grainlines, and notches, which guide the accurate cutting and sewing of the fabric.
- Pattern Adjustments: Adjusting patterns to fit individual body measurements is a crucial step. Techniques like adding or subtracting length, width, or adjusting darts ensure a custom fit.
1.2 Detailed Sewing Instructions
Sewing instructions provide step-by-step guidance on how to assemble the garment pieces. These instructions typically include diagrams, illustrations, and written explanations to ensure clarity.
- Step-by-Step Assembly: Instructions detail the order in which garment pieces should be sewn together, ensuring the garment is constructed in the most logical and efficient manner.
- Seam Types and Techniques: The guide specifies which seam types to use for different areas of the garment, along with detailed instructions on how to execute these seams. For instance, a flat-felled seam might be used for durability, while a serged edge might be used to prevent fraying.
- Finishing Techniques: Instructions include details on finishing techniques such as hemming, adding closures (buttons, zippers, snaps), and attaching linings or facings.
1.3 Technical Specifications and Documentation
Technical specifications provide detailed information about the garment’s construction, materials, and quality standards. This documentation is crucial for maintaining consistency and quality control in mass production.
- Material Specifications: This includes details about the type of fabric, thread, buttons, zippers, and other materials used in the garment. Specifications may include fiber content, weight, color, and care instructions.
- Seam and Stitch Specifications: Technical documents specify the type of seams, stitch density, and thread tension required for each seam. This ensures the garment is durable and meets quality standards.
- Measurements and Tolerances: Detailed measurement charts specify the dimensions of the garment at various points, along with acceptable tolerances. This helps ensure consistency in sizing and fit.
Image showing pattern pieces with labels indicating grainlines, seam allowances, and notches.
2. Essential Tools and Equipment as Guides
In addition to patterns and instructions, several tools and equipment serve as guides in garment construction. These tools help ensure accuracy, precision, and efficiency in the sewing process.
2.1 Measuring and Marking Tools
Accurate measuring and marking are critical for creating well-fitted garments. Various tools are used to guide these processes.
- Measuring Tape: A flexible measuring tape is used to take body measurements and measure fabric. It is essential for creating patterns and ensuring the garment fits correctly.
- Rulers and Yardsticks: These tools are used to draw straight lines and measure fabric accurately. Clear rulers with grid markings are particularly useful for pattern drafting and alterations.
- Seam Gauges: Seam gauges are small rulers used to measure seam allowances and hems. They help maintain consistent measurements and ensure professional-looking finishes.
- Marking Tools: Tailor’s chalk, fabric markers, and tracing wheels are used to transfer pattern markings onto fabric. These tools ensure accurate cutting and sewing.
2.2 Cutting Tools
Precise cutting is essential for assembling a garment correctly. The right cutting tools can significantly improve accuracy and efficiency.
- Fabric Shears: Sharp fabric shears are used to cut fabric along pattern lines. High-quality shears provide clean cuts and prevent fraying.
- Rotary Cutters: Rotary cutters are used with cutting mats to cut fabric in straight lines or curves. They are particularly useful for cutting multiple layers of fabric at once.
- Seam Rippers: Seam rippers are used to remove unwanted stitches or open seams. They are essential for correcting mistakes and making alterations.
2.3 Sewing Machines and Attachments
Sewing machines are the primary tools for assembling garments. Various attachments and feet can guide specific sewing tasks.
- Presser Feet: Different presser feet are used for various sewing tasks, such as sewing zippers, buttonholes, and rolled hems. Each foot guides the fabric and ensures accurate stitching.
- Seam Guides: Seam guides attach to the sewing machine and help maintain consistent seam allowances. They are particularly useful for beginners and for sewing long, straight seams.
- Edge Stitching Foot: This foot is designed to stitch close to the edge of the fabric, creating a clean, professional finish.
2.4 Pressing Equipment
Pressing is an integral part of garment construction. Proper pressing techniques and equipment can enhance the appearance and durability of the garment.
- Iron: A high-quality iron is essential for pressing seams, darts, and hems. Steam irons are particularly useful for removing wrinkles and shaping fabric.
- Pressing Board: A sturdy pressing board provides a stable surface for pressing. Padded boards with heat-resistant covers are ideal for garment construction.
- Tailor’s Ham and Seam Roll: These tools are used to press curved seams and darts. They help maintain the shape of the garment and prevent distortion.
3. Mastering Sewing Techniques as Guides
Proficiency in various sewing techniques is crucial for successful garment construction. These techniques guide the assembly process and ensure a professional finish.
