The question of Who Invented Guided Missiles leads us to Louis Brennan, an Irish engineer who pioneered remote-controlled torpedoes. CONDUCT.EDU.VN explores the history, application and impact of this innovation and its contribution to military technology. This innovative work laid the foundation for modern missile technology, inspiring future advancements in weapons guidance and remote control systems.
1. The Pioneering Work of Louis Brennan
Louis Brennan (1852-1932), an Irish-Australian engineer, is widely credited with inventing the world’s first guided missile. His invention, the Brennan torpedo, was developed in the 1870s and represented a significant advancement in naval defense technology. Brennan’s work was not just an isolated invention; it laid the groundwork for future developments in guided weaponry. Brennan’s guided missile system had a notable impact on naval defense strategies, particularly within the British Empire.
1.1. Early Life and Influences
Born in Castlebar, County Mayo, Ireland, Brennan’s family emigrated to Melbourne, Australia, when he was about nine years old. His early life in Australia exposed him to practical engineering challenges, which ignited his inventive spirit. He began his career as a clockmaker’s apprentice, honing his mechanical skills and developing a keen understanding of intricate mechanisms. Brennan’s training as a clockmaker taught him the importance of precision and attention to detail, qualities that would prove invaluable in his later inventions. His background as a clockmaker gave him a solid foundation in mechanical engineering, which he applied to more complex projects.
1.2. The Eureka Moment
The inspiration for the guided missile reportedly came to Brennan while observing a reel of thread. He noticed that pulling the thread caused the reel to move forward, sparking the idea of a torpedo that could be controlled remotely. This insight led him to conceive a torpedo that could be steered using wires, offering a new approach to naval defense. This simple observation led to a groundbreaking invention that would revolutionize naval warfare. Brennan’s ability to translate a simple observation into a practical solution demonstrates his inventive genius.
2. The Brennan Torpedo: Design and Functionality
The Brennan torpedo was a marvel of engineering for its time. It was designed to be launched from the shore and guided to its target using two high-speed wires wound around drums inside the torpedo. This innovative design allowed for precise control over the torpedo’s direction and speed. The system ensured that the torpedo could accurately strike enemy vessels, even at a distance.
2.1. Detailed Design
The torpedo featured two drums with steel wire spooled around them. These wires were connected to steam-powered winding engines on the shore. By varying the speed at which the wires were pulled, the operator could control the torpedo’s direction. The Brennan torpedo’s design included several key components that made it a unique and effective weapon. The design allowed for precise control over the torpedo’s movements, making it a formidable defensive weapon.
2.2. Operational Mechanics
The Brennan torpedo operated just below the water surface, with a small flag indicating its position. This allowed the operators on shore to track its movement and make necessary adjustments. The torpedo could reach speeds of up to 20 knots and had a range of approximately three miles. The torpedo’s operational mechanics were simple yet effective, providing a reliable means of coastal defense. The operational features allowed for real-time adjustments, enhancing the torpedo’s accuracy and effectiveness.
2.3. Strategic Deployment
The British Navy recognized the value of Brennan’s invention and invested heavily in its deployment. Brennan torpedo systems were installed in strategic locations around the British Empire, including Hong Kong, Malta, and Cork. These systems were intended to defend naval ports and harbors from enemy attacks. The strategic deployment of Brennan torpedoes significantly enhanced the defensive capabilities of the British Navy. The placement of these systems reflected a strategic understanding of naval defense, ensuring key ports were well-protected.
3. Impact and Legacy of the Brennan Torpedo
For nearly 30 years, the Brennan torpedo served as a primary defense against naval attacks on British ports. Though it was never used in live combat, its presence deterred potential aggressors and provided a sense of security. The Brennan torpedo’s legacy extends beyond its immediate military application, influencing future developments in guided missile technology. The Brennan torpedo’s impact can be assessed in terms of its strategic value and its influence on subsequent technological innovations.
3.1. Strategic Deterrent
The Brennan torpedo’s primary impact was as a strategic deterrent. Its presence in key naval locations signaled a strong defensive capability, discouraging potential enemies from launching attacks. The system’s effectiveness lay in its ability to control and direct torpedoes accurately, making it a credible threat. The torpedo’s role as a deterrent is a testament to its design and the strategic thinking behind its deployment. The Brennan torpedo provided a robust defense, deterring potential aggressors and maintaining naval superiority.
3.2. Technological Influence
The Brennan torpedo influenced subsequent developments in guided missile technology. It demonstrated the feasibility of remote-controlled weaponry and paved the way for more advanced systems. The concepts and technologies developed by Brennan were later refined and incorporated into modern guided missiles. Brennan’s work established a foundation for future innovations in guided weaponry. The influence of the Brennan torpedo can be seen in the evolution of missile technology, which incorporates similar principles of remote guidance and control.
