Which Statement Is Not True About The Itil Guiding Principles? Understanding the core tenets of ITIL 4 is crucial for effective service management. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive guide to navigating these principles, ensuring organizations can optimize their IT service delivery. Master ITIL guiding principles and enhance service value system with insights on governance practices and continual service improvement.
1. Understanding ITIL 4 Guiding Principles and the Service Value System
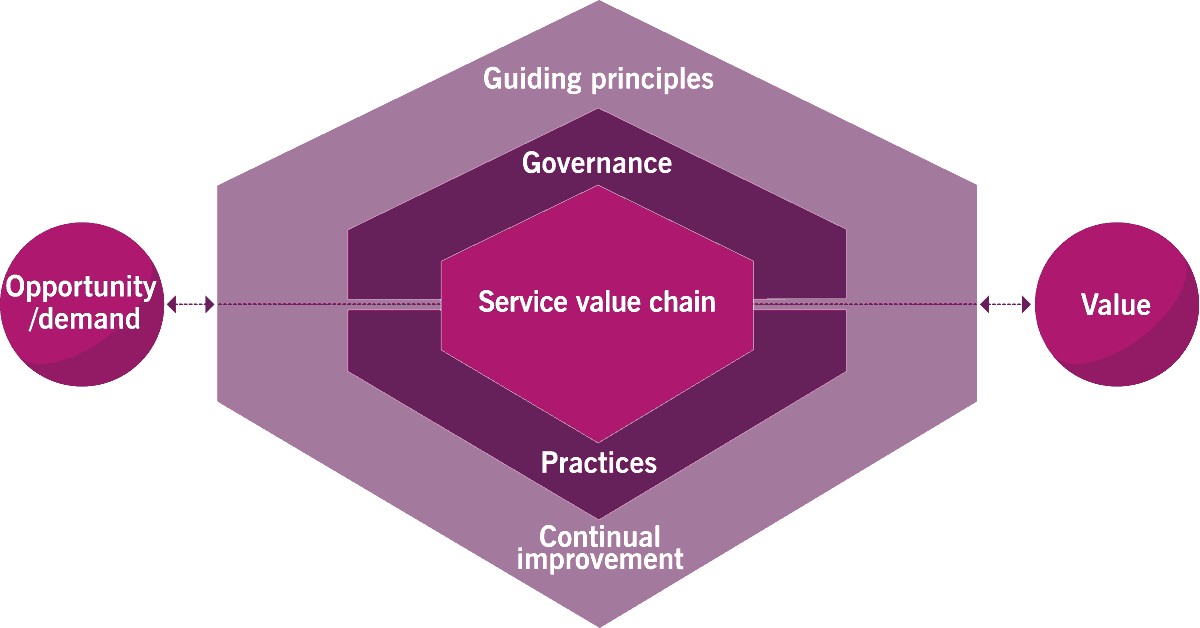
The ITIL 4 service value system (SVS) represents a holistic approach to value creation within an organization. It defines how various components and activities integrate to facilitate value realization. According to Axelos, the organization behind ITIL, the SVS encompasses the organizational interfaces that enable value for stakeholders.
The ITIL 4 service value system is best visualized as a comprehensive model:
This system leverages five key elements to transform stakeholder demand into tangible value:
- Guiding Principles: Recommendations that guide organizational decision-making, regardless of changes in goals, strategies, or management structures.
- Governance: Ensures that the organization’s activities are aligned with its strategic direction.
- Service Value Chain: An operating model outlining the key activities required to respond to demand and facilitate value realization.
- Management Practices: Sets of organizational resources designed for performing work or accomplishing an objective.
- Continual Improvement: An ongoing effort to enhance products, services, and practices.
The guiding principles, service value chain, and management practices warrant deeper exploration to fully understand their roles within the ITIL 4 SVS.