3.1 Basic Seams and Stitches
Understanding and mastering basic seams and stitches is fundamental to garment construction.
- Straight Stitch: The straight stitch is the most basic stitch used for joining fabric pieces. It is essential for constructing seams, hems, and topstitching.
- Zigzag Stitch: The zigzag stitch is used to finish raw edges, prevent fraying, and create decorative effects. It is also used for sewing stretchy fabrics.
- Seam Finishes: Various seam finishes, such as serging, binding, and zigzagging, are used to prevent fraying and create a clean finish.
3.2 Advanced Seam Techniques
Advanced seam techniques are used to create durable, professional-looking garments.
- Flat-Felled Seam: The flat-felled seam is a strong, durable seam used in jeans and workwear. It involves encasing the raw edges of the fabric within the seam.
- French Seam: The French seam is a clean, enclosed seam that is ideal for sheer or lightweight fabrics. It involves sewing the seam twice, with the raw edges enclosed within the seam.
- Welt Seam: The welt seam is a decorative seam that adds a raised ridge to the fabric. It is often used in tailored garments and outerwear.
3.3 Darts and Tucks
Darts and tucks are used to shape fabric and create a better fit. They are essential for contouring garments to the body.
- Darts: Darts are triangular folds of fabric that are stitched to a point. They are used to remove excess fabric and create shape in areas such as the bust, waist, and hips.
- Tucks: Tucks are folds of fabric that are stitched along their length. They are used to add texture and fullness to garments.
3.4 Gathering and Pleating
Gathering and pleating are techniques used to add fullness and volume to garments.
- Gathering: Gathering involves creating small, even folds in the fabric. It is often used to attach a ruffle or create a full skirt.
- Pleating: Pleating involves creating sharp, even folds in the fabric. Various types of pleats, such as knife pleats, box pleats, and inverted pleats, are used to add structure and design to garments.
4. Leveraging Industrial Sewing Instructions
Industrial sewing instructions offer detailed guidance for efficient and consistent garment production. These instructions are particularly valuable for those involved in manufacturing.
4.1 Understanding Industrial Sewing Manuals
Industrial sewing manuals provide comprehensive information on garment construction, including sewing operations, sequences, and machine specifications.
- Comprehensive Documentation: These manuals often include documentation for hundreds of garments, detailing every step of the construction process.
- Machine and Seam Types: The manuals specify the machine and seam types required for each operation, ensuring the correct equipment and techniques are used.
- Efficiency Estimates: Many manuals include estimates of how many of each seam can be completed in an hour, which is invaluable for production planning and cost estimation.
4.2 Benefits of Using Industrial Sewing Instructions
Using industrial sewing instructions can significantly improve the efficiency and quality of garment production.
- Standardization: These instructions promote standardization, ensuring that each garment is constructed consistently and meets quality standards.
- Efficiency: The detailed instructions and efficiency estimates help optimize the production process, reducing time and costs.
- Training: Industrial sewing manuals serve as excellent training resources for new employees, providing clear and comprehensive guidance.
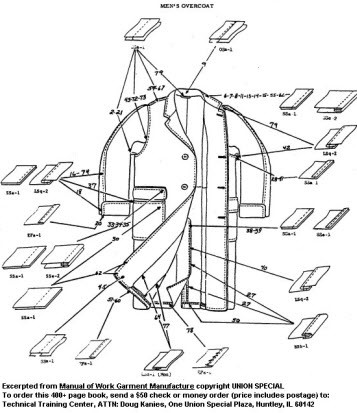
4.3 Example: Union Special Garment Construction Guide
The Union Special Garment Construction Guide is a well-regarded resource in the industry. It provides detailed instructions and specifications for a wide range of garments.
- Comprehensive Content: The guide includes documentation for over 200 garments, covering a wide range of styles and variations.
- Detailed Instructions: The instructions include step-by-step guidance on sewing operations, seam types, and finishing techniques.
- Machine Specifications: The guide specifies the machine models required for each operation, ensuring the correct equipment is used.
Example of detailed sewing instructions for a men’s overcoat, including machine types and operation sequences.
5. Adhering to Garment Specifications
Garment specifications are detailed documents that outline all aspects of a garment’s construction, materials, and quality standards. Adhering to these specifications is crucial for ensuring consistency and quality.
5.1 Components of Garment Specifications
Garment specifications typically include the following components:
- Technical Drawings: Detailed drawings of the garment, including front, back, and side views, with measurements and construction details.
- Material Specifications: Information about the type, weight, color, and care instructions for all materials used in the garment.