3.3. Evolution of Guided Missile Technology
The evolution of guided missile technology can be traced back to Brennan’s pioneering work. Over the years, guided missiles have become more sophisticated, incorporating advanced guidance systems, propulsion methods, and explosive capabilities. Today’s guided missiles use a variety of technologies, including radar, GPS, and laser guidance, to achieve pinpoint accuracy. The evolution of guided missiles reflects continuous advancements in engineering and technology. The progression from Brennan’s wire-guided torpedo to modern missile systems illustrates the ongoing quest for improved precision and effectiveness in weaponry.
4. Brennan’s Other Inventions and Contributions
Louis Brennan was not just a one-hit wonder. He also made significant contributions to other fields, including transportation and aviation. His work on the monorail and the helicopter showcases his versatility and innovative thinking. Brennan’s broader contributions highlight his remarkable ability to apply engineering principles to diverse challenges. Brennan’s diverse inventions demonstrate his commitment to pushing the boundaries of technology.
4.1. The Monorail System
Brennan invented a monorail system that used gyroscopes to maintain balance. This innovative design allowed the train to navigate tight corners and steep inclines, making it suitable for challenging terrains. Despite successful demonstrations, the monorail system never gained widespread adoption due to concerns about its stability. Brennan’s monorail system represented a bold attempt to revolutionize transportation technology. The monorail system’s innovative use of gyroscopes demonstrated Brennan’s forward-thinking approach to engineering.
4.2. The Brennan Helicopter
Brennan also designed a helicopter that could take off and land vertically. His helicopter design was backed by the British military, with even Winston Churchill taking a personal interest. Although test flights were successful, the project was eventually abandoned in favor of alternative designs. Brennan’s helicopter design showcased his ambition to innovate in the field of aviation. The helicopter project, though unsuccessful, added to Brennan’s reputation as a versatile and imaginative inventor.
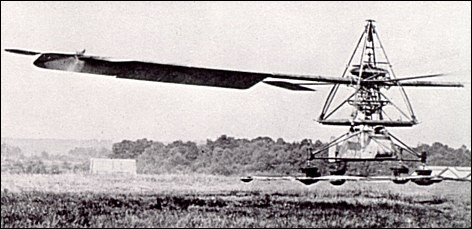 Louis Brennan’s prototype helicopter
Louis Brennan’s prototype helicopter
5. Overcoming Challenges in Guided Missile Development
The development of guided missiles involved numerous technical and logistical challenges. Brennan and other early pioneers had to overcome issues related to guidance systems, propulsion, and control mechanisms. These challenges required innovative solutions and a deep understanding of engineering principles. Overcoming these challenges was crucial to the successful development and deployment of guided missiles. The early challenges in guided missile development paved the way for future advancements and refinements.
5.1. Guidance System Limitations
Early guidance systems were limited by the available technology. Brennan’s wire-guided system, while innovative, had range and speed limitations. Improving the accuracy and range of guidance systems was a primary focus of subsequent research and development. The limitations of early guidance systems spurred the development of more advanced technologies. Overcoming these limitations was essential to enhancing the effectiveness of guided missiles.
5.2. Propulsion Technology
Developing effective propulsion systems was another major challenge. Early torpedoes and missiles relied on steam or compressed air for propulsion, which limited their speed and range. The development of more powerful and efficient engines was crucial to improving missile performance. Advances in propulsion technology have significantly increased the speed and range of modern guided missiles. The evolution of propulsion systems has been a key factor in the advancement of guided missile technology.
5.3. Control and Stability
Maintaining control and stability during flight was also a significant challenge. Early missiles were prone to instability, making it difficult to accurately guide them to their targets. The development of sophisticated control surfaces and stabilization systems was essential to ensuring accurate and reliable performance. Improving control and stability has been a continuous focus in guided missile development. The integration of advanced control systems has greatly enhanced the accuracy and reliability of modern guided missiles.
6. The Evolution of Guidance Systems: From Wires to GPS
The evolution of guidance systems has been a key factor in the advancement of guided missile technology. From Brennan’s wire-guided system to modern GPS-guided missiles, each generation of technology has brought improved accuracy and range. This evolution reflects continuous innovation and refinement in engineering and technology. The progression from wire-guided systems to GPS demonstrates the relentless pursuit of improved accuracy and reliability. The evolution of guidance systems has transformed guided missiles from simple defensive weapons to sophisticated strategic assets.