2. What Are the ITIL 4 Guiding Principles?
For those familiar with the 2016 ITIL Practitioner Guidance, the concept of guiding principles within the ITIL 4 service value system is not new. These principles are defined as:
“A guiding principle is a recommendation that guides an organization in all circumstances, regardless of changes in its goals, strategies, type of work, or management structure.” (AXELOS, “ITIL Foundation: ITIL 4 Edition” (2019))
ITIL 4 outlines seven guiding principles:
- Focus on value
- Start where you are
- Progress iteratively with feedback
- Collaborate and promote visibility
- Think and work holistically
- Keep it simple and practical
- Optimize and automate
3. In-Depth Look at the ITIL 4 Guiding Principles
These guiding principles provide a framework for organizations to enhance their service management practices and achieve their desired outcomes.
3.1. Focus on Value
This principle emphasizes the importance of aligning all organizational efforts with the creation of value for stakeholders. Value is not just about financial gains; it includes customer satisfaction, improved efficiency, and enhanced reputation.
- Understanding Stakeholder Value: Identify who your stakeholders are (customers, users, employees, partners) and what they value.
- Value-Driven Metrics: Define metrics that measure value creation and track progress towards achieving desired outcomes.
- Prioritize Value: Focus on activities that deliver the most value and eliminate those that do not.
3.2. Start Where You Are
Instead of trying to overhaul everything at once, this principle advises organizations to assess their current state and build upon what already exists.
- Assess Current Capabilities: Identify existing strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement.
- Leverage Existing Resources: Utilize current processes, tools, and knowledge to avoid unnecessary reinvention.
- Incremental Improvement: Focus on making small, manageable changes that build upon existing capabilities.
3.3. Progress Iteratively with Feedback
This principle promotes a continuous improvement approach, where changes are implemented in small iterations, and feedback is gathered to refine future efforts.
- Small Increments: Break down large projects into smaller, manageable iterations.
- Gather Feedback: Solicit feedback from stakeholders throughout the process to ensure alignment with their needs.
- Adapt and Improve: Use feedback to make adjustments and improvements in subsequent iterations.
3.4. Collaborate and Promote Visibility
Collaboration and transparency are essential for effective service management. This principle encourages organizations to break down silos and share information openly.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Foster collaboration between different teams and departments.
- Open Communication: Establish clear communication channels to share information and feedback.
- Transparency: Make processes and decisions visible to stakeholders to build trust and understanding.
3.5. Think and Work Holistically
This principle emphasizes the importance of considering the entire service value system when making decisions.
- System Thinking: Understand how different parts of the organization interact and impact each other.
- End-to-End Perspective: Consider the entire service lifecycle, from initial demand to value realization.
- Integrated Approach: Ensure that different processes and practices are integrated to deliver seamless services.
3.6. Keep It Simple and Practical
Complexity can hinder efficiency and effectiveness. This principle encourages organizations to simplify processes and focus on practical solutions.
- Eliminate Waste: Identify and eliminate unnecessary steps and complexity.
- Focus on Value: Prioritize activities that deliver the most value and avoid unnecessary bureaucracy.
- Practical Solutions: Implement solutions that are easy to understand and use.
3.7. Optimize and Automate
Automation can improve efficiency, reduce errors, and free up resources for more strategic activities. This principle encourages organizations to identify opportunities to optimize and automate processes.
- Identify Opportunities: Look for repetitive tasks and processes that can be automated.
- Optimize Processes: Streamline processes before automating them to ensure maximum efficiency.
- Implement Automation: Use technology to automate tasks and processes, freeing up resources for more strategic initiatives.
4. The ITIL 4 Service Value Chain: A Core Component
The service value chain (SVC) is central to the ITIL 4 service value system. Axelos defines it as:
“The central element of the service value system is the service value chain, an operating model which outlines the key activities required to respond to demand and facilitate value realization through the creation and management of products and services.” (AXELOS, “ITIL Foundation: ITIL 4 Edition” (2019))
The ITIL 4 service value chain consists of six key activities:
- Plan: Establishes strategic direction and resource allocation.
- Improve: Ensures continual improvement of products, services, and practices.
- Engage: Fosters relationships with stakeholders.
- Design and Transition: Creates new or modified services.
- Obtain/Build: Acquires or develops necessary resources.
- Deliver and Support: Provides services to customers and resolves issues.
These activities represent the steps an organization takes to create value. Each activity transforms inputs into outputs, with all activities interconnected and triggering further actions.