- Construction Details: Detailed instructions on how to assemble the garment, including seam types, stitch density, and finishing techniques.
- Measurement Charts: Charts specifying the dimensions of the garment at various points, along with acceptable tolerances.
- Quality Standards: Criteria for evaluating the quality of the garment, including seam strength, colorfastness, and appearance.
5.2 Importance of Following Specifications
Following garment specifications is essential for maintaining consistency and quality in mass production.
- Consistency: Specifications ensure that each garment is constructed to the same standards, regardless of who is making it.
- Quality Control: Specifications provide a framework for quality control, allowing manufacturers to identify and correct defects.
- Cost Control: By standardizing the construction process, specifications help control costs and minimize waste.
5.3 Developing Your Own Specifications
Creating your own garment specifications can be beneficial for small businesses and independent designers.
- Start with a Template: Use a template to ensure you include all the necessary information.
- Be Detailed: Provide as much detail as possible, including technical drawings, material specifications, and construction instructions.
- Review and Revise: Review and revise your specifications regularly to ensure they are accurate and up-to-date.
6. Utilizing Online Resources and Communities
The internet offers a wealth of resources and communities for garment construction enthusiasts. These resources can provide guidance, inspiration, and support.
6.1 Online Tutorials and Courses
Numerous websites and platforms offer tutorials and courses on garment construction.
- YouTube: YouTube is a great resource for free tutorials on various sewing techniques and garment construction projects.
- Online Learning Platforms: Platforms like Skillshare, Udemy, and Coursera offer comprehensive courses on garment construction, pattern drafting, and sewing techniques.
- Blogs and Websites: Many blogs and websites dedicated to sewing and garment construction offer detailed tutorials, patterns, and advice.
6.2 Online Communities and Forums
Online communities and forums provide a platform for sharing knowledge, asking questions, and getting feedback.
- Sewing Forums: Websites like PatternReview and SewingForums offer forums where users can discuss sewing techniques, share projects, and ask for advice.
- Social Media Groups: Facebook groups and other social media platforms dedicated to sewing and garment construction provide a space for sharing ideas, getting feedback, and connecting with other enthusiasts.
6.3 Digital Pattern Resources
Digital pattern resources make it easy to access a wide variety of patterns and designs.
- Etsy: Etsy offers a vast selection of digital patterns from independent designers.
- Pattern Companies: Many pattern companies, such as Simplicity, McCall’s, and Vogue, offer digital versions of their patterns that can be downloaded and printed at home.
- Online Pattern Libraries: Some websites offer subscription-based access to a library of digital patterns.
7. Best Practices for Effective Garment Construction
Following best practices can significantly improve the quality and efficiency of garment construction.
7.1 Pre-Washing Fabrics
Pre-washing fabrics before cutting and sewing is essential to prevent shrinkage and color bleeding.
- Why Pre-Wash: Pre-washing removes any sizing or finishes from the fabric and allows it to shrink before it is sewn into a garment.
- How to Pre-Wash: Wash the fabric in the same way you plan to wash the finished garment. Dry it in the dryer or hang it to dry, depending on the fabric type.
7.2 Accurate Cutting and Marking
Accurate cutting and marking are crucial for ensuring the garment fits correctly.
- Use Sharp Tools: Use sharp fabric shears or a rotary cutter to cut fabric along pattern lines.
- Follow Pattern Markings: Carefully transfer pattern markings onto the fabric using tailor’s chalk or a fabric marker.
- Cut on a Flat Surface: Cut fabric on a flat, stable surface to ensure accurate cuts.
7.3 Pressing as You Go
Pressing seams and darts as you sew is essential for creating a professional-looking garment.
- Press Seams Flat: Press seams flat after sewing to set the stitches and prevent puckering.
- Use a Pressing Cloth: Use a pressing cloth to protect delicate fabrics from scorching.
- Shape with a Tailor’s Ham: Use a tailor’s ham to press curved seams and darts, maintaining the shape of the garment.
7.4 Fitting and Adjusting
Fitting the garment as you sew allows you to make adjustments and ensure a perfect fit.
- Make a Muslin: Create a muslin (test garment) to check the fit of the pattern before cutting into your final fabric.
- Adjust as Needed: Adjust the pattern as needed to achieve the desired fit. Common adjustments include lengthening or shortening the bodice, adjusting the bust or hip width, and altering the shoulder slope.
- Check the Fit Regularly: Check the fit of the garment as you sew, making adjustments as needed to ensure a comfortable and flattering fit.
8. Incorporating Ethical and Sustainable Practices
In today’s world, incorporating ethical and sustainable practices into garment construction is increasingly important.