6.1. Wire-Guided Systems
Brennan’s wire-guided system was a revolutionary concept for its time. However, it had limitations in terms of range and maneuverability. The wires could only be so long, and the system was vulnerable to interference. Despite these limitations, the wire-guided system proved the feasibility of remote-controlled weaponry. Wire-guided systems laid the groundwork for future advancements in guidance technology. The success of the Brennan torpedo demonstrated the potential of guided missiles and inspired further research and development.
6.2. Radio-Controlled Systems
The development of radio-controlled systems marked a significant advancement in guidance technology. Radio control allowed for greater range and maneuverability compared to wire-guided systems. However, radio signals were susceptible to jamming and interference, which could compromise the accuracy of the missiles. Radio-controlled systems offered increased flexibility but also presented new challenges. Overcoming the limitations of radio control was a key focus of subsequent research.
6.3. Radar Guidance
Radar guidance systems use radar waves to track and guide missiles to their targets. These systems can operate in all weather conditions and are less susceptible to jamming than radio-controlled systems. However, radar guidance systems can be complex and expensive to develop and maintain. Radar guidance systems have significantly improved the accuracy and reliability of guided missiles. The use of radar technology has enabled guided missiles to operate effectively in a wider range of conditions.
6.4. GPS Guidance
GPS (Global Positioning System) guidance is the most advanced form of guidance technology. GPS-guided missiles use satellite signals to determine their position and navigate to their targets with pinpoint accuracy. GPS guidance systems are highly accurate and reliable, but they are also vulnerable to cyberattacks and signal interference. GPS guidance has revolutionized the accuracy and effectiveness of guided missiles. The integration of GPS technology has transformed guided missiles into highly precise strategic weapons.
7. Modern Guided Missiles: Capabilities and Applications
Modern guided missiles are sophisticated weapons systems with a wide range of capabilities and applications. They are used by militaries around the world for various purposes, including air defense, anti-ship warfare, and ground attack. The capabilities and applications of modern guided missiles reflect continuous advancements in technology and engineering. Modern guided missiles have become indispensable tools for military operations.
7.1. Air-to-Air Missiles
Air-to-air missiles are designed to be launched from aircraft to destroy enemy aircraft. These missiles use a variety of guidance systems, including radar, infrared, and GPS, to track and intercept their targets. Air-to-air missiles are a critical component of modern air defense systems. The effectiveness of air-to-air missiles is essential for maintaining air superiority.
7.2. Surface-to-Air Missiles
Surface-to-air missiles are designed to be launched from the ground or sea to intercept enemy aircraft or missiles. These missiles use radar or infrared guidance systems to track and destroy their targets. Surface-to-air missiles provide a vital layer of defense against aerial attacks. The deployment of surface-to-air missiles enhances the protection of critical infrastructure and military assets.
7.3. Anti-Ship Missiles
Anti-ship missiles are designed to destroy enemy ships. These missiles can be launched from aircraft, ships, or submarines and use radar or GPS guidance systems to locate and strike their targets. Anti-ship missiles are a potent weapon in naval warfare. The deployment of anti-ship missiles strengthens a nation’s ability to project power at sea.
7.4. Cruise Missiles
Cruise missiles are long-range, self-propelled missiles that can be launched from aircraft, ships, or submarines. These missiles use GPS guidance systems to navigate to their targets with high precision. Cruise missiles are capable of striking targets thousands of miles away. The strategic deployment of cruise missiles enhances a nation’s ability to conduct long-range strikes.
8. Ethical Considerations in Guided Missile Technology
The development and use of guided missile technology raise several ethical considerations. These include concerns about the potential for civilian casualties, the risk of escalation, and the moral implications of autonomous weapons systems. Addressing these ethical considerations is essential for ensuring responsible use of guided missile technology. The ethical implications of guided missile technology require careful consideration and ongoing dialogue.
8.1. Civilian Casualties
The use of guided missiles carries the risk of civilian casualties. Even with precise guidance systems, there is always a possibility of unintended harm to non-combatants. Minimizing civilian casualties is a paramount concern in the development and deployment of guided missiles. Efforts to reduce collateral damage are essential for maintaining ethical standards in warfare.
8.2. Risk of Escalation
The deployment of guided missiles can escalate conflicts. The ability to strike targets deep within enemy territory can provoke retaliatory actions, leading to a cycle of escalation. Careful consideration of the potential consequences is essential before deploying guided missiles. Strategic restraint is crucial for preventing escalation and maintaining stability.
8.3. Autonomous Weapons Systems
The development of autonomous weapons systems raises complex ethical questions. These systems can make decisions without human intervention, raising concerns about accountability and control. The moral implications of autonomous weapons systems require careful scrutiny. Ensuring human oversight and control is essential for responsible development of autonomous weapons.