5. ITIL 4 Management Practices
ITIL v3 focused on processes, while ITIL 4 shifts to management practices. These practices are sets of organizational resources designed for performing work or accomplishing an objective.
According to Axelos:
“In ITIL, a management practice is a set of organizational resources designed for performing work or accomplishing an objective. The origins of the practices are as follows:
– General management practices have been adopted and adapted for service management from general business management domains.
– Service management practices have been developed in service management and ITSM industries.
– Technical management practices have been adapted from technology management domains for service management purposes by expanding or shifting their focus from technology solutions to IT services.”
Examples of service management practices include:
- Availability management
- Business analysis
- Capacity and performance management
- Change control
- Incident management
- IT asset management
- Monitoring and event management
- Problem management
- Release management
- Service catalog management
- Service configuration management
- Service continuity management
- Service design
- Service desk
- Service level management
- Service request management
- Service validation and testing
These practices have evolved from ITIL v3 processes and incorporate new areas of focus that align with the ITIL 4 service value system.
6. Common Misconceptions About the ITIL 4 Guiding Principles
To fully grasp the ITIL 4 guiding principles, it’s important to address some common misconceptions that can lead to misinterpretations and ineffective implementation. Here are a few key points to clarify:
6.1. Misconception: The Guiding Principles Are a Rigid Framework
Reality: The ITIL 4 guiding principles are not meant to be a rigid set of rules, but rather flexible guidelines that can be adapted to suit the specific context of an organization. They are designed to be used in combination and should be applied with common sense and a focus on achieving desired outcomes.
6.2. Misconception: “Start Where You Are” Means Sticking with Inefficient Processes
Reality: While “Start Where You Are” encourages organizations to leverage existing resources and build upon current capabilities, it does not mean accepting inefficient processes or outdated technologies. It means understanding the current state, identifying areas for improvement, and making incremental changes that build upon what already works.
6.3. Misconception: “Optimize and Automate” Means Automating Everything
Reality: Automation can be a powerful tool for improving efficiency and reducing errors, but it is not a silver bullet. “Optimize and Automate” does not mean automating every task or process, but rather identifying opportunities to streamline processes and automate repetitive tasks that free up resources for more strategic activities.
6.4. Misconception: The Guiding Principles Are Only Relevant to IT
Reality: While ITIL 4 is primarily focused on IT service management, the guiding principles are applicable to all areas of an organization. They can be used to improve processes, foster collaboration, and drive value creation across different departments and functions.
6.5. Misconception: Following the Guiding Principles Guarantees Success
Reality: While the ITIL 4 guiding principles provide a solid foundation for effective service management, they do not guarantee success. Success depends on a variety of factors, including leadership commitment, organizational culture, and the ability to adapt and learn from experience.
7. Applying ITIL 4 Guiding Principles in Real-World Scenarios
To illustrate how the ITIL 4 guiding principles can be applied in practice, let’s consider a few real-world scenarios:
7.1. Scenario 1: Implementing a New Service Desk
Challenge: An organization wants to implement a new service desk to improve IT support.
Applying the Guiding Principles:
- Focus on Value: The primary goal is to improve customer satisfaction and resolve issues more efficiently.
- Start Where You Are: Assess the current IT support processes, tools, and resources.
- Progress Iteratively with Feedback: Implement the new service desk in phases, gathering feedback from users and making adjustments along the way.
- Collaborate and Promote Visibility: Involve IT staff, end-users, and other stakeholders in the implementation process.
- Think and Work Holistically: Consider the impact of the new service desk on other IT processes and services.
- Keep It Simple and Practical: Focus on implementing a solution that is easy to use and maintain.
- Optimize and Automate: Automate common tasks, such as password resets and ticket routing.
7.2. Scenario 2: Improving Incident Management
Challenge: An organization is experiencing a high volume of incidents and wants to improve its incident management process.
Applying the Guiding Principles:
- Focus on Value: The goal is to reduce the impact of incidents on business operations and restore services quickly.
- Start Where You Are: Analyze the current incident management process, identify bottlenecks, and gather data on incident types and resolution times.