8.1 Sustainable Fabric Choices
Choosing sustainable fabrics can reduce the environmental impact of garment construction.
- Organic Fabrics: Organic cotton, linen, and hemp are grown without the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers.
- Recycled Fabrics: Recycled fabrics, such as recycled polyester and recycled cotton, reduce waste and conserve resources.
- Upcycled Fabrics: Upcycling involves using discarded fabrics or garments to create new items, reducing waste and giving new life to old materials.
8.2 Ethical Production Practices
Ethical production practices ensure that garments are made in safe and fair working conditions.
- Fair Labor Standards: Choose manufacturers that adhere to fair labor standards, ensuring that workers are paid a living wage and work in safe conditions.
- Transparency: Support brands that are transparent about their supply chain and production processes.
- Reduce Waste: Minimize waste by using fabric efficiently, recycling scraps, and designing garments that are durable and long-lasting.
8.3 DIY and Local Production
DIY garment construction and local production can reduce the environmental impact of the fashion industry and support local economies.
- DIY Projects: Creating your own garments allows you to control the materials and production processes, ensuring that they are ethical and sustainable.
- Support Local Businesses: Support local fabric stores, sewing supply shops, and manufacturers to reduce transportation emissions and support your local economy.
9. Innovations in Garment Construction
Garment construction is constantly evolving with new technologies and innovations.
9.1 3D Printing
3D printing is being used to create custom-fitted garments and intricate designs.
- Customization: 3D printing allows for highly customized garments that are tailored to individual body measurements.
- Complex Designs: 3D printing can create complex and intricate designs that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional sewing methods.
- Sustainability: 3D printing can reduce waste by creating garments on demand and using sustainable materials.
9.2 Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is used to cut fabric with precision and efficiency.
- Accuracy: Laser cutting provides highly accurate cuts, ensuring that garment pieces are perfectly aligned.
- Efficiency: Laser cutting can cut multiple layers of fabric at once, reducing time and labor costs.
- Intricate Designs: Laser cutting can create intricate designs and patterns that are difficult to achieve with traditional cutting methods.
9.3 Smart Textiles
Smart textiles are fabrics that incorporate electronic components, such as sensors and actuators.
- Wearable Technology: Smart textiles are used to create wearable technology, such as fitness trackers and medical monitors.
- Interactive Garments: Smart textiles can be used to create interactive garments that respond to the environment or the wearer’s body.
- Functional Fabrics: Smart textiles can enhance the functionality of garments, such as providing insulation, moisture management, or UV protection.
10. FAQs about Garment Construction Guides
Q1: What is the most important guide in garment construction?
A: The pattern is arguably the most critical guide, as it dictates the shape and size of the fabric pieces needed to construct the garment.
Q2: How do I choose the right pattern size?
A: Measure your body accurately and compare your measurements to the pattern’s sizing chart. Choose the size that best matches your measurements.
Q3: What is the purpose of seam allowances?
A: Seam allowances provide extra fabric for sewing the seams and prevent the raw edges from fraying.
Q4: How do I adjust a pattern for a better fit?
A: Common adjustments include lengthening or shortening the bodice, adjusting the bust or hip width, and altering the shoulder slope.
Q5: What are the essential tools for garment construction?
A: Essential tools include a measuring tape, fabric shears, seam ripper, sewing machine, iron, and pressing board.
Q6: How do I prevent fabric from fraying?
A: Use seam finishes such as serging, binding, or zigzagging to prevent fabric from fraying.
Q7: What is the best way to press seams?
A: Press seams flat after sewing to set the stitches and prevent puckering. Use a pressing cloth to protect delicate fabrics.
Q8: How do I choose the right fabric for a garment?
A: Consider the garment’s design, the fabric’s weight and drape, and the care instructions.
Q9: What is a muslin, and why is it important?
A: A muslin is a test garment made from inexpensive fabric. It is used to check the fit of the pattern before cutting into your final fabric.
Q10: How can I learn more about garment construction?
A: Explore online tutorials, courses, and communities dedicated to sewing and garment construction. Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN for additional resources and guidance.
Navigating the intricacies of garment construction requires reliable guidance, from understanding patterns and technical documentation to mastering sewing techniques. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers a wealth of information and resources to help you succeed in your garment construction endeavors. Address your challenges in finding trustworthy standards and behavior guidelines. Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN, located at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (707) 555-1234, to explore comprehensive guides and detailed instructions that ensure you stay informed and compliant. Let conduct.edu.vn be your guide to creating exceptional garments with confidence.