9. The Future of Guided Missile Technology
The future of guided missile technology is likely to involve further advancements in guidance systems, propulsion, and autonomous capabilities. These advancements will lead to more precise, efficient, and versatile weapons systems. The ongoing development of guided missile technology will continue to shape military strategies and capabilities. The future of guided missile technology promises both opportunities and challenges.
9.1. Hypersonic Missiles
Hypersonic missiles are capable of traveling at speeds of Mach 5 or greater. These missiles can reach their targets in a matter of minutes, making them difficult to intercept. The development of hypersonic missiles is a major focus of military research and development. Hypersonic technology is poised to revolutionize missile warfare.
9.2. Directed Energy Weapons
Directed energy weapons use high-energy lasers or microwaves to destroy or disable their targets. These weapons offer the potential for precise and low-collateral damage strikes. The development of directed energy weapons is a promising area of research. Directed energy weapons could potentially replace traditional missiles in certain applications.
9.3. Swarm Technology
Swarm technology involves the use of multiple, coordinated missiles or drones to overwhelm enemy defenses. These swarms can adapt to changing conditions and coordinate their attacks to maximize effectiveness. Swarm technology represents a new paradigm in missile warfare. The deployment of missile swarms could significantly enhance offensive capabilities.
10. How CONDUCT.EDU.VN Can Help
Navigating the complex landscape of ethical conduct and technological advancements can be challenging. CONDUCT.EDU.VN offers a comprehensive resource for understanding ethical guidelines and best practices across various fields. Our platform provides detailed information, practical guidance, and real-world examples to help individuals and organizations make informed decisions. We address the difficulties individuals face in finding credible information and offer clear, understandable guidelines.
10.1. Comprehensive Resource
CONDUCT.EDU.VN serves as a comprehensive resource for ethical guidelines and best practices. Our platform covers a wide range of topics, including professional ethics, organizational conduct, and technological responsibility. We provide in-depth information and practical guidance to help users navigate complex ethical dilemmas. Our extensive resources ensure that users have access to the information they need to make informed decisions.
10.2. Practical Guidance
We offer practical guidance on applying ethical principles in real-world situations. Our platform includes case studies, examples, and step-by-step instructions to help users understand how to implement ethical practices effectively. Our practical guidance ensures that users can translate ethical principles into actionable strategies. We focus on providing clear and understandable instructions that users can easily apply.
10.3. Real-World Examples
CONDUCT.EDU.VN features real-world examples of ethical dilemmas and their resolutions. These examples illustrate how ethical principles can be applied in various contexts and provide valuable insights for users facing similar challenges. Our real-world examples help users understand the practical implications of ethical decision-making. We showcase a diverse range of scenarios to provide comprehensive coverage of ethical issues.
Are you seeking reliable information and guidance on ethical conduct? Visit CONDUCT.EDU.VN at 100 Ethics Plaza, Guideline City, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (707) 555-1234. Let us help you navigate the complexities of ethical decision-making. Explore our resources and discover the guidance you need to uphold the highest standards of conduct.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Who is credited with inventing the first guided missile?
Louis Brennan, an Irish-Australian engineer, is credited with inventing the first guided missile, known as the Brennan torpedo.
2. What was the Brennan torpedo designed for?
The Brennan torpedo was designed to defend naval ports and harbors from enemy attacks.
3. How did the Brennan torpedo work?
The Brennan torpedo was guided by wires spooled from drums inside the torpedo, allowing operators on shore to control its direction and speed.
4. Where were Brennan torpedo systems deployed?
Brennan torpedo systems were deployed in strategic locations around the British Empire, including Hong Kong, Malta, and Cork.
5. What were some limitations of the Brennan torpedo?
The Brennan torpedo had limitations in range and maneuverability due to its wire-guided system.
6. What other inventions did Louis Brennan contribute to?
Louis Brennan also invented a monorail system and a helicopter.
7. How have guidance systems evolved since the Brennan torpedo?
Guidance systems have evolved from wire-guided systems to radio-controlled, radar-guided, and GPS-guided systems.
8. What are some ethical considerations related to guided missile technology?
Ethical considerations include the risk of civilian casualties, the potential for escalation, and the moral implications of autonomous weapons systems.
9. What are some potential future developments in guided missile technology?
Potential future developments include hypersonic missiles, directed energy weapons, and swarm technology.
10. Where can I find more information on ethical conduct and technological advancements?
conduct.edu.vn offers a comprehensive resource for understanding ethical guidelines and best practices across various fields.