- Progress Iteratively with Feedback: Implement changes to the incident management process in phases, gathering feedback from IT staff and end-users.
- Collaborate and Promote Visibility: Foster collaboration between different IT teams and communicate incident status to stakeholders.
- Think and Work Holistically: Consider the underlying causes of incidents and address them through problem management.
- Keep It Simple and Practical: Streamline the incident management process and focus on resolving incidents quickly and efficiently.
- Optimize and Automate: Automate incident logging, routing, and escalation.
7.3. Scenario 3: Implementing a Change Management Process
Challenge: An organization wants to implement a change management process to reduce the risk of disruptions caused by IT changes.
Applying the Guiding Principles:
- Focus on Value: The goal is to minimize the impact of changes on business operations and ensure that changes are implemented successfully.
- Start Where You Are: Assess the current change management process, identify areas for improvement, and gather data on change-related incidents.
- Progress Iteratively with Feedback: Implement the change management process in phases, gathering feedback from IT staff and business stakeholders.
- Collaborate and Promote Visibility: Involve IT staff, business stakeholders, and change advisory board members in the change management process.
- Think and Work Holistically: Consider the impact of changes on other IT processes and services.
- Keep It Simple and Practical: Implement a change management process that is easy to understand and follow.
- Optimize and Automate: Automate change approvals, scheduling, and documentation.
8. The Importance of Understanding “Which Statement Is Not True About The ITIL Guiding Principles”
Understanding which statements about the ITIL guiding principles are false is just as important as knowing the correct ones. Misinterpretations can lead to ineffective implementation and hinder the achievement of desired outcomes.
8.1. Avoiding Common Pitfalls
By understanding common misconceptions, organizations can avoid falling into common pitfalls and ensure that they are applying the guiding principles correctly.
8.2. Ensuring Effective Implementation
A clear understanding of the guiding principles is essential for effective implementation. Organizations that have a solid grasp of the principles are more likely to be successful in their IT service management efforts.
8.3. Maximizing Value Creation
The ultimate goal of ITIL 4 is to maximize value creation. By understanding and applying the guiding principles correctly, organizations can ensure that they are delivering value to their stakeholders.
9. Practical Steps to Ensure Correct Understanding and Implementation
To ensure that your organization has a correct understanding of the ITIL 4 guiding principles and can implement them effectively, consider the following practical steps:
9.1. Training and Education
Provide comprehensive training and education to IT staff and other stakeholders on the ITIL 4 guiding principles. This will help to ensure that everyone has a clear understanding of the principles and how they should be applied.
9.2. Workshops and Discussions
Organize workshops and discussions to explore the guiding principles in more detail. This will provide an opportunity for participants to share their experiences and learn from each other.
9.3. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Use real-world examples and case studies to illustrate how the guiding principles can be applied in practice. This will help to make the principles more concrete and relevant.
9.4. Continuous Review and Improvement
Continuously review and improve your understanding and implementation of the guiding principles. This will help to ensure that you are staying up-to-date with the latest best practices and that you are adapting the principles to suit your specific needs.
9.5. Seek Expert Guidance
Consider seeking guidance from ITIL 4 experts who can provide advice and support on the implementation of the guiding principles. This can be particularly helpful for organizations that are new to ITIL 4.
10. Resources for Further Learning About ITIL 4
To deepen your understanding of ITIL 4 and its guiding principles, consider exploring the following resources:
- Axelos ITIL 4 Foundation Publication: The official ITIL 4 Foundation publication provides a comprehensive overview of the ITIL 4 framework and its key concepts.
- ITIL 4 Training Courses: Attend ITIL 4 training courses to gain a deeper understanding of the framework and its practical application.
- Online Articles and Blogs: Read online articles and blogs from ITIL 4 experts to stay up-to-date with the latest best practices.
- ITIL 4 Forums and Communities: Join ITIL 4 forums and communities to connect with other professionals and share your experiences.
11. The Role of CONDUCT.EDU.VN in Understanding ITIL
CONDUCT.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing accessible and reliable information on various professional standards and ethical guidelines. Our platform offers valuable insights into the ITIL framework, helping professionals and organizations understand and implement best practices in service management.
11.1. Comprehensive Guides and Articles
CONDUCT.EDU.VN features comprehensive guides and articles that explain the ITIL 4 guiding principles in detail, providing practical examples and real-world scenarios to illustrate their application.
11.2. Expert Insights and Analysis
Our team of experts offers insights and analysis on the latest trends and developments in ITIL 4, helping you stay informed and make informed decisions about your service management practices.
11.3. Community Forum and Support
CONDUCT.EDU.VN hosts a community forum where you can connect with other professionals, share your experiences, and ask questions about ITIL 4. Our support team is also available to provide assistance and guidance.
12. FAQs About ITIL 4 Guiding Principles
Here are some frequently asked questions about ITIL 4 guiding principles:
-
What are the ITIL 4 guiding principles?
The ITIL 4 guiding principles are a set of recommendations that guide organizations in all circumstances, regardless of changes in their goals, strategies, type of work, or management structure. They include Focus on Value, Start Where You Are, Progress Iteratively with Feedback, Collaborate and Promote Visibility, Think and Work Holistically, Keep It Simple and Practical, and Optimize and Automate.
-
Why are the ITIL 4 guiding principles important?
The ITIL 4 guiding principles are important because they provide a framework for organizations to enhance their service management practices and achieve their desired outcomes.
-
How can the ITIL 4 guiding principles be applied in practice?
The ITIL 4 guiding principles can be applied in practice by considering them in all decisions and activities related to service management. They can be used to improve processes, foster collaboration, and drive value creation across different departments and functions.
-
What are some common mistakes to avoid when implementing the ITIL 4 guiding principles?
Some common mistakes to avoid when implementing the ITIL 4 guiding principles include treating them as a rigid framework, failing to adapt them to the specific context of the organization, and not involving stakeholders in the implementation process.
-
Where can I learn more about the ITIL 4 guiding principles?
You can learn more about the ITIL 4 guiding principles from the official ITIL 4 Foundation publication, ITIL 4 training courses, online articles and blogs, and ITIL 4 forums and communities.
-
How do the ITIL 4 guiding principles relate to the ITIL 4 service value system?
The ITIL 4 guiding principles are a key component of the ITIL 4 service value system, which describes how all the components and activities of the organization work together as a system to enable value creation.
-
Can the ITIL 4 guiding principles be applied to non-IT organizations?
Yes, the ITIL 4 guiding principles can be applied to non-IT organizations. They are applicable to all areas of an organization and can be used to improve processes, foster collaboration, and drive value creation across different departments and functions.
-
How often should the ITIL 4 guiding principles be reviewed and updated?
The ITIL 4 guiding principles should be reviewed and updated on a regular basis to ensure that they remain relevant and effective.
-
What is the role of leadership in implementing the ITIL 4 guiding principles?
Leadership plays a critical role in implementing the ITIL 4 guiding principles. Leaders must champion the principles and create a culture that supports their implementation.
-
How can I measure the success of implementing the ITIL 4 guiding principles?
The success of implementing the ITIL 4 guiding principles can be measured by tracking key metrics related to service management, such as customer satisfaction, incident resolution times, and change success rates.
13. Final Thoughts: Embracing the ITIL 4 Guiding Principles
The ITIL 4 guiding principles offer a flexible and adaptable framework for organizations seeking to enhance their service management practices and drive value creation. By understanding and applying these principles correctly, organizations can improve processes, foster collaboration, and achieve their desired outcomes.
Remember, the key is to tailor the principles to your specific context, involve stakeholders in the implementation process, and continuously review and improve your approach. With the right mindset and commitment, you can leverage the ITIL 4 guiding principles to transform your service management practices and deliver exceptional value to your stakeholders.
Are you struggling to find reliable guidelines for ethical conduct in your specific situation? Do you feel overwhelmed by the amount of conflicting information available? Are you worried about the legal and ethical consequences of making the wrong decision?
Visit conduct.edu.vn today to access a wealth of information and guidance on ethical standards and best practices. Our resources can help you navigate complex situations with confidence and ensure that you are always acting in accordance with the highest ethical standards. Contact us at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (707) 555-1234.